Creatine: Benefits, Side Effects, And How To Use It Safely
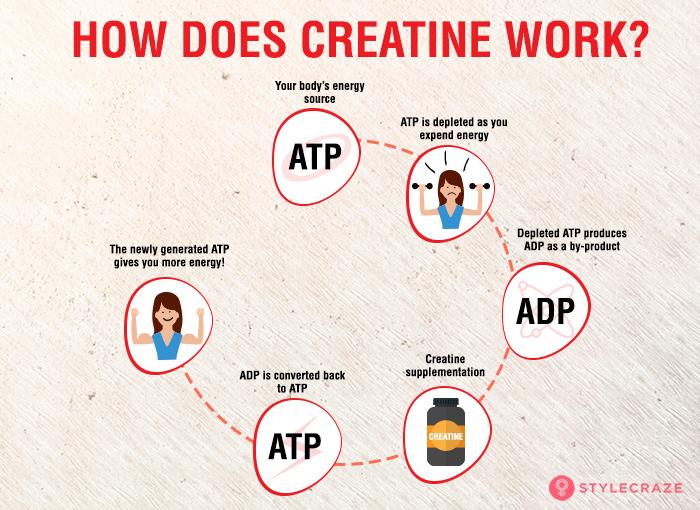
Table of Contents
Understanding Creatine Monohydrate
Creatine is a naturally occurring organic compound primarily found in skeletal muscle. It plays a crucial role in energy production within the body, specifically by helping to replenish adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells. While our bodies naturally produce creatine, and we obtain it from dietary sources like red meat and fish, supplementation can significantly increase muscle creatine stores, leading to enhanced athletic performance.
Several types of creatine exist, including creatine monohydrate, creatine HCL, creatine ethyl ester, and others. However, creatine monohydrate remains the most extensively researched and proven effective form. Its efficacy and safety have been demonstrated in countless studies, solidifying its position as the gold standard in creatine supplementation.
- Creatine's primary function: ATP replenishment for muscle contractions.
- Sources of creatine: Red meat, fish, and creatine supplements.
- Why creatine monohydrate is the preferred choice: Extensive research backing its efficacy and safety profile.
Benefits of Creatine Supplementation
Creatine supplementation offers a range of benefits, particularly for individuals engaged in high-intensity exercise and strength training.
Increased Strength and Power
Creatine significantly enhances muscle strength and power output. By increasing ATP availability, creatine allows for more forceful and sustained muscle contractions during short bursts of activity. This translates to improved performance in various activities:
- Improved performance in weightlifting: Increased reps, heavier weights, and faster recovery times.
- Increased speed and agility: Enhanced explosive power for sprints and quick movements.
- Enhanced power output during short bursts of activity: Beneficial for sports like sprinting, jumping, and plyometrics.
- Studies showing significant strength gains with creatine use: Numerous peer-reviewed studies demonstrate significant improvements in strength and power following creatine supplementation.
Muscle Growth and Hypertrophy
Creatine plays a crucial role in muscle growth and hypertrophy (muscle enlargement). Its effects are multifaceted:
- Creatine's effect on water retention in muscles (cell volumization): This increased cellular hydration promotes muscle protein synthesis.
- Increased muscle protein synthesis: Creatine supports the processes that build and repair muscle tissue.
- Studies showing significant muscle growth with creatine supplementation: Research consistently demonstrates that creatine supplementation, combined with resistance training, significantly increases muscle mass.
Cognitive Benefits
Emerging research suggests potential cognitive benefits of creatine supplementation, such as improvements in memory and brain function. However, this area requires further investigation:
- Potential improvements in cognitive function: Studies indicate possible benefits in specific populations, like older adults or individuals with certain neurological conditions.
- Need for further research to confirm cognitive benefits: More studies are needed to fully understand the extent and mechanisms of creatine's cognitive effects.
- Link between creatine and improved brain health in specific populations: Preliminary findings suggest potential benefits for brain health in certain groups, warranting further research.
Potential Side Effects of Creatine
While generally considered safe, creatine supplementation can cause some side effects, although these are typically mild and infrequent. Proper hydration is key to mitigating these potential issues.
- Water retention and weight gain: This is often the most reported side effect, primarily due to increased water retention in muscle cells.
- Gastrointestinal discomfort (cramps, diarrhea): These are usually temporary and can be reduced by gradually increasing the dosage.
- Muscle cramps (often due to dehydration): Adequate hydration is crucial to prevent muscle cramps.
- Kidney issues (rare, mainly in individuals with pre-existing conditions): Creatine is generally safe for individuals with healthy kidneys, but those with pre-existing kidney conditions should consult their doctor.
How to Use Creatine Safely and Effectively
To maximize the benefits and minimize the risks of creatine supplementation, follow these guidelines:
Loading Phase vs. Maintenance Phase
Two common approaches exist: a loading phase (higher dosage for a shorter period) and a maintenance phase (lower dosage for a longer period).
- Loading phase: Typically involves taking 20g of creatine monohydrate daily for 5-7 days. This rapidly saturates muscle creatine stores.
- Maintenance phase: After the loading phase, a daily dosage of 3-5g is sufficient to maintain elevated creatine levels.
The choice depends on individual preferences and goals. Many find the loading phase convenient for quicker results, while others prefer the maintenance phase for its simplicity.
Dosage and Timing
The recommended daily dosage is typically 3-5g of creatine monohydrate, taken daily, regardless of whether you use a loading phase. Optimal timing is often with or after workouts, as this is when muscle cells are most receptive to creatine uptake.
Cycling Creatine
Cycling creatine involves periods of supplementation followed by periods of discontinuation. This is often done to prevent potential tolerance or side effects. However, research suggests that continuous creatine use is equally safe and effective. Consult your doctor or a registered dietitian to determine the best approach for your individual needs.
- Importance of hydration while using creatine: Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially during and after workouts.
- Combining creatine with a balanced diet and exercise program: Creatine supplementation works best when combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise.
- Consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen: It's always advisable to seek professional advice before starting any new supplement.
Conclusion
Creatine monohydrate is a safe and effective supplement for enhancing athletic performance, promoting muscle growth, and potentially boosting cognitive function. However, it's crucial to understand its potential side effects and use it responsibly. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can maximize the benefits of creatine and minimize any risks. Remember to consult your doctor before starting any new supplement regime, including creatine. Start your journey towards improved strength and performance with safe and effective creatine supplementation today!

Featured Posts
-
 How Ha Seong Kim And Blake Snells Friendship Benefits Korean Baseball Players
May 16, 2025
How Ha Seong Kim And Blake Snells Friendship Benefits Korean Baseball Players
May 16, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Ha Seong Kim And Blake Snells Relationship On Korean Baseball
May 16, 2025
The Impact Of Ha Seong Kim And Blake Snells Relationship On Korean Baseball
May 16, 2025 -
 Mitigasi Bencana Pesisir Pembangunan Giant Sea Wall Sebagai Langkah Antisipatif
May 16, 2025
Mitigasi Bencana Pesisir Pembangunan Giant Sea Wall Sebagai Langkah Antisipatif
May 16, 2025 -
 Ufc Fighter Paddy Pimblett Liverpool Fc Dictates Fight Travel Plans
May 16, 2025
Ufc Fighter Paddy Pimblett Liverpool Fc Dictates Fight Travel Plans
May 16, 2025 -
 Police Investigate Armed Individual Near Gsw Campus
May 16, 2025
Police Investigate Armed Individual Near Gsw Campus
May 16, 2025
