Analysis: Justice Department's School Desegregation Order And Its Consequences

Table of Contents
Historical Context of School Desegregation Orders
Before the landmark Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court case, school segregation was legally mandated in many parts of the United States, particularly in the South. This legal framework, established through Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) and upheld through decades of discriminatory practices, enshrined the principle of "separate but equal," a doctrine that was demonstrably unequal in practice.
-
Overview of the legal landscape before Brown v. Board: Segregation was deeply ingrained in society, with Black children forced to attend inferior schools, often lacking resources and qualified teachers. This systematic disinvestment contributed significantly to the educational and economic disparities that persist today.
-
The Supreme Court's ruling in Brown v. Board and its immediate impact: The unanimous 1954 decision in Brown v. Board of Education declared state laws establishing separate public schools for Black and white students unconstitutional, overturning Plessy v. Ferguson. However, the ruling's implementation faced significant resistance in many states, leading to protracted legal battles and a slow, uneven process of desegregation.
-
The role of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 in enforcing desegregation: This landmark legislation provided the legal framework and federal tools to enforce desegregation more effectively. It authorized the Department of Justice to intervene in cases of school segregation, providing a powerful weapon in the fight for equal educational opportunities.
-
Early examples of Justice Department intervention in desegregation cases: The DOJ used a variety of methods, including court injunctions, investigations, and the withholding of federal funds, to pressure school districts into compliance with desegregation orders. These early interventions laid the groundwork for broader desegregation efforts in subsequent years.
Key Strategies Employed by the Justice Department
The Department of Justice employed a multifaceted approach to enforce school desegregation orders, combining legal action with negotiation and support for desegregation initiatives.
-
Court injunctions and legal challenges: The DOJ filed numerous lawsuits against school districts that resisted desegregation, seeking court orders to mandate integration. These legal battles often resulted in significant changes to school district policies and practices.
-
Negotiation and mediation with school districts: In some cases, the DOJ worked with school districts to develop desegregation plans through negotiation and mediation, aiming for collaborative solutions that avoided lengthy legal battles.
-
Funding and resource allocation to support desegregation efforts: The federal government provided financial assistance to school districts to support the costs of desegregation, including busing and the development of new programs. This funding was crucial in facilitating a smoother transition in some areas.
-
Monitoring and enforcement mechanisms to ensure compliance: The DOJ established monitoring mechanisms to ensure that school districts complied with desegregation orders. This oversight was essential in preventing backsliding and maintaining the momentum of desegregation efforts.
Successes and Failures of Desegregation Efforts
The impact of the Justice Department's interventions in school desegregation has been mixed, with significant successes alongside notable failures.
-
Examples of successful desegregation initiatives and their long-term impact: In some areas, desegregation led to improved educational outcomes for Black students and a greater sense of social cohesion. Increased access to better resources and opportunities resulted in improved academic performance and social mobility.
-
Instances where desegregation efforts fell short of expectations: Many school districts resisted desegregation, employing tactics like gerrymandering school districts or employing "freedom of choice" plans that allowed for continued segregation. These strategies hampered the effectiveness of desegregation efforts.
-
Analysis of factors contributing to both success and failure (e.g., resistance from communities, inadequate funding): Resistance from white communities, including "white flight" to suburban schools, and inadequate funding for desegregation initiatives significantly impacted the effectiveness of the DOJ's interventions. These factors often undermined progress and perpetuated segregation in practice.
-
The emergence of "white flight" and its consequences: The phenomenon of "white flight"—the movement of white families from urban areas to suburbs in response to desegregation—led to the creation of racially segregated school systems in many areas. This contributed to the persistence of educational inequality.
The Long Shadow of De Facto Segregation
Even with the legal dismantling of de jure segregation (segregation mandated by law), de facto segregation (segregation resulting from residential patterns and other factors) persisted and continues to be a major challenge.
-
Defining de facto segregation: De facto segregation refers to segregation that occurs in practice, even without explicit legal mandates. This type of segregation is often driven by housing patterns, economic disparities, and other factors that contribute to racial segregation in schools.
-
The role of housing policies in perpetuating segregation: Historically discriminatory housing policies, such as redlining, contributed significantly to residential segregation and, consequently, school segregation. These policies continue to have a lasting impact on school demographics.
-
The ongoing struggle for equitable school funding and resources in segregated communities: Schools in predominantly Black and minority communities often receive less funding and resources than those in predominantly white communities, further perpetuating educational inequality.
Lasting Consequences and Ongoing Challenges
The consequences of the Justice Department's school desegregation orders continue to shape American education today.
-
The achievement gap between different racial and ethnic groups: The achievement gap between white students and students of color persists, highlighting the ongoing need for interventions to address the lasting effects of segregation.
-
The debate surrounding school choice and its impact on desegregation efforts: The rise of school choice initiatives has sparked debates about their potential impact on desegregation. Some argue that school choice can exacerbate segregation, while others believe it can offer alternatives to failing schools in segregated communities.
