Clean Energy's Unexpected Enemies: Threats To A Growing Industry

Table of Contents
Political and Regulatory Hurdles
The journey to a clean energy future is heavily influenced by the political landscape. Unstable or inconsistent policies can significantly impact investment and development.
Shifting Political Landscapes
Changes in government administration often bring shifts in policy priorities. This volatility creates uncertainty for investors and developers.
- Tax breaks for fossil fuels: Subsidies for the fossil fuel industry directly compete with clean energy investments, hindering the economic viability of renewable projects.
- Deregulation of emissions: Relaxing environmental regulations undermines the incentives for clean energy adoption and can lead to increased pollution.
- Political instability: Uncertainty in government policy discourages long-term investments in renewable energy infrastructure, as projects risk becoming unviable due to sudden changes in regulations.
Bureaucratic Bottlenecks
Navigating the complex web of permits and approvals can be a major hurdle for clean energy projects. Lengthy processes and inconsistent regulations across jurisdictions often lead to delays and increased costs.
- Lengthy environmental impact assessments: Rigorous assessments, while necessary, can cause significant delays, impacting project timelines and budgets.
- Permitting delays: Bureaucratic inefficiencies and lack of coordination between different agencies can significantly delay project approvals.
- Inconsistent regulations: Variations in regulations across different states or countries create uncertainty and increase the complexity of developing large-scale clean energy projects.
Economic and Financial Constraints
Despite the growing market, economic and financial challenges remain significant barriers to widespread clean energy adoption.
High Upfront Costs
Renewable energy technologies, especially large-scale solar and wind farms, require substantial upfront capital investment. Securing financing can be difficult, especially for emerging technologies.
- Challenges of securing financing: Clean energy projects often require long-term financing, which can be challenging to obtain due to perceived risks and uncertainties.
- Government subsidies and incentives: Government support, through tax credits, grants, and loan guarantees, is crucial for mitigating high upfront costs and attracting private investment.
Intermittency and Grid Integration Challenges
The intermittent nature of solar and wind power poses a challenge for grid stability. Integrating these renewable sources requires significant upgrades to existing infrastructure.
- Energy storage solutions: Battery storage and pumped hydro technologies are essential for addressing the intermittency of renewable energy sources, but they are costly and require further development.
- Upgrading existing power grids: Modernizing the grid to accommodate increased renewable energy generation requires significant investment and careful planning.
Competition from Fossil Fuels
The entrenched fossil fuel industry continues to pose a strong competitive threat, leveraging its established infrastructure and political influence.
- Government subsidies and tax breaks: Continued government support for fossil fuels undermines the competitiveness of clean energy.
- Lobbying power of the fossil fuel industry: Powerful lobbying efforts by fossil fuel companies influence policy decisions and hinder the progress of clean energy initiatives.
Technological and Infrastructure Limitations
Technological advancements and reliable supply chains are crucial for the continued growth of the clean energy sector.
Technological Advancements
Ongoing innovation is vital to improve the efficiency, affordability, and scalability of clean energy technologies.
- Battery storage: Further advancements in battery technology are needed to reduce costs, increase capacity, and improve lifespan.
- Solar panel efficiency: Research and development continue to focus on increasing the efficiency of solar panels, reducing their cost and land requirements.
- Role of research and development: Continued investment in research and development is crucial for overcoming technological limitations and driving innovation.
Supply Chain Issues
The supply chain for raw materials and components essential for clean energy technologies faces potential bottlenecks and geopolitical risks.
- Critical materials: Rare earth elements, crucial for wind turbines and electric vehicles, are often sourced from a limited number of countries, creating supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Sustainable and responsible sourcing: Ensuring sustainable and responsible sourcing of raw materials is crucial for the long-term viability of the clean energy sector.
Public Perception and Acceptance
Public perception and acceptance play a crucial role in the successful deployment of clean energy projects.
Addressing Public Concerns
Concerns regarding visual impacts, land use, and potential environmental effects of clean energy infrastructure need to be addressed through transparent communication and community engagement.
- Community engagement and public education: Open dialogue and proactive engagement with communities are crucial for addressing concerns and building support for clean energy projects.
- Addressing misinformation: Combating misinformation and promoting accurate information about the benefits of clean energy is essential for building public trust.
The NIMBY Factor
The "Not In My Backyard" (NIMBY) phenomenon, where local communities oppose clean energy projects near their homes, can significantly hinder development.
- Community engagement and benefit-sharing programs: Developing benefit-sharing programs and ensuring that local communities benefit from clean energy projects can help overcome NIMBYism.
