Behind The Scenes: China's US Dealmaking Strategy

Table of Contents
Key Players and Their Roles in China's US Dealmaking
Negotiations between China and the US are rarely simple, involving a complex interplay of individuals and institutions. Understanding the key players and their roles is essential to deciphering China's US dealmaking strategy.
- Bullet points:
- Primary Decision-Makers: The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) Politburo Standing Committee ultimately holds the power to approve major deals. Specific individuals within this committee, often including the Premier and the Vice Premier in charge of economic affairs, play crucial roles in setting the negotiating parameters and approving final agreements. The Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) is the primary government agency responsible for conducting trade negotiations.
- Influence of State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs): Powerful SOEs like Sinopec, State Grid, and China Mobile often participate directly in negotiations, leveraging their economic might to secure advantageous terms. Their actions are closely aligned with the government's strategic goals.
- Think Tanks and Advisors: A network of influential think tanks and advisors provides crucial expertise and policy recommendations, shaping the overall China's US dealmaking strategy. These groups conduct extensive research and analysis to inform the negotiating teams.
Expand: Internal power dynamics within the Chinese negotiating team can significantly impact the dealmaking process. Competition between different government agencies or SOEs for resources and influence can lead to compromises and shifts in strategy. The need for consensus and the hierarchical nature of the CCP decision-making process can sometimes lead to lengthy negotiations and a cautious approach.
Tactics and Negotiating Styles Employed by China
China employs a distinct set of tactics and negotiating styles when dealing with the US. These strategies are rooted in a long-term perspective and a focus on securing national interests. Analyzing these approaches is key to understanding China's US dealmaking strategy.
- Bullet points:
- Long-Term Relationships: China prioritizes building strong, long-term relationships with key US counterparts. This approach fosters trust and facilitates future collaboration.
- Reciprocity and Concessions: While assertive in pursuing their goals, Chinese negotiators often utilize reciprocity, offering concessions strategically to achieve their overarching objectives. This tactic helps build rapport and secure favorable outcomes.
- Public Opinion Management: China carefully manages public opinion both domestically and internationally, framing narratives to support its negotiating positions and influencing perceptions of the deals themselves.
Expand: Consider the 2012 acquisition of US wind turbine manufacturer AMSC by a Chinese company. This case exemplifies both the patient approach and the emphasis on acquiring critical technologies that are key components of China's US dealmaking strategy. The negotiations were lengthy, and while ultimately successful for the Chinese company, it also showcased a willingness to compromise and adapt to achieve its long-term technological goals. The Chinese approach often contrasts with a more transactional, short-term perspective sometimes seen in US negotiations. They often aim for a "win-win" outcome, but this is always viewed through the lens of achieving China's strategic objectives.
Leveraging Economic Power: Trade, Investment, and Technology
China's economic might is a significant factor in its US dealmaking strategy. The country strategically utilizes its market access, investment capabilities, and technological prowess to secure favorable terms.
- Bullet points:
- Chinese Investment in the US: Significant Chinese investment in US infrastructure projects and businesses provides leverage in negotiations. This investment can influence policy decisions and create dependencies.
- Impact of Trade Policies: China's trade policies, including tariffs and quotas, can significantly impact US industries, creating incentives for compromise in negotiations.
- Acquiring Advanced Technologies: China aggressively pursues the acquisition of advanced technologies from the US, often through joint ventures, acquisitions, and technology transfers. This strategy is central to its economic and military modernization plans.
Expand: The Belt and Road Initiative is a prime example of how China uses economic leverage in its global strategy, though not always directly aimed at the US. This initiative increases China's global influence and provides access to key resources and markets, strengthening its position in future negotiations. This approach indirectly affects the US by shifting global economic power dynamics. The acquisition of American companies possessing advanced technologies highlights China's determination to reduce its technological dependence on the US, a crucial aspect of China's US dealmaking strategy.
Long-Term Strategic Goals Behind China's US Dealmaking
China's deals with the US are not isolated events but integral parts of its broader strategic vision. Understanding these long-term goals is key to deciphering China's US dealmaking strategy.
- Bullet points:
- Global Leadership Ambitions: China aims to increase its global influence and challenge the US's traditional dominance in international affairs. Deals with the US can enhance its standing and credibility on the world stage.
