3,521% Tariffs: US's Aggressive Action Against Southeast Asian Solar Imports

Table of Contents
The Rationale Behind the 3,521% Tariffs
The US Department of Commerce justified the staggering 3,521% tariffs on the basis of alleged circumvention of existing anti-dumping and countervailing duties and concerns about national security.
Allegations of Circumvention and Duty Evasion
The Commerce Department's investigation found that Southeast Asian solar manufacturers were allegedly bypassing tariffs intended for Chinese solar companies by shipping panels through their countries. This practice, often described as "circumvention" or "duty evasion," undermines previous trade actions aimed at leveling the playing field for US solar manufacturers.
- Evidence presented by the US government: Included evidence of interconnected ownership structures, shared production facilities, and similar manufacturing processes between Chinese and Southeast Asian solar companies.
- Responses from Southeast Asian countries: These countries strongly contested the allegations, arguing that their solar industries are distinct and independent of Chinese operations. They also pointed out the negative economic repercussions of these tariffs.
- The role of Chinese solar companies: The investigation highlighted the significant role Chinese companies play in the Southeast Asian solar supply chain, leading to the assertion that the tariffs are necessary to address the underlying issue of unfair trade practices originating from China.
National Security Concerns
Beyond allegations of circumvention, the US government also framed the tariffs as a measure to protect national security by reducing dependence on foreign sources for solar panels. This argument emphasizes the importance of a resilient domestic solar manufacturing base for achieving renewable energy security.
- Analysis of US solar panel production capacity: Currently, US solar panel manufacturing capacity is significantly less than the demand, leading to a heavy reliance on imports. The tariffs aim to boost domestic production and create jobs.
- The potential impact on the clean energy transition: Critics argue that the tariffs could hinder the US's clean energy transition by raising solar energy costs and slowing down the deployment of renewable energy systems.
- Arguments for and against national security justification: The national security argument is highly debated. Supporters emphasize energy independence and the vulnerability of relying on foreign suppliers, while opponents counter that the evidence supporting the national security threat is weak and the economic consequences outweigh the benefits.
Economic Impact of the 3,521% Tariffs
The 3,521% tariffs have far-reaching economic consequences, affecting both US consumers and Southeast Asian economies.
Impact on US Solar Prices and Installation Costs
The tariffs have already resulted in a significant increase in the price of solar panels in the US, impacting solar energy adoption.
- Data showing price increases: Industry reports indicate substantial price hikes, making solar power less competitive with traditional energy sources.
- Projections for solar installations: The higher prices are expected to lead to a decrease in new solar installations, potentially delaying the achievement of renewable energy goals.
- The impact on jobs in the solar installation sector: While the tariffs aim to boost domestic manufacturing jobs, they threaten jobs in the solar installation sector due to reduced demand.
Repercussions for Southeast Asian Economies
The tariffs inflict severe economic damage on the solar industries and overall economies of Cambodia, Malaysia, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- Job losses: Thousands of jobs in the Southeast Asian solar manufacturing sector are at risk due to reduced exports to the US.
- Reduced exports: The tariffs have drastically reduced the volume of solar panels exported from these countries to the US, impacting their trade balances and economic growth.
- The potential for retaliatory measures from affected countries: The affected countries may retaliate by imposing tariffs on US goods, escalating the trade conflict.
Long-Term Implications and Potential Solutions
The long-term implications of the 3,521% tariffs are profound, raising questions about the future of US solar energy development and the stability of global trade relations.
The Future of US Solar Energy Development
The tariffs pose a serious challenge to the US's ambitious renewable energy goals and its commitment to addressing climate change.
- Possible delays in renewable energy deployment: The higher costs of solar panels could significantly slow down the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
- The increased reliance on other energy sources: The slower deployment of solar power could lead to increased reliance on fossil fuels, undermining climate change mitigation efforts.
- Alternative strategies for achieving clean energy targets: The US needs to explore alternative strategies to reach its clean energy targets, potentially including greater investment in domestic manufacturing and diversification of supply chains.
Potential Negotiation and Resolution
Resolving this trade dispute requires diplomatic efforts and a willingness to find mutually beneficial solutions.
- Opportunities for diplomacy: Open communication and negotiation between the US and Southeast Asian governments are crucial to de-escalate the conflict and find common ground.
- The possibility of tariff reductions: A phased reduction or complete removal of the tariffs could be explored to mitigate the economic damage.
- The role of international organizations: Organizations like the World Trade Organization could play a mediating role in resolving the dispute and ensuring compliance with international trade law.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex Landscape of 3,521% Solar Tariffs
The 3,521% tariffs represent a significant escalation in the US-Southeast Asia trade relationship, carrying substantial consequences for the US solar industry, Southeast Asian economies, and global trade relations. The rationale behind these tariffs, involving allegations of circumvention and national security concerns, remains highly contentious. The economic impact, characterized by price increases in the US and job losses in Southeast Asia, highlights the complex trade-offs involved. Looking ahead, resolving this dispute requires diplomatic efforts focused on negotiation, potential tariff reductions, and leveraging international cooperation. Staying informed about developments related to these tariffs is crucial. Follow the US trade policy related to renewable energy and learn more about the impact of solar panel tariffs to better understand this intricate situation and participate in the crucial public discourse surrounding US trade policy and its implications for clean energy.

