Addressing The Urgent Mental Health Needs Of Young People In Canada: Lessons From A Global Commission

Table of Contents
The Scope of the Youth Mental Health Crisis in Canada
Prevalence of Mental Health Issues
Canadian youth are experiencing alarmingly high rates of mental health challenges. Statistics Canada and the Canadian Mental Health Association (CMHA) report significant increases in anxiety, depression, self-harm, and suicide attempts. These issues are not limited to a specific demographic; they affect young people across various backgrounds and regions.
- Anxiety disorders: Affecting approximately 1 in 5 Canadian youth.
- Depression: Impacting a significant portion of young people, with rates increasing steadily over the past decade.
- Self-harm and suicide attempts: Represent a serious concern, particularly among adolescents. The rates vary depending on age, gender, and other factors.
- Disparities: Significant disparities exist in the prevalence of mental health issues based on factors such as geographic location (rural youth often face greater barriers), socioeconomic status, and ethnicity. Indigenous youth, for example, experience disproportionately higher rates of mental health problems.
Barriers to Accessing Mental Health Care
Even when young people recognize they need help, accessing timely and appropriate mental healthcare in Canada can be extremely challenging. Several systemic barriers hinder their ability to get the support they require.
- Long wait times: Many youth face lengthy delays in accessing specialized mental health services, leading to worsening symptoms and potential crises.
- Lack of specialized services: A shortage of child and youth psychiatrists, therapists, and other mental health professionals creates significant access limitations.
- Financial constraints: The cost of mental healthcare can be prohibitive for many families, especially those with limited financial resources.
- Stigma: The persistent stigma associated with mental illness prevents many young people from seeking help, fearing judgment and social repercussions.
- Geographical limitations: Access to specialized mental health services is often limited in rural and remote areas.
- Navigating the system: The complexity of the Canadian healthcare system can be overwhelming, creating further barriers for youth and their families.
Key Findings from the Global Commission on Youth Mental Health
The Global Commission on Youth Mental Health has provided invaluable insights into improving youth mental health globally. Its recommendations offer a roadmap for Canada to address its own challenges.
Early Intervention and Prevention Strategies
The Commission strongly emphasizes the crucial role of early identification and intervention. Investing in preventative measures is key to reducing the burden of mental illness in the long term.
- School-based mental health programs: Implementing comprehensive programs that provide mental health education, early screening, and access to support services within schools.
- Community-based initiatives: Developing community-based programs that promote mental well-being and provide accessible mental health services for youth and families.
- Parental education: Equipping parents with the knowledge and skills to recognize the signs of mental health issues in their children and provide appropriate support.
- Promoting mental wellness: Creating school and community environments that prioritize mental well-being through initiatives such as mindfulness programs, peer support groups, and social-emotional learning curricula.
Strengthening Mental Healthcare Systems
The Commission advocates for significant improvements to the accessibility, affordability, and quality of youth mental health services.
- Increased funding: Substantial investment is needed to expand the workforce, enhance service delivery, and improve access to evidence-based treatments.
- Training for healthcare professionals: Providing comprehensive training for healthcare professionals in the assessment and treatment of youth mental health issues.
- Integration into primary care: Integrating mental health services into primary care settings to facilitate early detection and access to care.
- Technology in mental health care: Utilizing technology, such as telehealth and online therapy, to expand access to care, especially in remote areas.
- Culturally safe and inclusive services: Ensuring that mental health services are culturally appropriate and inclusive for all young people, addressing the specific needs of diverse populations.
Addressing Systemic Factors
The Commission recognizes that broader societal factors significantly impact youth mental health. Poverty, inequality, and social isolation contribute to increased vulnerability.
- Policy changes: Implementing policies that address the social determinants of health, such as poverty reduction initiatives, improved access to education and employment, and affordable housing.
- Social determinants of health: Focusing on addressing systemic inequalities that disproportionately affect certain groups of young people.
- Promoting social inclusion: Creating inclusive communities that promote belonging and reduce social isolation.
- Reducing stigma: National public awareness campaigns are needed to reduce the stigma associated with mental illness.
Adapting Global Commission Recommendations to the Canadian Context
Applying the Global Commission's recommendations requires careful consideration of Canada's unique healthcare system and social landscape.
Canadian-Specific Challenges and Opportunities
- Diverse populations: Canada’s diverse population necessitates culturally sensitive and linguistically accessible services.
- Regional variations: Addressing the significant disparities in access to mental health services across different regions of Canada.
- Integration with existing initiatives: Leveraging existing Canadian initiatives and resources to avoid duplication and maximize impact.
- Partnerships: Building strong partnerships between government, healthcare providers, schools, community organizations, and families.
Policy Recommendations for Canada
Based on the Global Commission's report, here are concrete policy recommendations for Canada:
- Increased government funding: Significant increase in federal and provincial funding for youth mental health services.
- Expansion of school-based programs: Implement comprehensive mental health programs in all schools across Canada.
- Improved training: Enhance training for healthcare professionals, educators, and community workers in youth mental health.
- National awareness campaigns: Launch national campaigns to reduce stigma and promote help-seeking behavior.
Conclusion
The urgency of the youth mental health crisis in Canada cannot be overstated. The insights from the Global Commission on Youth Mental Health provide a crucial framework for action. By implementing evidence-based strategies for prevention, early intervention, and improved access to care, we can create a healthier future for young people in Canada. We must act now to ensure that all young Canadians have access to the mental health support they need. Learn more about how you can contribute to improving youth mental health in Canada by visiting the websites of the Canadian Mental Health Association (CMHA) and Kids Help Phone. Collaborative efforts are key to creating a supportive and inclusive environment where all young people can thrive.

