Bank Of Canada Navigates Rising Core Inflation: A Balancing Act

Table of Contents
Understanding the Current Inflationary Pressure
The Canadian economy is currently grappling with elevated core inflation. Core inflation, which excludes volatile items like food and energy from the Consumer Price Index (CPI), provides a more stable measure of underlying inflationary pressures. Currently, Canada’s core inflation rate remains above the Bank of Canada’s target range of 1-3%, indicating persistent inflationary pressures.
Several factors contribute to this elevated core inflation:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Ongoing global supply chain bottlenecks continue to impact the availability and cost of goods, contributing to cost-push inflation. This means increased production costs are passed onto consumers in the form of higher prices.
- Demand-Pull Inflation: Robust consumer spending and strong demand for goods and services are also fueling inflationary pressures. This demand-pull inflation signifies that high demand outstrips supply, pushing prices upward.
- Commodity Price Increases: Fluctuations in global commodity prices, particularly energy, significantly impact the overall inflation rate, both directly and indirectly through their effect on transportation and production costs.
The persistence of inflation raises concerns about its potential impact on consumer confidence and spending habits. High inflation erodes purchasing power, potentially leading to decreased consumer demand and slowing economic growth.
The Bank of Canada's Monetary Policy Response
In response to rising core inflation, the Bank of Canada has employed a series of monetary policy tools, primarily focusing on interest rate hikes. These increases aim to cool down the economy by making borrowing more expensive, thus reducing consumer spending and investment.
- Recent Interest Rate Hikes: The Bank has implemented several interest rate hikes in recent months, raising the overnight rate to curb inflation.
- Quantitative Tightening: In addition to interest rate adjustments, the Bank might employ quantitative tightening, reducing the money supply by selling government bonds.
- Inflation Targeting Framework: The Bank operates within an inflation targeting framework, aiming to maintain inflation within its target range. However, the effectiveness of this framework in the current climate is being rigorously tested due to the complexity of global and domestic factors.
The impact of these interest rate changes on borrowing costs is substantial. Higher interest rates increase the cost of mortgages, business loans, and other forms of credit, potentially impacting economic activity. The Bank must carefully balance its inflation-control measures with the potential for negative consequences on economic growth.
Economic Growth vs. Inflation Control: The Trade-off
The Bank of Canada faces a significant trade-off: controlling inflation without triggering a recession or significantly impacting employment. Aggressive interest rate hikes, while effective in curbing inflation, risk slowing economic growth and potentially causing job losses.
- Recession Risk: The aggressive interest rate increases raise the risk of a recession, a prolonged period of economic decline.
- Unemployment Rate: Higher interest rates can lead to decreased business investment and hiring, increasing the unemployment rate.
- GDP Growth: Slowing economic activity translates to lower GDP growth, impacting overall economic prosperity.
- Soft Landing: The Bank aims for a "soft landing," a scenario where inflation is reduced without causing a significant economic downturn. Achieving this delicate balance is a considerable challenge in the current economic environment.
The current state of the Canadian economy is a key factor in the Bank's decision-making. Analyzing economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment levels, and consumer confidence is crucial in determining the appropriate monetary policy response.
The Impact on Canadian Households and Businesses
Rising interest rates have tangible consequences for both Canadian households and businesses.
- Higher Mortgage Rates: Homeowners with variable-rate mortgages are directly impacted by interest rate hikes, facing higher monthly payments.
- Reduced Consumer Spending: Increased borrowing costs can lead to reduced consumer spending, as individuals prioritize debt repayment.
- Increased Business Borrowing Costs: Businesses face higher borrowing costs for loans and lines of credit, potentially hindering investment and expansion plans.
These factors influence consumer confidence and business investment decisions, leading to broader impacts on the Canadian economy. The Bank of Canada needs to consider the ripple effect of its policy decisions on all economic actors.
Conclusion
The Bank of Canada's management of rising core inflation is a complex balancing act, requiring careful consideration of economic growth and the repercussions of its monetary policy choices. The current inflationary environment necessitates a nuanced approach, weighing the necessity to control prices against the risks of triggering a recession or significantly affecting employment. Understanding the Bank's actions and their consequences is vital for individuals and businesses navigating the Canadian economy.
Stay informed about the Bank of Canada's decisions and their impact on the Canadian economy by following their announcements and engaging with reputable financial news sources. Understanding the complexities of managing core inflation is crucial for all Canadians to navigate the evolving economic landscape. Continue to monitor the Bank of Canada's actions as they continue to manage core inflation effectively.

