Behind The Double Standard: UK And Australian Sanctions On Myanmar – A Critical Analysis

Table of Contents
The Nature of UK and Australian Sanctions on Myanmar
Types of Sanctions Imposed
Both the UK and Australia have implemented targeted sanctions against individuals and entities deemed responsible for human rights violations in Myanmar. These targeted sanctions primarily consist of:
- Financial sanctions: Asset freezes, prohibiting individuals and entities from accessing financial systems within the UK and Australia.
- Travel bans: Preventing sanctioned individuals from entering either country.
- Arms embargo: Restrictions on the sale and supply of arms and related materials to Myanmar.
Examples of sanctioned individuals include members of the Myanmar military junta, and entities include businesses linked to the military regime. The legal basis for these sanctions is usually rooted in national legislation aimed at protecting human rights and preventing the financing of terrorism and serious crimes.
Scope and Effectiveness of Sanctions
The effectiveness of sanctions remains a subject of intense debate. While some argue that targeted sanctions can pressure the regime and limit its ability to finance atrocities, others point to their limitations.
- Successes: Some evidence suggests that financial sanctions have hampered the military's access to international capital. Travel bans may also curtail the movement and activities of key perpetrators.
- Failures: Sanctions evasion remains a significant challenge. The military regime can utilize illicit networks and alternative financial channels to circumvent restrictions. The impact on the civilian population, already suffering immensely, is also a critical concern. There is limited evidence of a significant shift in the military's behavior due to the sanctions imposed so far.
- Unintended Consequences: The sanctions could inadvertently harm ordinary Myanmar citizens who may rely on businesses tied to sanctioned entities. This underscores the need for careful targeting and ongoing impact assessments.
Comparison with Sanctions Regimes Against Other Countries
Case Studies of Similar Situations
Comparing the UK and Australia's approach to Myanmar with their responses to other countries facing severe human rights violations reveals potential inconsistencies.
- Russia: The comprehensive sanctions imposed on Russia following its invasion of Ukraine differ significantly in scope and intensity compared to the sanctions on Myanmar. This disparity may be linked to the geopolitical importance of Russia and the potentially greater threat it poses to global security.
- Sudan: The sanctions regime against Sudan, while complex and evolving, has also seen varied approaches from Western governments over time. The focus and intensity of sanctions often fluctuated depending on geopolitical contexts and concerns beyond purely human rights issues.
- Syria: The protracted conflict in Syria has led to a complex web of sanctions, with varying levels of engagement from different countries. This illustrates how geopolitical considerations and national interests can influence the implementation and enforcement of sanctions.
The reasons for these discrepancies are multi-faceted, including differing assessments of the threat level posed by each regime and the complexities of international relations.
The Role of Geopolitical Factors
Geopolitical factors play a significant role in shaping the response to human rights crises and the application of sanctions.
- National Interest: The perceived national interest of the UK and Australia, including their economic ties and strategic alliances, might influence their approach to sanctions.
- Economic Ties: Countries with strong economic ties with Myanmar or other nations facing sanctions might be less inclined to impose stringent measures.
- Bias in Application: Concerns exist about potential biases in the selection of targets for sanctions and the intensity of sanctions applied. This raises questions about fairness and consistency.
Criticisms and Gaps in the Current Approach
Effectiveness of Targeted Sanctions
While targeted sanctions aim to hold specific individuals and entities accountable, their effectiveness in addressing the root causes of human rights abuses in Myanmar remains questionable.
- Limitations and Loopholes: The capacity for sanctions evasion and the limited impact on the military's overall power structure suggest substantial limitations.
- Potential Alternatives: Stronger, more comprehensive sanctions, including those targeting the military's main sources of revenue, could be considered. Collaboration with international organizations to improve monitoring and enforcement mechanisms is also crucial.
Calls for Stronger Action
Many human rights organizations advocate for more comprehensive and robust international action against the Myanmar junta.
- Arguments for Stronger Action: Critics argue that current sanctions are insufficient and that more decisive action, including a referral to the International Criminal Court (ICC), is necessary. The principle of universal jurisdiction also allows some states to prosecute perpetrators regardless of where the crimes occurred.
- Arguments Against Stronger Action: Concerns are raised about potential negative consequences for the civilian population and the challenges of effectively enforcing stricter sanctions.
- Ongoing Advocacy: Various international and domestic advocacy groups continue to call for increased pressure on the Myanmar junta and for greater accountability for the widespread human rights abuses occurring there.