-
Ongoing legal challenges related to school segregation: Legal battles continue to be fought to address issues of school segregation, particularly in the context of de facto segregation and disparities in school funding.
-
The need for continued federal and local action to ensure equitable education: To achieve true educational equity, continued federal and local action is needed to address issues of school funding, resource allocation, and the persistent effects of historical segregation.
Conclusion
The Justice Department's school desegregation orders represent a pivotal moment in American history, leaving a complex and enduring legacy. While significant progress has been made, challenges remain. The achievement gap persists, and de facto segregation continues to hinder equal educational opportunities for many students. To truly achieve the promise of Brown v. Board, continued vigilance, proactive policies, and a commitment to equitable school funding are essential. Further research and analysis of the Justice Department's school desegregation orders are crucial to inform future strategies for creating a more just and equitable education system for all. Addressing the ongoing legacy of school desegregation requires a sustained commitment to equitable education policies and practices.

Featured Posts
-
 Become A Play Station Beta Tester Sonys New Program Explained
May 02, 2025
Become A Play Station Beta Tester Sonys New Program Explained
May 02, 2025 -
 Goedkoper Auto Opladen Met Enexis In Noord Nederland Een Gids Voor Buiten De Piektijden
May 02, 2025
Goedkoper Auto Opladen Met Enexis In Noord Nederland Een Gids Voor Buiten De Piektijden
May 02, 2025 -
 Stroomnetaansluiting Kampen Gemeente Start Kort Geding Tegen Enexis
May 02, 2025
Stroomnetaansluiting Kampen Gemeente Start Kort Geding Tegen Enexis
May 02, 2025 -
 Is This Christina Aguilera Fans React To Heavily Edited Photoshoot Images
May 02, 2025
Is This Christina Aguilera Fans React To Heavily Edited Photoshoot Images
May 02, 2025 -
 Souness On Arsenal A Champions League Threat Emerges Leaving Gunners Behind
May 02, 2025
Souness On Arsenal A Champions League Threat Emerges Leaving Gunners Behind
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Macron Alerte Sur La Militarisation Potentielle De L Aide Humanitaire A Gaza Par Israel
May 03, 2025
Macron Alerte Sur La Militarisation Potentielle De L Aide Humanitaire A Gaza Par Israel
May 03, 2025 -
 La Militarisation De L Aide Humanitaire A Gaza La Mise En Garde De Macron
May 03, 2025
La Militarisation De L Aide Humanitaire A Gaza La Mise En Garde De Macron
May 03, 2025 -
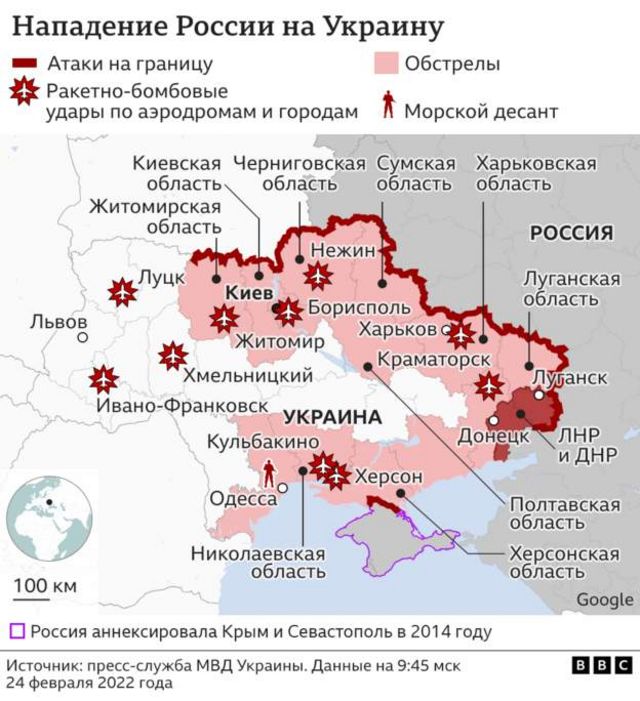 Reaktsiya S Sh A Na Deystviya Rossii V Ukraine Makron O Novykh Sanktsiyakh
May 03, 2025
Reaktsiya S Sh A Na Deystviya Rossii V Ukraine Makron O Novykh Sanktsiyakh
May 03, 2025 -
 Aide Humanitaire A Gaza Macron Denonce Le Risque De Militarisation Par Israel
May 03, 2025
Aide Humanitaire A Gaza Macron Denonce Le Risque De Militarisation Par Israel
May 03, 2025 -
 Makron Dobilsya Usileniya Davleniya S Sh A Na Rossiyu V Svyazi S Ukrainoy
May 03, 2025
Makron Dobilsya Usileniya Davleniya S Sh A Na Rossiyu V Svyazi S Ukrainoy
May 03, 2025