- Transparent communication: Open communication and addressing community concerns are crucial for building trust and securing local support for clean energy projects.
Conclusion: Overcoming the Unexpected Enemies of Clean Energy
The transition to a sustainable energy future faces numerous hurdles, including political instability, economic constraints, technological limitations, and public perception challenges. Addressing these "clean energy's unexpected enemies" requires a multifaceted approach involving government policies, private investment, technological innovation, and public engagement. Overcoming these obstacles is critical for achieving a sustainable energy future. We must continue to advocate for policies that support clean energy development, invest in research and development, and foster transparent communication with communities. Learn more about supporting clean energy initiatives and combatting the challenges facing this vital sector at [link to a relevant resource].

Featured Posts
-
 Germanys Determined Bid For Victory Against Italy
May 21, 2025
Germanys Determined Bid For Victory Against Italy
May 21, 2025 -
 Ex Tory Councillors Wifes Racial Hatred Tweet Appeal Decision Delayed
May 21, 2025
Ex Tory Councillors Wifes Racial Hatred Tweet Appeal Decision Delayed
May 21, 2025 -
 Costcos Saskatchewan Campaign A Political Panel Analysis
May 21, 2025
Costcos Saskatchewan Campaign A Political Panel Analysis
May 21, 2025 -
 Nyt Crossword Clue Answers April 25 2025
May 21, 2025
Nyt Crossword Clue Answers April 25 2025
May 21, 2025 -
 5 Podcasts De Misterio Suspenso Y Terror Que Debes Escuchar
May 21, 2025
5 Podcasts De Misterio Suspenso Y Terror Que Debes Escuchar
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Germanys Determined Bid For Victory Against Italy
May 21, 2025
Germanys Determined Bid For Victory Against Italy
May 21, 2025 -
 Bangladeshinfo Com Reliable Information About Bangladesh
May 21, 2025
Bangladeshinfo Com Reliable Information About Bangladesh
May 21, 2025 -
 Finding Information On Bangladesh A Guide To Bangladeshinfo Com
May 21, 2025
Finding Information On Bangladesh A Guide To Bangladeshinfo Com
May 21, 2025 -
 Bangladeshinfo Com Exploring Bangladesh Online
May 21, 2025
Bangladeshinfo Com Exploring Bangladesh Online
May 21, 2025 -
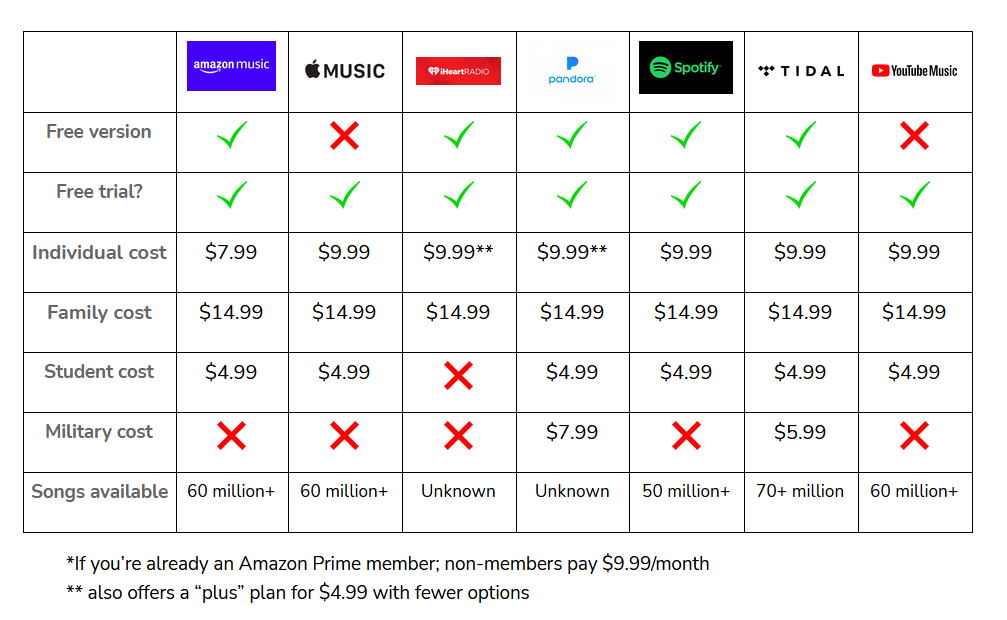 Live Bundesliga Matches Online Top Streaming Services Compared
May 21, 2025
Live Bundesliga Matches Online Top Streaming Services Compared
May 21, 2025
