CNIL's New AI Regulations: Practical Steps For Businesses
Table of Contents
Understanding the Scope of CNIL's AI Regulations
Defining "AI" under CNIL's Framework
The CNIL's definition of AI encompasses a broad range of systems capable of processing data and making decisions with minimal human intervention. This includes, but is not limited to:
- Machine learning: Algorithms that learn from data without explicit programming.
- Deep learning: A subset of machine learning using artificial neural networks with multiple layers.
- Natural language processing (NLP): Enabling computers to understand and process human language.
- Computer vision: Enabling computers to "see" and interpret images and videos.
These regulations significantly affect sectors heavily reliant on AI, including:
- Finance
- Healthcare
- Marketing and Advertising
- Human Resources
Businesses operating in these sectors must carefully examine their AI systems to ensure compliance. For a complete definition, refer to the official CNIL documentation [link to relevant CNIL document].
Key Principles of the Regulations
CNIL's AI regulations are built on several core principles:
- Data protection: AI systems must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the French Data Protection Act. This means ensuring the lawful, fair, and transparent processing of personal data.
- Transparency: Users should be informed about the use of AI systems and how their data is processed. This includes providing clear and accessible information about the AI's capabilities and limitations.
- Accountability: Businesses are responsible for the actions of their AI systems and must be able to demonstrate compliance with the regulations. This includes implementing appropriate technical and organizational measures to manage risks.
- Human oversight: While AI systems automate processes, human intervention and control must remain central.
Understanding these principles is the cornerstone of successful AI compliance under CNIL’s framework.
Practical Steps for Compliance
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
For high-risk AI systems, conducting a DPIA is mandatory. This assessment identifies potential risks to individuals' rights and freedoms and outlines mitigation strategies. The DPIA process typically involves:
- Defining the system: Clearly describe the AI system, its purpose, and how it processes personal data.
- Identifying risks: Analyze potential risks to individuals, such as discrimination, bias, and data breaches.
- Implementing safeguards: Detail the technical and organizational measures to mitigate identified risks.
- Monitoring and review: Regularly monitor the AI system’s performance and update the DPIA as needed.
Examples of high-risk AI systems requiring DPIAs include those used in:
- Credit scoring
- Law enforcement
- Healthcare diagnosis
Ensuring Transparency and User Control
Transparency is crucial. Users need to understand how an AI system affects them. This can be achieved through:
- Clear and concise explanations: Providing easily understandable information about the AI's purpose and functionality.
- Data access and correction: Allowing users to access, rectify, or erase their data processed by the AI system.
- Right to explanation: When appropriate, offering users explanations regarding AI-driven decisions that affect them.
Best practices for user control include giving individuals the ability to opt-out of AI-driven profiling or decision-making.
Implementing Appropriate Technical and Organisational Measures
Robust security measures are vital for protecting personal data processed by AI systems. This includes:
- Data encryption: Protecting data both in transit and at rest.
- Access control: Limiting access to sensitive data to authorized personnel only.
- Regular security audits: Identifying and addressing vulnerabilities.
- Data minimization: Collecting and processing only the minimum amount of data necessary.
- Purpose limitation: Using data only for the specified purpose.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Potential Fines and Penalties
Non-compliance with CNIL's AI regulations can result in significant fines. The CNIL has the power to impose penalties up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher. The severity of the penalty depends on factors such as:
- The nature and severity of the violation
- The extent of the damage caused
- The cooperation of the organization
The CNIL has a history of imposing substantial fines for data protection violations; reviewing past cases provides valuable insight into potential risks.
Reputational Damage and Loss of Trust
Beyond financial penalties, non-compliance can severely damage a company's reputation and erode customer trust. Data breaches and regulatory fines can lead to:
- Loss of customers
- Negative media coverage
- Difficulty attracting investors
Proactive compliance with CNIL's new AI regulations helps mitigate these risks and fosters public trust.
Conclusion
Successfully navigating CNIL's new AI regulations requires a proactive and comprehensive approach. By understanding the scope of the regulations, implementing appropriate technical and organizational measures, and conducting thorough DPIAs, businesses can minimize risks and ensure compliance. Ignoring these regulations could result in significant fines and irreparable damage to your reputation. Take the necessary steps today to ensure your business is compliant with CNIL's new AI regulations and protect your data. Learn more about AI compliance in France and French data protection by exploring the CNIL website and seeking expert advice.

