Construction Slowdown: Fewer Housing Permits Issued
Table of Contents
Economic Factors Contributing to the Construction Slowdown
Several intertwined economic factors are contributing significantly to the current construction slowdown. These factors create a perfect storm, making it difficult for developers to justify new projects and thus, limiting the number of permits sought.
Rising Interest Rates and Mortgage Costs
Higher interest rates are a major culprit. The increased cost of borrowing money directly impacts affordability, reducing the purchasing power of prospective homebuyers. This decreased demand ripples through the market, discouraging developers from seeking permits for new construction.
- Increased borrowing costs: Higher interest rates translate to significantly higher mortgage payments for homebuyers.
- Reduced buyer purchasing power: With higher mortgage payments, buyers can afford less expensive homes, dampening demand for new construction.
- Impact on developer financing: Developers rely on loans to fund projects. Higher interest rates increase financing costs, making projects less profitable and less likely to proceed.
Recent data reveals a strong correlation between interest rate hikes and the subsequent decline in housing permit applications. For example, [Insert Statistic: e.g., a 1% increase in interest rates led to an X% decrease in permit applications in Q[Quarter] of [Year]].
Inflation and Material Costs
Soaring inflation and the subsequent increase in the cost of building materials are further exacerbating the construction slowdown. The price increases for lumber, steel, concrete, and other essential materials are squeezing profit margins, making many projects economically unviable.
- Supply chain disruptions: Ongoing global supply chain issues have contributed to material shortages and price volatility.
- Escalating material prices: The cost of key building materials has risen dramatically, significantly impacting project budgets.
- Impact on project budgets and timelines: Increased material costs necessitate budget revisions and potential project delays, making developers hesitant to commit to new projects.
[Insert Statistic: e.g., The cost of lumber has increased by Y% in the past year, adding Z dollars to the average cost of a new home].
Reduced Consumer Confidence
Economic uncertainty and decreased consumer confidence are also playing a crucial role. Concerns about job security, inflation impacting disposable income, and general economic anxiety all contribute to a decline in housing demand.
- Job market concerns: Fears of job losses or reduced income can make potential homebuyers hesitant to commit to a large purchase.
- Inflation impacting disposable income: Rising prices for everyday goods and services leave less disposable income for significant purchases like a new home.
- Consumer sentiment indices: A decline in consumer confidence indices often precedes a slowdown in the housing market.
[Insert Statistic: e.g., Consumer confidence has fallen by X points in the last [time period], reflecting reduced willingness to make large purchases].
Regulatory and Policy Challenges Impacting Housing Permit Issuance
Beyond economic factors, regulatory and policy challenges are significantly hindering the pace of new housing construction and the issuance of related permits.
Lengthy Permitting Processes
Complex and lengthy permitting processes often act as a significant deterrent for developers. Bureaucratic hurdles and delays can add substantial time and cost to projects.
- Complex regulations: Navigating numerous regulations and compliance requirements can be time-consuming and costly.
- Lengthy review times: Excessive delays in permit approvals can disrupt project timelines and increase development costs.
- Lack of streamlined processes: Inefficient permitting processes often lead to unnecessary delays and frustrations.
[Insert Example: e.g., In [City/Region], the average time to obtain a building permit is [Number] months, significantly longer than in other areas].
Land Use Restrictions and Zoning Regulations
Restrictive zoning laws and land use policies further limit the availability of land suitable for development. These regulations often constrain density, building heights, and the types of housing permitted.
- Density restrictions: Limits on housing density restrict the number of units that can be built on a given plot of land.
- Limitations on building heights: Height restrictions can reduce the overall number of housing units that can be constructed.
- Environmental regulations: Stringent environmental regulations, while crucial, can sometimes add complexity and delays to the permitting process.
[Insert Example: e.g., [City/Region]'s zoning regulations restrict development to single-family homes, limiting the supply of more affordable multi-family housing].
Labor Shortages in the Construction Industry
A shortage of skilled labor in the construction industry is also contributing to the construction slowdown. The lack of skilled workers impacts the ability of firms to complete projects on time and within budget, further dampening the desire to seek new permits.
- Lack of skilled workers: A shortage of skilled tradespeople, such as carpenters, electricians, and plumbers, hinders project completion.
- Aging workforce: The construction industry is facing an aging workforce, with many experienced workers approaching retirement.
- Training and recruitment challenges: Attracting and training a new generation of construction workers is a significant challenge.
[Insert Statistic: e.g., The construction industry is facing a shortage of X number of skilled workers nationwide].
