Cybercriminal Makes Millions From Executive Office365 Infiltration
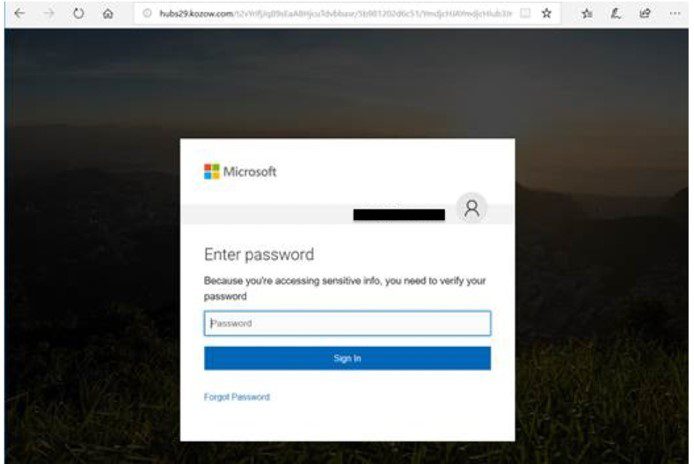
Table of Contents
The Methods Employed by the Cybercriminal
The success of this sophisticated cyberattack hinged on a multi-pronged approach exploiting human vulnerabilities and technological weaknesses within the target organization's Office365 environment.
Sophisticated Phishing Attacks
The cybercriminal employed highly targeted phishing techniques, focusing specifically on executives. This involved spear phishing and whaling attacks, leveraging personalized emails designed to appear legitimate and bypass spam filters. These attacks relied heavily on social engineering, manipulating the recipients into revealing sensitive information or clicking malicious links.
- Examples of phishing emails: Emails mimicking legitimate business communications, urgent payment requests, or seemingly harmless notifications containing malicious attachments.
- Use of social engineering: Creating a sense of urgency or authority, exploiting trust relationships, and playing on the recipient's fear of missing out (FOMO).
- Exploitation of vulnerabilities: Using known vulnerabilities in email clients or Office365 applications to deliver malware or gain unauthorized access.
- Keyword integration: The attacker likely utilized advanced persistent threats (APTs) to maintain long-term access, evading traditional security measures. Failure to properly configure email authentication protocols such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC further facilitated the success of these attacks.
Exploiting Weak Passwords and Credentials
Weak passwords and poor password hygiene significantly contributed to the breach. The cybercriminal likely employed various techniques to gain access to accounts, including:
- Importance of strong, unique passwords: Using complex passwords containing a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, and changing them regularly.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security, requiring a second form of verification beyond a password.
- Password management tools: Utilizing reputable password managers to securely store and manage complex passwords for multiple accounts.
- Keyword integration: Techniques like credential stuffing (using stolen credentials from other breaches), brute-force attacks (trying numerous password combinations), and password spraying (trying a single password across many accounts) were likely employed.
Leveraging Insider Threats (if applicable)
While not always the case, insider threats can significantly increase the risk of successful Office365 infiltration. In this case, further investigation may reveal if negligence, compromised accounts, or malicious insiders aided the cybercriminal's efforts.
- Negligence: Employees accidentally clicking malicious links or revealing sensitive information.
- Compromised accounts: Employee accounts compromised through phishing or malware.
- Malicious insiders: Deliberate actions by employees to leak information or grant access to unauthorized individuals.
- Keyword integration: Robust insider threat detection mechanisms, comprehensive employee training programs on security awareness, and regular security audits are essential for mitigating this risk.
The Financial Ramifications of the Breach
The financial consequences of this Office365 executive email compromise were far-reaching and devastating.
Direct Financial Losses
The direct financial impact included significant losses due to fraudulent transactions and the costs associated with recovery.
- Examples of fraudulent transactions: Unauthorized wire transfers, fake invoice payments, and fraudulent expense reports.
- The cost of remediation: The expense of incident response, forensic analysis, legal fees, and regulatory compliance.
- Business interruption costs: Lost revenue, productivity losses, and damage to ongoing projects.
- Keyword integration: Effective financial crime prevention measures and robust fraud detection systems are crucial to minimize losses. The costs associated with incident response are substantial and highlight the importance of proactive security measures.
Reputational Damage and Loss of Customer Trust
Beyond direct financial losses, the breach caused significant reputational damage and erosion of customer trust.
- Impact on stock price: A sharp decline in stock value following public disclosure of the breach.
- Loss of contracts: Clients may terminate contracts due to concerns about data security and the company’s ability to protect sensitive information.