Conclusion
This analysis reveals a concerning double standard in the application of sanctions against Myanmar by the UK and Australia, compared to their approaches towards other nations facing similar human rights crises. The current UK and Australian sanctions on Myanmar, although well-intentioned, suffer from limitations in their scope, effectiveness, and consistency with responses to comparable situations. Geopolitical considerations and economic factors undeniably influence the decision-making process. To foster a more just and equitable international response to human rights violations, a more consistent and effective approach to sanctions is crucial. We must demand stronger action on Myanmar, actively support human rights organizations, and continue to hold governments accountable for their inaction. Learn more about UK and Australian sanctions on Myanmar and how you can contribute to a more just world.

Featured Posts
-
 80 Let Pobedy Vlasti Eao O Vyplatakh Veteranam Velikoy Otechestvennoy Voyny
May 13, 2025
80 Let Pobedy Vlasti Eao O Vyplatakh Veteranam Velikoy Otechestvennoy Voyny
May 13, 2025 -
 Application Invited Professorship In Fine Arts Spatial Concepts Focus
May 13, 2025
Application Invited Professorship In Fine Arts Spatial Concepts Focus
May 13, 2025 -
 Oregon Ducks Fall Short Against Duke In Ncaa Tournament
May 13, 2025
Oregon Ducks Fall Short Against Duke In Ncaa Tournament
May 13, 2025 -
 Heatwave Emergency Record Breaking Temperatures In La And Orange Counties
May 13, 2025
Heatwave Emergency Record Breaking Temperatures In La And Orange Counties
May 13, 2025 -
 Las Vegas Aces Win Thanks To Deja Kellys Clutch Performance
May 13, 2025
Las Vegas Aces Win Thanks To Deja Kellys Clutch Performance
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Pregnant Cassie Ventura And Husband Alex Fine Shine At Mob Land Premiere
May 13, 2025