Geographic Variations in Construction Slowdown
The impact of the construction slowdown is not uniform across all regions. Some areas are experiencing a more significant decline in permit issuance than others. These variations can be attributed to a combination of factors, including local economic conditions, specific regulatory environments, and geographical limitations.
[Include a map or chart visually representing the geographic disparities in permit issuance. Label areas with higher or lower rates of slowdown and provide brief explanations].
Conclusion: Understanding the Construction Slowdown and Fewer Housing Permits
The decline in housing permit issuance is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. This construction slowdown is driven by a confluence of economic pressures, including rising interest rates, inflation, and reduced consumer confidence, coupled with regulatory challenges such as lengthy permitting processes, restrictive zoning, and labor shortages. Geographic variations further complicate the picture. Understanding these multifaceted forces is crucial for developing effective strategies to address the ongoing housing shortage. The number of housing permits issued remains a critical indicator of the overall health of the construction sector and the housing market. To stay informed about the latest trends in the housing market and the impact of the housing permit decline, subscribe to our updates or follow relevant industry news sources. Stay informed about the ongoing construction market slowdown and its impact on your community.

Featured Posts
-
 Angel Loss To Yankees A Single Inning Sinks Kochanowiczs Performance
May 28, 2025
Angel Loss To Yankees A Single Inning Sinks Kochanowiczs Performance
May 28, 2025 -
 Friday Euro Millions E245m Jackpot Live Draw Updates And Results
May 28, 2025
Friday Euro Millions E245m Jackpot Live Draw Updates And Results
May 28, 2025 -
 Josh Allens Dating Preferences How They Contrast With Taylor Swift And Travis Kelces Dynamic
May 28, 2025
Josh Allens Dating Preferences How They Contrast With Taylor Swift And Travis Kelces Dynamic
May 28, 2025 -
 How Journaling Helped Kyle Stowers Find Success With The Miami Marlins
May 28, 2025
How Journaling Helped Kyle Stowers Find Success With The Miami Marlins
May 28, 2025 -
 Google Veo 3 Ai Video Generation And Its Potential Pitfalls
May 28, 2025
Google Veo 3 Ai Video Generation And Its Potential Pitfalls
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ticketmaster Setlist Fm Todo Lo Que Necesitas Para Tu Concierto
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Setlist Fm Todo Lo Que Necesitas Para Tu Concierto
May 30, 2025 -
 Gorillaz 25th Anniversary House Of Kong Exhibition Details And London Gig Information
May 30, 2025
Gorillaz 25th Anniversary House Of Kong Exhibition Details And London Gig Information
May 30, 2025 -
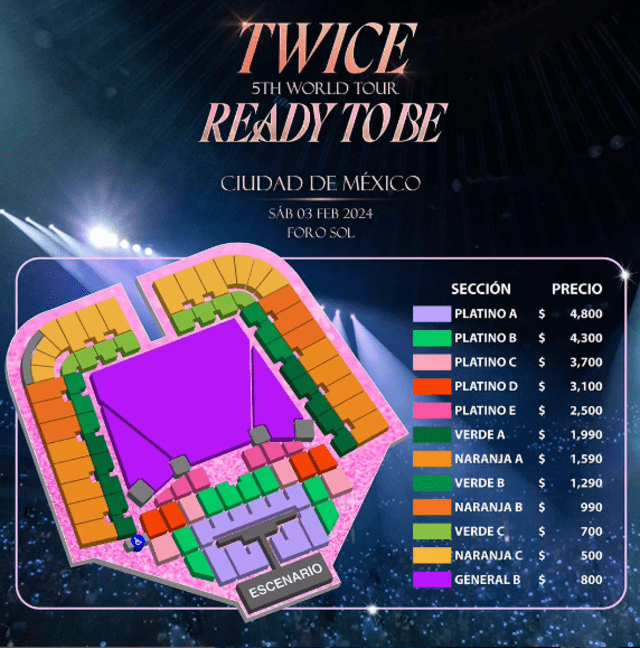 Preparate Para El Concierto Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm Se Unen Para Fans
May 30, 2025
Preparate Para El Concierto Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm Se Unen Para Fans
May 30, 2025 -
 Celebrating 25 Years Of Gorillaz House Of Kong And London Performances
May 30, 2025
Celebrating 25 Years Of Gorillaz House Of Kong And London Performances
May 30, 2025 -
 Gorillazs 25th Anniversary House Of Kong Exhibition And Exclusive London Shows
May 30, 2025
Gorillazs 25th Anniversary House Of Kong Exhibition And Exclusive London Shows
May 30, 2025