Featured Posts
-
 The Power Of Crispr Successfully Inserting Whole Genes Into Human Dna
May 30, 2025
The Power Of Crispr Successfully Inserting Whole Genes Into Human Dna
May 30, 2025 -
 Tennis Legend Andre Agassi Enters The World Of Professional Pickleball
May 30, 2025
Tennis Legend Andre Agassi Enters The World Of Professional Pickleball
May 30, 2025 -
 Europe 1 Soir Week End Aurelien Veron Et Laurent Jacobelli
May 30, 2025
Europe 1 Soir Week End Aurelien Veron Et Laurent Jacobelli
May 30, 2025 -
 Kodiak Waters Two Consecutive Harmful Algal Blooms Warn Shellfish Harvesters
May 30, 2025
Kodiak Waters Two Consecutive Harmful Algal Blooms Warn Shellfish Harvesters
May 30, 2025 -
 Solicitar Reembolso Cancelacion Festival Axe Ceremonia 2025 Ticketmaster
May 30, 2025
Solicitar Reembolso Cancelacion Festival Axe Ceremonia 2025 Ticketmaster
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Rosemary And Thyme From Garden To Plate
May 31, 2025
Rosemary And Thyme From Garden To Plate
May 31, 2025 -
 Growing And Using Rosemary And Thyme A Practical Handbook
May 31, 2025
Growing And Using Rosemary And Thyme A Practical Handbook
May 31, 2025 -
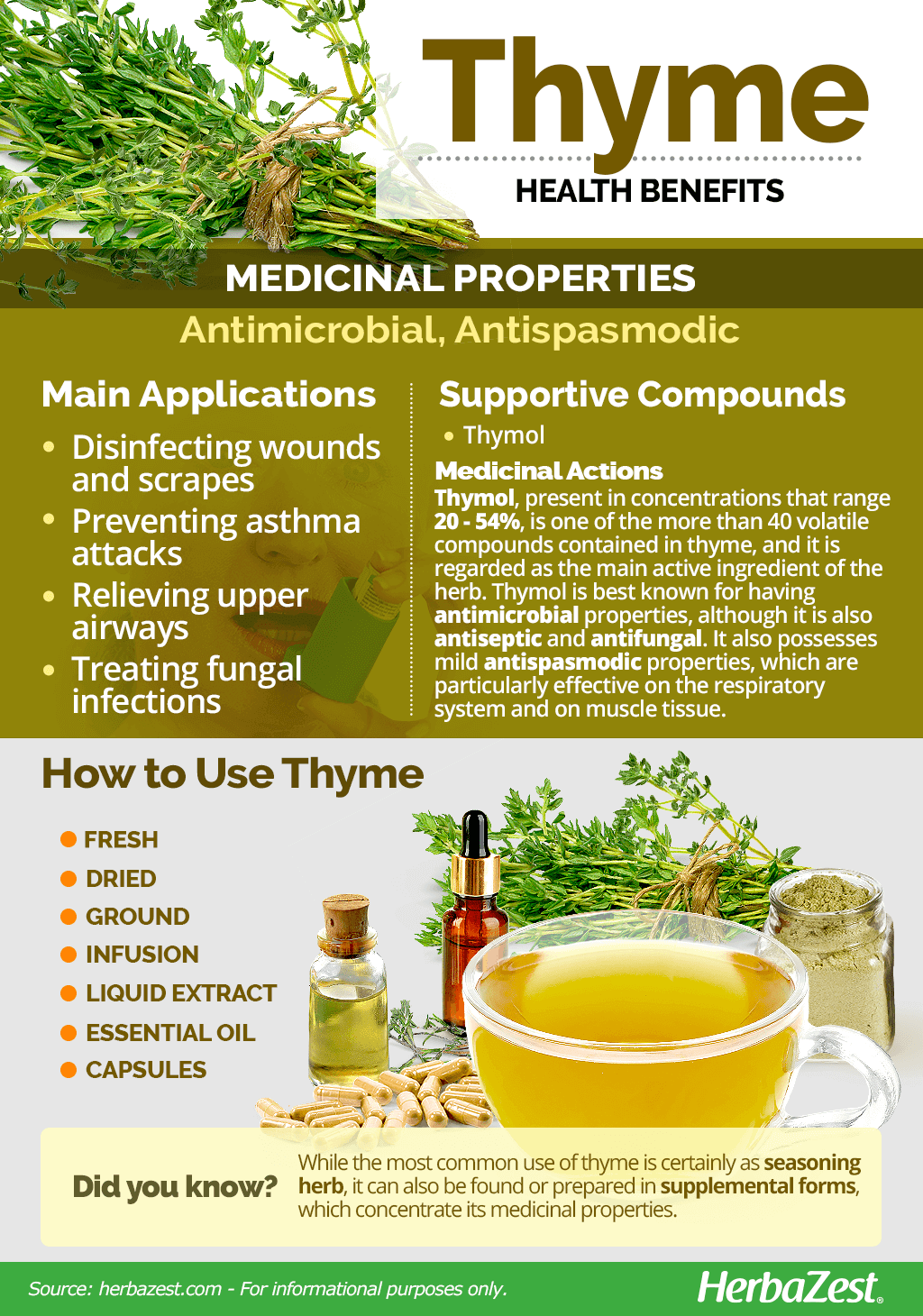 Rosemary And Thyme Benefits Uses And Recipes
May 31, 2025
Rosemary And Thyme Benefits Uses And Recipes
May 31, 2025 -
 Growing Your Own Rosemary And Thyme A Beginners Guide
May 31, 2025
Growing Your Own Rosemary And Thyme A Beginners Guide
May 31, 2025 -
 Rosemary And Thyme A Culinary Guide To Herb Gardening And Cooking
May 31, 2025
Rosemary And Thyme A Culinary Guide To Herb Gardening And Cooking
May 31, 2025