Featured Posts
-
 Middle Managers Their Value In Driving Company Performance And Employee Engagement
May 22, 2025
Middle Managers Their Value In Driving Company Performance And Employee Engagement
May 22, 2025 -
 Du An Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Dong Nai Kien Nghi Ket Noi Giao Thong Voi Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025
Du An Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Dong Nai Kien Nghi Ket Noi Giao Thong Voi Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025 -
 Rossiya I Nato Ugroza Kaliningradu I Otvet Patrusheva
May 22, 2025
Rossiya I Nato Ugroza Kaliningradu I Otvet Patrusheva
May 22, 2025 -
 Understanding Core Weave Crwv Jim Cramers Perspective And Market Analysis
May 22, 2025
Understanding Core Weave Crwv Jim Cramers Perspective And Market Analysis
May 22, 2025 -
 Hands On With Googles New Ai Smart Glasses Prototype
May 22, 2025
Hands On With Googles New Ai Smart Glasses Prototype
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Fed Ex Truck Fire Closes Route 283 In Lancaster County Pennsylvania
May 22, 2025
Fed Ex Truck Fire Closes Route 283 In Lancaster County Pennsylvania
May 22, 2025 -
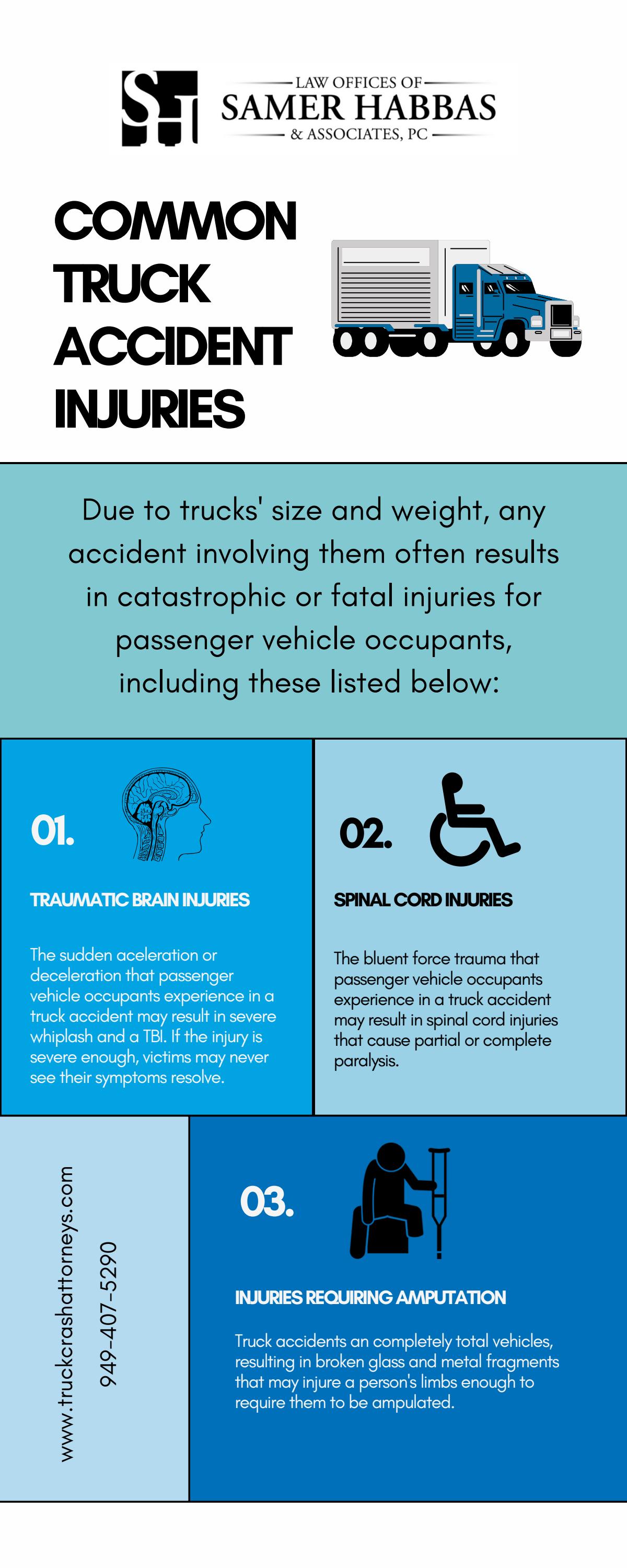 Interstate 83 Produce Truck Accident Injuries Reported
May 22, 2025
Interstate 83 Produce Truck Accident Injuries Reported
May 22, 2025 -
 Lancaster County Fed Ex Truck Catches Fire On Route 283
May 22, 2025
Lancaster County Fed Ex Truck Catches Fire On Route 283
May 22, 2025 -
 I 83 Closed After Tractor Trailer Produce Shipment Crash
May 22, 2025
I 83 Closed After Tractor Trailer Produce Shipment Crash
May 22, 2025 -
 Produce Hauling Truck Accident On I 83 Details Emerge
May 22, 2025
Produce Hauling Truck Accident On I 83 Details Emerge
May 22, 2025