Featured Posts
-
 Fortnite Servers Offline Epic Games Update 34 40 Causes Downtime
May 02, 2025
Fortnite Servers Offline Epic Games Update 34 40 Causes Downtime
May 02, 2025 -
 Stage And Screen Veteran Priscilla Pointer Dies At 100
May 02, 2025
Stage And Screen Veteran Priscilla Pointer Dies At 100
May 02, 2025 -
 Check Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Results Latest Draw Numbers
May 02, 2025
Check Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Results Latest Draw Numbers
May 02, 2025 -
 Finom Es Kivalo Minosegu Kme Baromfi A Mecsek Baromfi Kft Tol
May 02, 2025
Finom Es Kivalo Minosegu Kme Baromfi A Mecsek Baromfi Kft Tol
May 02, 2025 -
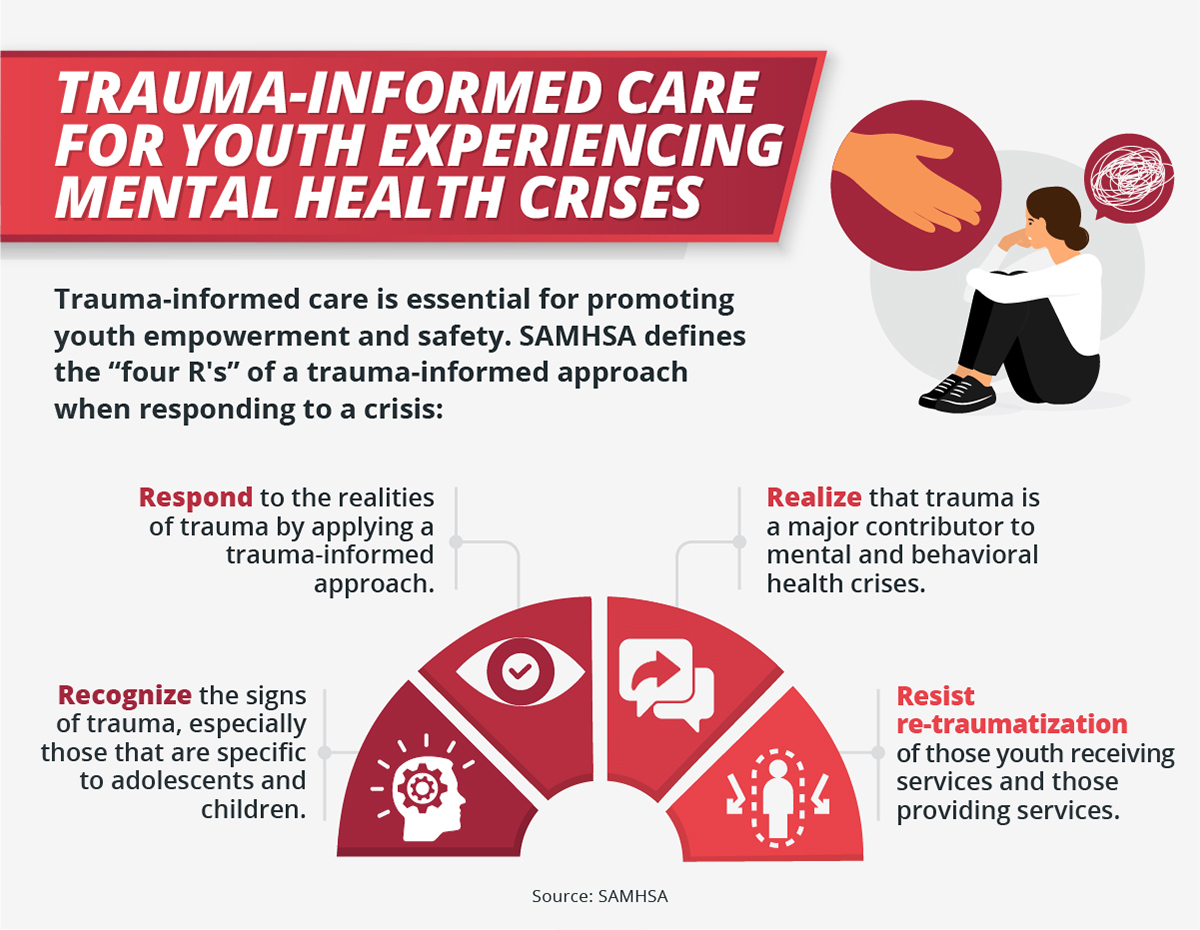 Canadas Youth Mental Health A Call To Action Based On Global Commission Findings
May 02, 2025
Canadas Youth Mental Health A Call To Action Based On Global Commission Findings
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Dispute Erupts Between Farage And Teaching Union Over Far Right Claim
May 03, 2025
Dispute Erupts Between Farage And Teaching Union Over Far Right Claim
May 03, 2025 -
 Understanding Reform Uks Influence The Farage Factor
May 03, 2025
Understanding Reform Uks Influence The Farage Factor
May 03, 2025 -
 Farage Faces Backlash From Teaching Union Over Far Right Allegations
May 03, 2025
Farage Faces Backlash From Teaching Union Over Far Right Allegations
May 03, 2025 -
 The Influence Of Nigel Farage On Reform Uks Political Rise
May 03, 2025
The Influence Of Nigel Farage On Reform Uks Political Rise
May 03, 2025 -
 La Nouvelle Loi Sur Les Partis Algeriens Reactions Du Pt Ffs Rcd Et Jil Jadid
May 03, 2025
La Nouvelle Loi Sur Les Partis Algeriens Reactions Du Pt Ffs Rcd Et Jil Jadid
May 03, 2025