Pregnant Cassie Ventura And Husband Alex Fine Shine At Mob Land Premiere
May 13, 2025 -
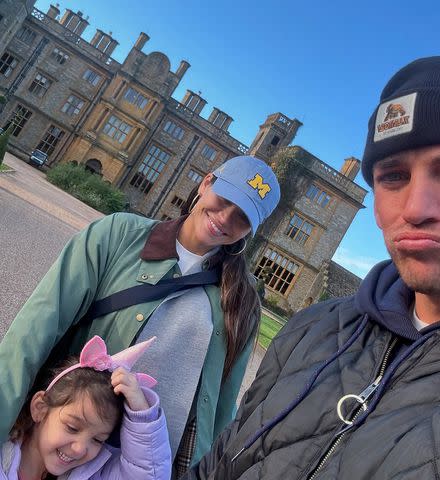 Third Times The Charm Cassie Announces Another Pregnancy
May 13, 2025
Third Times The Charm Cassie Announces Another Pregnancy
May 13, 2025 -
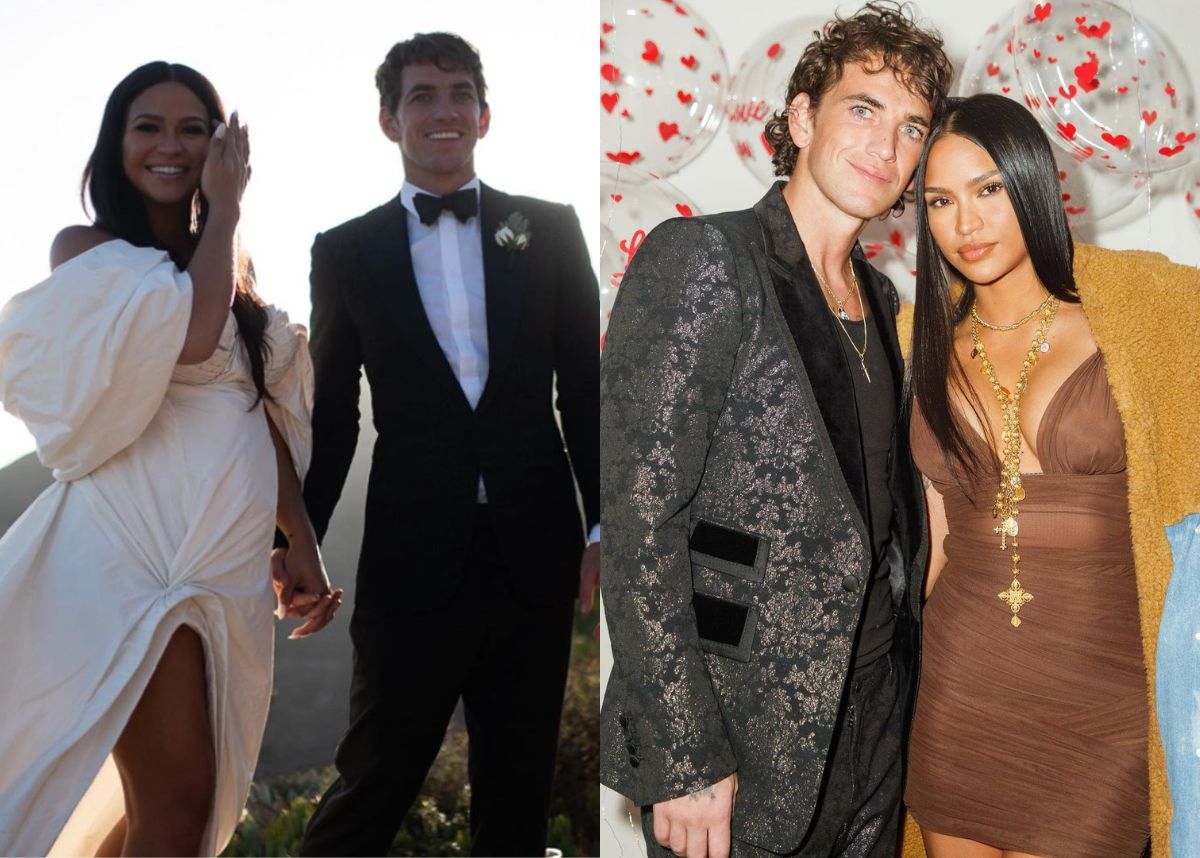 Cassie And Alex Fine Mob Land Premiere Photos Featuring Pregnant Cassie
May 13, 2025
Cassie And Alex Fine Mob Land Premiere Photos Featuring Pregnant Cassie
May 13, 2025 -
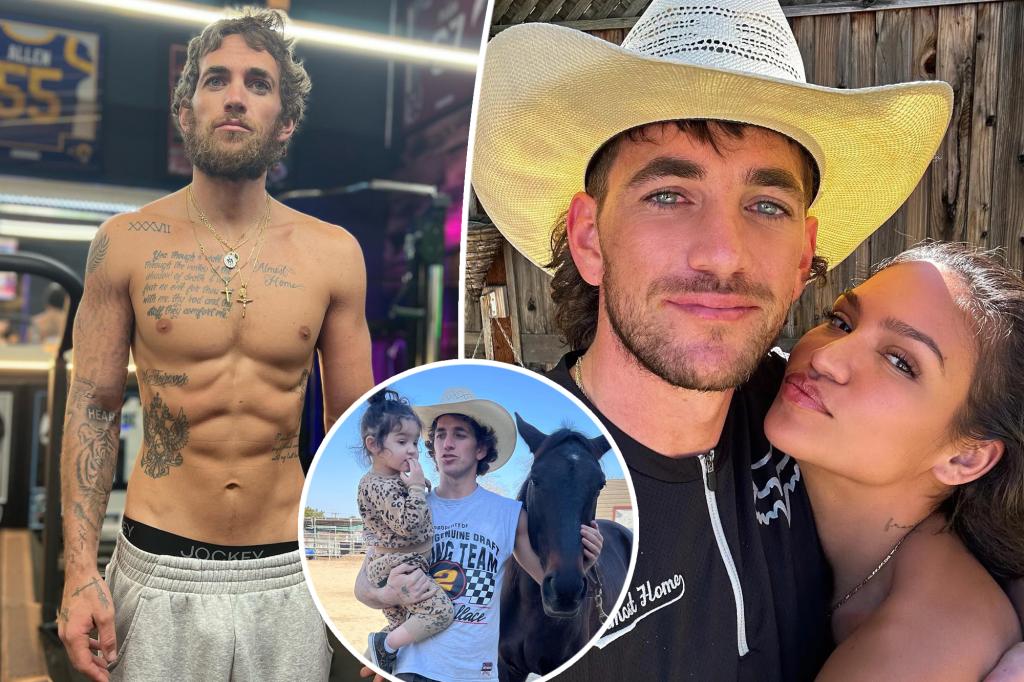 Pregnant Cassie Ventura And Husband Alex Fine Make First Public Appearance
May 13, 2025
Pregnant Cassie Ventura And Husband Alex Fine Make First Public Appearance
May 13, 2025 -
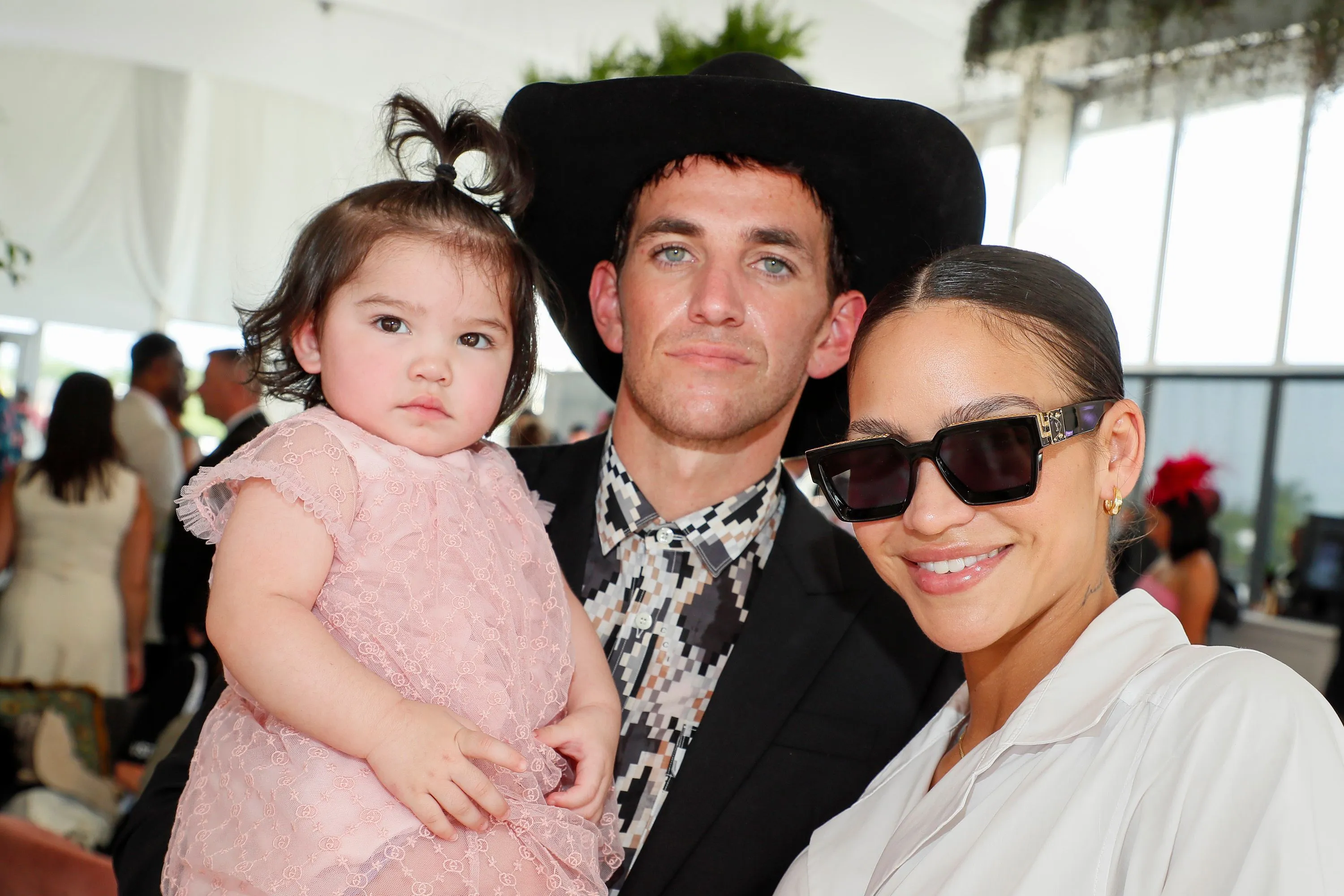 Cassie Ventura And Alex Fines Red Carpet Appearance Photos From The Mob Land Premiere
May 13, 2025
Cassie Ventura And Alex Fines Red Carpet Appearance Photos From The Mob Land Premiere
May 13, 2025
