Apple Crop Losses: Rosy Apple Aphid Infestation Impacts Harvest
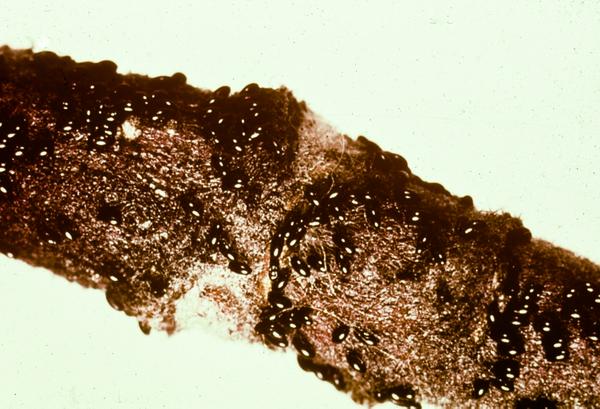

Table of Contents
Understanding the Rosy Apple Aphid and its Life Cycle
The rosy apple aphid is a small, pear-shaped insect, typically measuring only 2-3 mm in length. Its distinctive rosy-pink color (hence the name) and powdery wax coating make it relatively easy to identify, though careful inspection may be needed, especially in early stages. Understanding the rosy apple aphid lifecycle is key to effective control.
- Eggs: The lifecycle begins with overwintering eggs laid on the apple tree branches, typically in the crevices of bark.
- Nymphs: In spring, these eggs hatch into wingless nymphs, which feed on the young leaves and shoots. These nymphs rapidly mature.
- Adults: Adult aphids can be both winged and wingless, allowing for efficient dispersal throughout the orchard. A single aphid can produce numerous offspring through parthenogenesis (asexual reproduction), leading to exponential population growth.
- Preferred Apple Varieties: While it attacks various apple trees, some varieties are more susceptible than others to rosy apple aphid infestations.
Identifying Signs of Rosy Apple Aphid Infestation in Apple Orchards
Early detection of a rosy apple aphid infestation is crucial for minimizing crop damage. Several telltale signs indicate the presence of these destructive pests:
- Curled or Distorted Leaves: Aphids feed on the sap of young leaves, causing them to curl, distort, and become stunted.
- Sticky Honeydew Excretion: The aphids excrete a sticky substance called honeydew, which coats the leaves and fruit. This honeydew provides a breeding ground for sooty mold, further impacting the tree's health and the fruit's marketability.
- Stunting of New Growth: Infestations can severely restrict the growth of new shoots and branches, impacting overall tree vigor.
- Reduced Fruit Size and Quality: Heavy aphid infestations lead to smaller, less attractive apples with poor taste and texture.
- Premature Fruit Drop: Infested trees often experience premature fruit drop, resulting in significantly reduced yields.
Regular orchard inspections, particularly during the spring and early summer months when aphid populations peak, are essential for early detection and timely intervention.
Effective Management Strategies for Rosy Apple Aphid Control
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is the most effective approach to controlling rosy apple aphid infestations. This involves a combination of preventative and reactive strategies, minimizing the reliance on chemical insecticides.
-
Preventative Measures:
- Orchard Sanitation: Removing fallen leaves and pruning infected branches helps eliminate overwintering eggs.
- Resistant Apple Varieties: Planting apple varieties with some natural resistance to rosy apple aphids can significantly reduce the risk of severe infestations.
- Monitoring Aphid Populations: Regularly monitoring aphid populations using sticky traps or visual inspections helps detect infestations early, allowing for timely intervention.
-
Biological Control: Introducing natural predators, such as ladybugs, lacewings, and hoverflies, can significantly suppress aphid populations. These beneficial insects prey on aphids, providing a sustainable and environmentally friendly control method.
-
Chemical Control: In cases of severe infestations where other methods are insufficient, targeted application of approved insecticides might be necessary. However, this should be a last resort, carefully considering the impact on beneficial insects and the environment. Always adhere to label instructions and safety precautions when using insecticides.
The Economic Impact of Rosy Apple Aphid Infestations on Apple Farmers
Rosy apple aphid infestations represent a significant financial burden on apple farmers. The reduced yields, increased costs associated with pest control measures, and the diminished quality of the harvested fruit directly impact profitability. Significant infestations can translate to substantial losses, affecting farmers' livelihoods and potentially impacting the overall stability of the apple market. These costs extend beyond the immediate loss of yield, also encompassing the cost of labor, insecticide application, and potential crop replacement.
Conclusion
Rosy apple aphid infestations pose a considerable threat to apple production globally. Understanding the aphid's life cycle, recognizing the symptoms of infestation, and employing effective integrated pest management (IPM) strategies are crucial for minimizing crop losses and safeguarding the apple harvest. By implementing proactive measures, including regular orchard monitoring, utilizing biological control methods, and resorting to chemical interventions only when absolutely necessary, apple growers can effectively combat rosy apple aphid infestations and protect their valuable crops. Protect your apple harvest; learn more about effective rosy apple aphid control and integrated pest management techniques today!

Featured Posts
-
 Nyt Mini Crossword Solution March 18
May 19, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Solution March 18
May 19, 2025 -
 British Myths And Legends New Stamp Artwork Unveiled
May 19, 2025
British Myths And Legends New Stamp Artwork Unveiled
May 19, 2025 -
 Cohep Transparencia Y Observacion Del Proceso Electoral
May 19, 2025
Cohep Transparencia Y Observacion Del Proceso Electoral
May 19, 2025 -
 Postman Powerful Tips And Tricks For Api Testing
May 19, 2025
Postman Powerful Tips And Tricks For Api Testing
May 19, 2025 -
 Tampoy Anakalyptontas Nea Stoixeia Gia Toys Fonoys
May 19, 2025
Tampoy Anakalyptontas Nea Stoixeia Gia Toys Fonoys
May 19, 2025