- Negative media coverage: Public scrutiny and damage to the company’s brand image through negative media reports.
- Keyword integration: Maintaining a strong brand reputation and customer loyalty requires proactive security measures and a transparent communication strategy during and after a security incident. Effective public relations crisis management is essential to minimize reputational harm.
Best Practices for Preventing Office365 Executive Infiltration
Preventing executive Office365 infiltration demands a multi-layered security approach.
Implementing Robust Security Measures
Essential security practices include:
- MFA: Mandatory multi-factor authentication for all accounts, especially executive accounts.
- Strong password policies: Enforcing complex and regularly changed passwords.
- Regular security audits: Conducting periodic audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Employee training programs: Regular security awareness training for all employees to educate them about phishing threats and best security practices.
- Keyword integration: Implementing a robust Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system, utilizing threat intelligence feeds to proactively identify and mitigate potential threats, and fostering a strong security culture within the organization are all critical.
Leveraging Microsoft's Security Features
Microsoft offers numerous built-in Office365 security features:
- Advanced Threat Protection (ATP): Utilizing ATP to identify and block malicious emails and attachments.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implementing DLP to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization's network.
- Microsoft Defender for Office 365: Leveraging Microsoft Defender for Office 365 for comprehensive threat protection.
- Keyword integration: Understanding and utilizing Microsoft security solutions is paramount for mitigating risk. Utilizing cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools helps organizations assess their cloud security posture.
Regular Security Assessments and Penetration Testing
Proactive security measures are crucial:
- Vulnerability scanning: Regularly scanning systems for vulnerabilities and patching them promptly.
- Penetration testing: Simulating real-world attacks to identify weaknesses in the security infrastructure.
- Security audits: Conducting regular security audits to assess the effectiveness of security controls.
- Keyword integration: Employing red teaming exercises to test the organization's defenses, robust vulnerability management processes, and frequent security audits are all part of a comprehensive approach.
Conclusion
This case study vividly illustrates the devastating consequences of a successful Office365 executive email compromise, highlighting the sophisticated methods employed by cybercriminals and the substantial financial and reputational repercussions. The methods used—sophisticated phishing, weak passwords, and potential insider threats—underscore the critical need for robust security measures. Implementing multi-factor authentication, strong password policies, regular security audits, employee training, and leveraging Microsoft's built-in security features are crucial steps to prevent becoming the next victim. Don’t wait until it’s too late. Take immediate action to protect your Office365 accounts and bolster your overall cybersecurity posture. Explore resources like Microsoft's security center and invest in comprehensive cybersecurity training to safeguard your organization from the devastating impact of executive Office365 infiltration. Ignoring these threats is not an option; proactive Office365 security is a necessity.

Featured Posts
-
 Where To Watch Grand Slam Track Kingston A Comprehensive Guide
May 11, 2025
Where To Watch Grand Slam Track Kingston A Comprehensive Guide
May 11, 2025 -
 Millions Stolen In Executive Office365 Account Compromise
May 11, 2025
Millions Stolen In Executive Office365 Account Compromise
May 11, 2025 -
 Grand Slam Track A New League Aims To Revitalize Athletics
May 11, 2025
Grand Slam Track A New League Aims To Revitalize Athletics
May 11, 2025 -
 Iftar Programi Hakkari Deki Hakim Ve Savcilar Bir Araya Geldi
May 11, 2025
Iftar Programi Hakkari Deki Hakim Ve Savcilar Bir Araya Geldi
May 11, 2025 -
 Analyzing Juan Sotos Performance After Michael Kays Comments
May 11, 2025
Analyzing Juan Sotos Performance After Michael Kays Comments
May 11, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Henry Goldings Excitement For The Crazy Rich Asians Tv Series What We Know
May 11, 2025
Henry Goldings Excitement For The Crazy Rich Asians Tv Series What We Know
May 11, 2025 -
 Updates On The Potential Crazy Rich Asians Television Series
May 11, 2025
Updates On The Potential Crazy Rich Asians Television Series
May 11, 2025 -
 Henry Golding Discusses Crazy Rich Asians Tv Series And Cast Reunions
May 11, 2025
Henry Golding Discusses Crazy Rich Asians Tv Series And Cast Reunions
May 11, 2025 -
 Is A Crazy Rich Asians Tv Series Really Happening
May 11, 2025
Is A Crazy Rich Asians Tv Series Really Happening
May 11, 2025 -
 Henry Golding On Crazy Rich Asians Reunions And The Upcoming Tv Series
May 11, 2025
Henry Golding On Crazy Rich Asians Reunions And The Upcoming Tv Series
May 11, 2025