- Technological Advancement: Acquiring advanced technologies from the US is crucial for China's economic development and military modernization. This drive underpins many of its negotiations.
- Securing Resources and Markets: China actively seeks access to key resources and markets globally, including the US. Securing these resources is vital for its economic growth and national security.
Expand: China's long-term goal of achieving technological self-reliance ("technological independence") significantly shapes its negotiating tactics. While it may seek collaboration and technology transfers in certain areas, it also invests heavily in domestic R&D to reduce its reliance on foreign technologies. This broader context is essential when analyzing specific deals and understanding the underlying motivations behind China's US dealmaking strategy.
Conclusion
In summary, China's US dealmaking strategy is characterized by long-term vision, strategic patience, skillful leverage of economic power, and a clear focus on national interests. Key players within the Chinese government and SOEs work in concert, employing a range of tactics to achieve specific objectives within the broader context of China's ambitions for global leadership and technological self-reliance. Understanding the nuances of this strategy is crucial for navigating the complexities of the US-China relationship. Further research into the specifics of individual deals and the evolving geopolitical landscape will continue to refine our understanding of China's US dealmaking strategy. Stay informed and continue learning about the intricacies of this crucial aspect of international relations.

Featured Posts
-
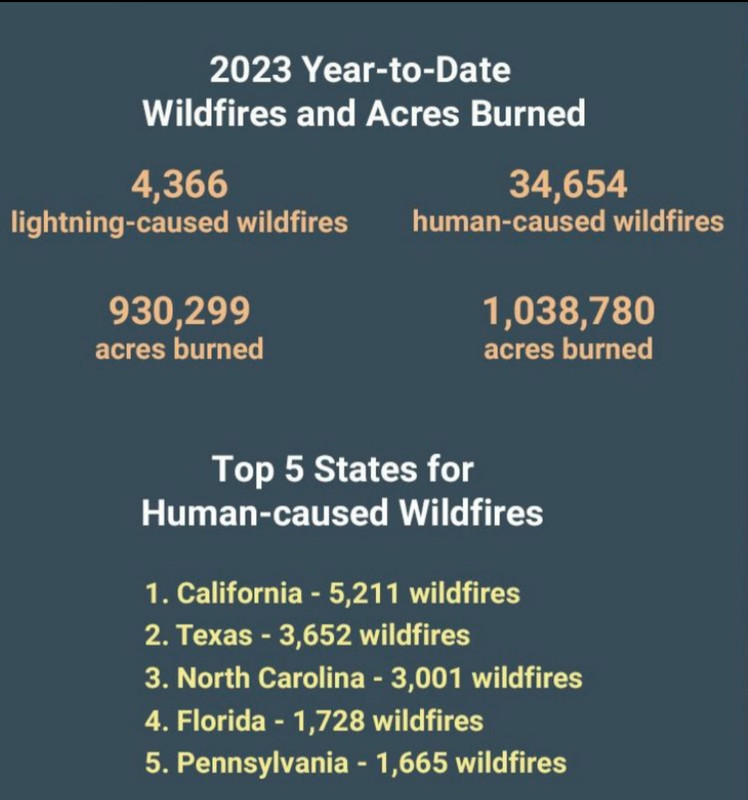 Are We Normalizing Disaster Betting The La Wildfires Example
May 15, 2025
Are We Normalizing Disaster Betting The La Wildfires Example
May 15, 2025 -
 Boston Celtics Face Orlando Magic In Crucial Playoff Game 3
May 15, 2025
Boston Celtics Face Orlando Magic In Crucial Playoff Game 3
May 15, 2025 -
 Penarol Vs Olimpia Resultado Final 0 2 Resumen Y Analisis Del Partido
May 15, 2025
Penarol Vs Olimpia Resultado Final 0 2 Resumen Y Analisis Del Partido
May 15, 2025 -
 Cobalt Market Instability The Impact Of Congos Export Restrictions
May 15, 2025
Cobalt Market Instability The Impact Of Congos Export Restrictions
May 15, 2025 -
 Lafcs Focus Shifts To Mls Crucial San Jose Matchup
May 15, 2025
Lafcs Focus Shifts To Mls Crucial San Jose Matchup
May 15, 2025
