Addressing China's Soybean Deficit: Sinograin's Auction Strategy

Table of Contents
The Scale of China's Soybean Deficit and its Implications
China's massive soybean imports highlight the scale of its deficit. Driven by soaring domestic demand, primarily for animal feed (pork production being a major driver), and limitations in domestic soybean production due to factors like arable land availability and climate constraints, the country consistently imports vast quantities of soybeans. This dependence has significant implications:
-
Impact on Food Security and Animal Feed Production: A disruption in soybean imports directly threatens China's animal feed supply, impacting meat production and potentially leading to food price instability. Soybean meal is a crucial protein source for livestock, and any shortfall can have cascading effects throughout the food chain.
-
Economic Consequences of Reliance on Imports: The substantial cost of soybean imports represents a significant drain on China's foreign exchange reserves. Fluctuations in global soybean prices expose the Chinese economy to considerable price volatility, impacting both consumers and producers.
-
Geopolitical Implications: China's heavy reliance on foreign soybean suppliers, primarily the US and Brazil, creates geopolitical vulnerabilities. Trade disputes or disruptions in global supply chains can significantly impact China's food security and economic growth. This dependence also necessitates careful management of international relations within the agricultural sector.
Sinograin's Role in Managing Soybean Imports
Sinograin, a state-owned enterprise, plays a pivotal role in China's grain market, acting as a key player in managing the country's soybean imports. Its responsibilities extend far beyond simple procurement:
-
Procuring and Distributing Soybeans: Sinograin is responsible for a significant portion of China's soybean imports, coordinating purchases from international suppliers and ensuring the efficient distribution of these commodities across the country.
-
Maintaining National Food Reserves: A crucial function of Sinograin is maintaining strategic reserves of soybeans to mitigate the risk of supply disruptions and stabilize domestic prices. This is paramount for ensuring food security, especially during times of uncertainty.
-
Influence on Soybean Pricing and Market Stability: Sinograin's actions significantly influence soybean prices in China. Its purchasing decisions and strategic reserve management have a direct impact on market stability, mitigating potentially sharp price fluctuations.
The Mechanics of Sinograin's Auction System
Sinograin employs a sophisticated auction system to procure soybeans. This mechanism offers several advantages, particularly in terms of transparency and market efficiency:
-
Auction Process: Eligible participants, including both domestic and international traders, submit bids for soybean supplies. The auctions are usually conducted online, ensuring transparency and fairness.
-
Frequency and Volume: Auctions are held regularly, with varying volumes of soybeans offered depending on market conditions and Sinograin's strategic needs. The sheer volume traded through these auctions underscores their significance in managing China's soybean imports.
-
Transparency and Fairness: While the complete details of the Sinograin auction system are not always publicly available, the use of an auction process aims to create a relatively transparent and competitive marketplace for soybean procurement.
Effectiveness of Sinograin's Auction Strategy in Addressing the Deficit
Sinograin's auction strategy has demonstrated some success in mitigating the China's soybean deficit, although challenges remain.
-
Impact on Soybean Prices in China: The auction system, to a degree, helps control the price volatility of soybeans in the domestic market. However, global price fluctuations still impact domestic prices.
-
Contribution to Ensuring Domestic Supply: By securing large volumes of soybeans through auctions, Sinograin helps to ensure a consistent supply to meet domestic demand, reducing the risk of shortages.
-
Limitations and Challenges: The effectiveness of the strategy is dependent on several factors, including global soybean prices, geopolitical stability, and the efficiency of Sinograin's operations. Moreover, reliance on auctions alone may not be sufficient to completely solve the long-term issue of China's soybean deficit.
Global Implications of Sinograin's Actions
Sinograin's auction strategy significantly impacts global soybean markets:
-
Influence on Global Soybean Prices: China's massive purchases, facilitated through auctions, exert a considerable influence on global soybean prices. Increased demand can drive prices up, affecting soybean producers and importers worldwide.
-
Implications for Competing Importers: Other major soybean importers face increased competition from China's substantial purchases, potentially affecting their ability to secure supplies at competitive prices.
-
Effects on Soybean-Producing Countries: Sinograin's purchasing decisions have a profound impact on soybean-producing countries like the US, Brazil, and Argentina. These countries benefit from China's demand but are also exposed to its market power.
Conclusion
This article has explored the significant challenge posed by China's soybean deficit and examined Sinograin's strategic use of auctions as a primary mechanism to address this. We've analyzed the mechanics of the auction system, its effectiveness in mitigating the deficit, and its broader global implications. The strategy has shown some success in stabilizing domestic supply and mitigating price volatility, but its long-term efficacy depends on several factors including global market dynamics and geopolitical stability. Furthermore, addressing the underlying causes of the deficit, such as increasing domestic demand and production limitations, remains crucial.