Featured Posts
-
 Le Realisateur De Black Panther S Attaque Aux X Files
Apr 30, 2025
Le Realisateur De Black Panther S Attaque Aux X Files
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Giai Bong Da Thanh Nien Sinh Vien Quoc Te 2025 Cap Nhat Lich Thi Dau Moi Nhat
Apr 30, 2025
Giai Bong Da Thanh Nien Sinh Vien Quoc Te 2025 Cap Nhat Lich Thi Dau Moi Nhat
Apr 30, 2025 -
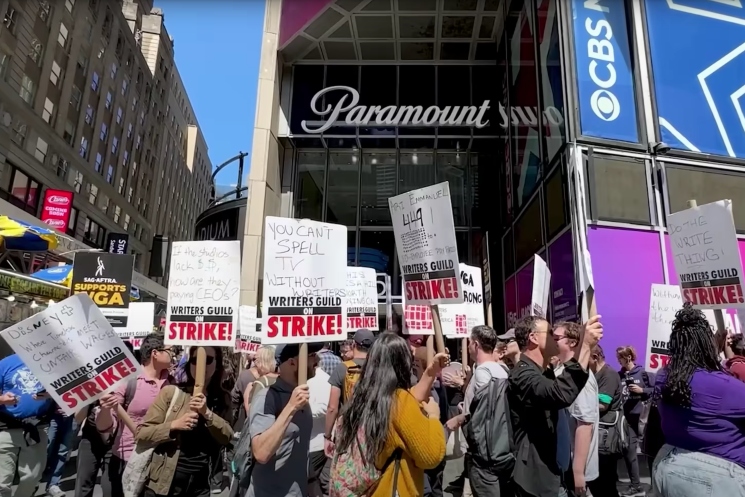 Hollywood Strike Actors Join Writers Bringing Industry To A Standstill
Apr 30, 2025
Hollywood Strike Actors Join Writers Bringing Industry To A Standstill
Apr 30, 2025 -
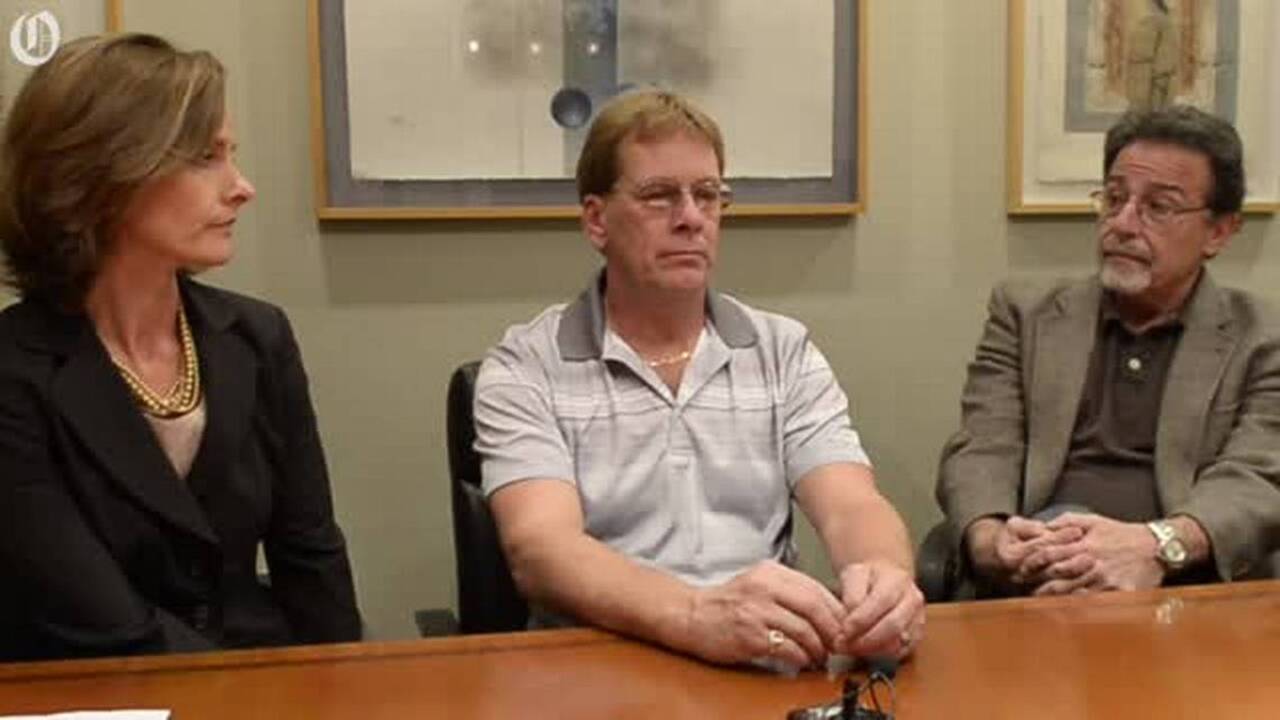 Jury Selection Underway In Charlotte Mothers Death Trial
Apr 30, 2025
Jury Selection Underway In Charlotte Mothers Death Trial
Apr 30, 2025 -
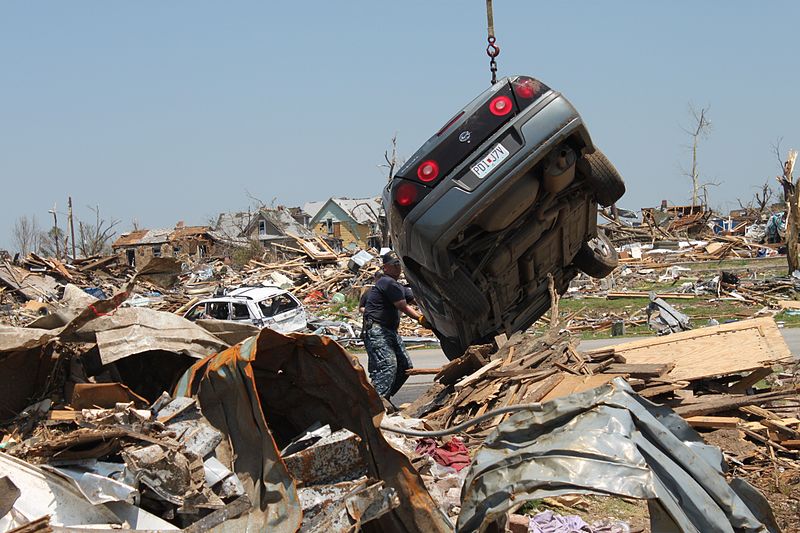 2025 Louisville Battered By Snow Tornadoes And Unprecedented Flooding
Apr 30, 2025
2025 Louisville Battered By Snow Tornadoes And Unprecedented Flooding
Apr 30, 2025