Call to Action: Understanding Sinograin's auction strategy is crucial for anyone involved in the global soybean market. Further research into the dynamics of China's soybean imports and the effectiveness of Sinograin's approach to managing this crucial commodity is vital for predicting future market trends and addressing China's soybean deficit effectively. Analyzing alternative strategies for improving domestic soybean production and reducing reliance on imports remains a critical area for future study.

Featured Posts
-
 Chainalysis Acquisition Of Alterya A Strategic Move In Ai Powered Blockchain Security
May 29, 2025
Chainalysis Acquisition Of Alterya A Strategic Move In Ai Powered Blockchain Security
May 29, 2025 -
 Starships Flight Readiness Overcoming Recent Test Setbacks
May 29, 2025
Starships Flight Readiness Overcoming Recent Test Setbacks
May 29, 2025 -
 Stellantis Turnaround Strategy Antonio Filosas Appointment And Its Implications
May 29, 2025
Stellantis Turnaround Strategy Antonio Filosas Appointment And Its Implications
May 29, 2025 -
 B C Billionaire Weihong Lius Hudsons Bay Investment
May 29, 2025
B C Billionaire Weihong Lius Hudsons Bay Investment
May 29, 2025 -
 Pokemon Tcg Pocket Celestial Guardians Expansion And Event Information
May 29, 2025
Pokemon Tcg Pocket Celestial Guardians Expansion And Event Information
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Tracking The Measles Virus Recent Outbreaks In The Usa
May 30, 2025
Tracking The Measles Virus Recent Outbreaks In The Usa
May 30, 2025 -
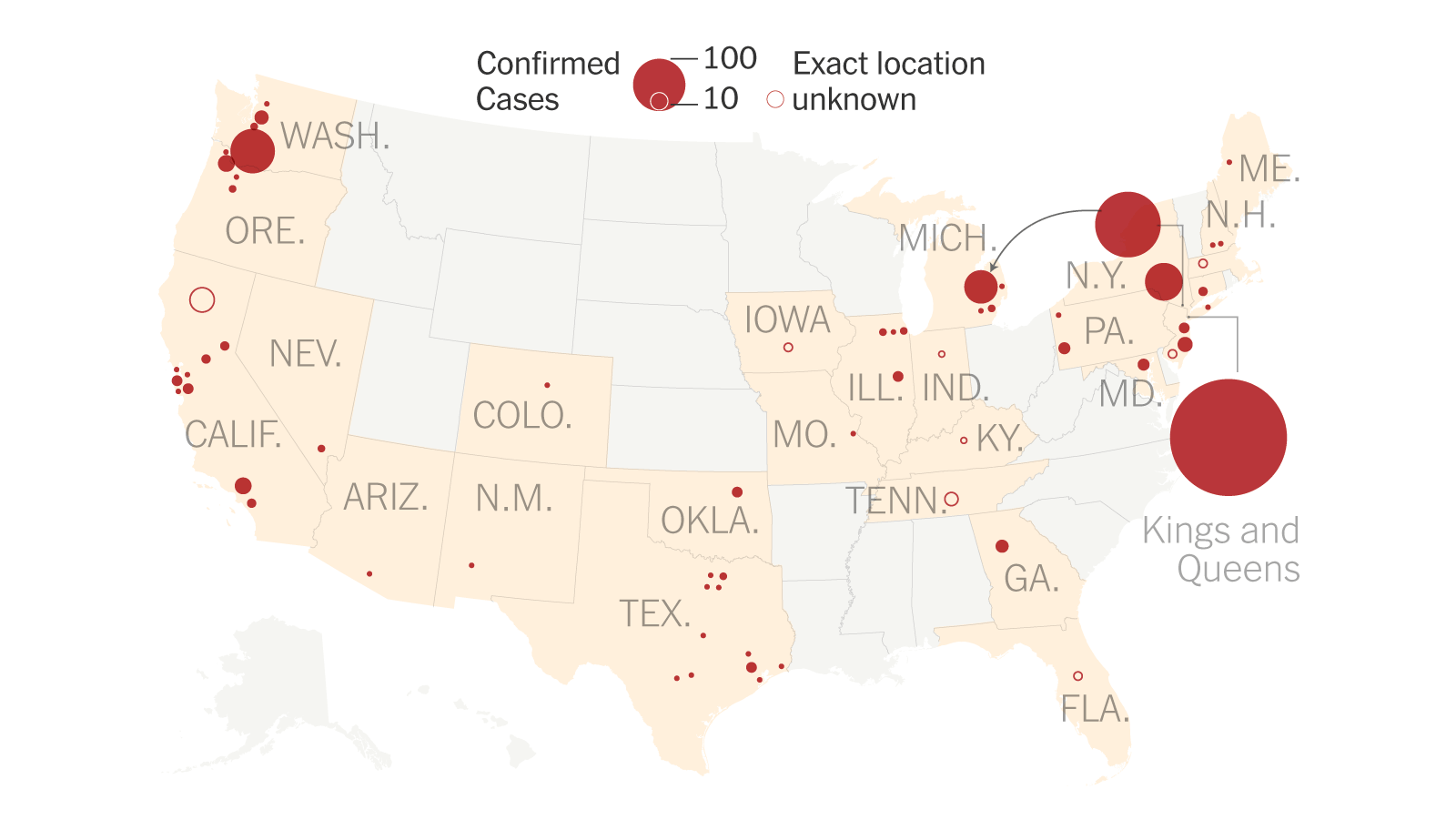 Current Measles Outbreak A Map Of U S Cases
May 30, 2025
Current Measles Outbreak A Map Of U S Cases
May 30, 2025 -
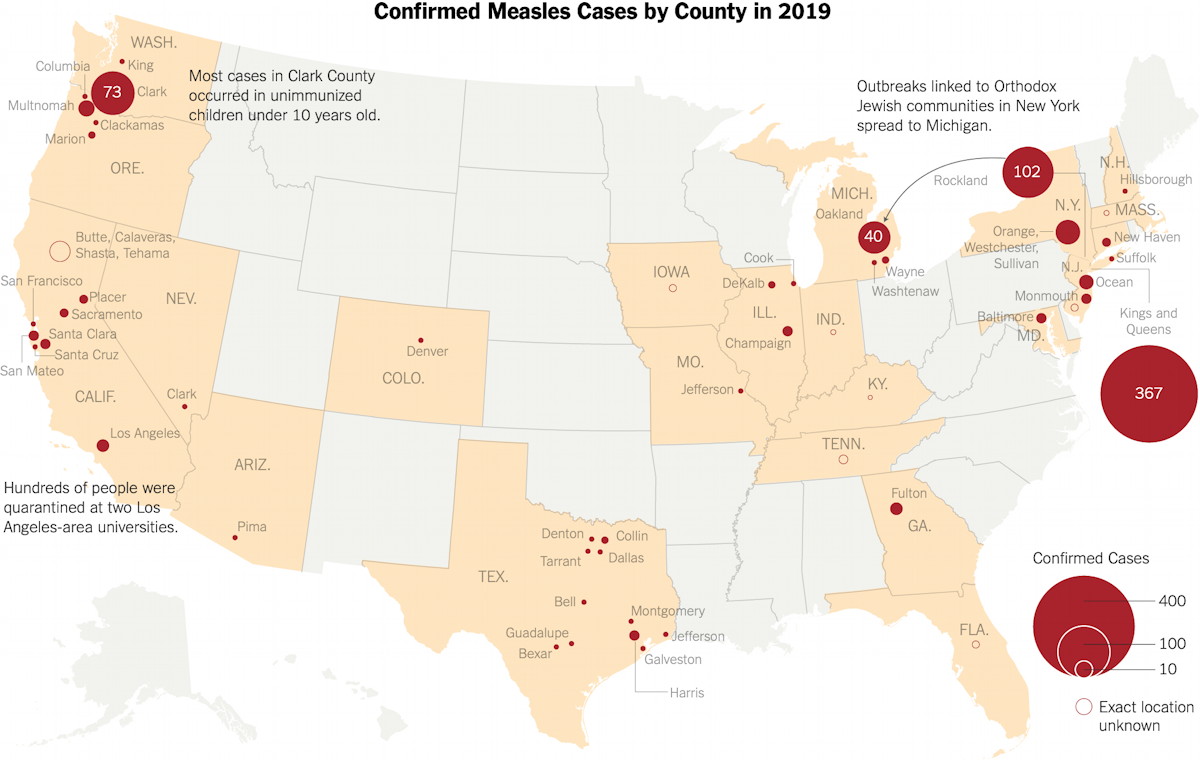 Where Is Measles Spreading In The United States
May 30, 2025
Where Is Measles Spreading In The United States
May 30, 2025 -
 Measles Cases In The U S Latest Updates And Locations
May 30, 2025
Measles Cases In The U S Latest Updates And Locations
May 30, 2025 -
 U S Measles Outbreak Tracking The Spread Of Cases
May 30, 2025
U S Measles Outbreak Tracking The Spread Of Cases
May 30, 2025
