Decades-Old School Desegregation Order Terminated: A Turning Point?
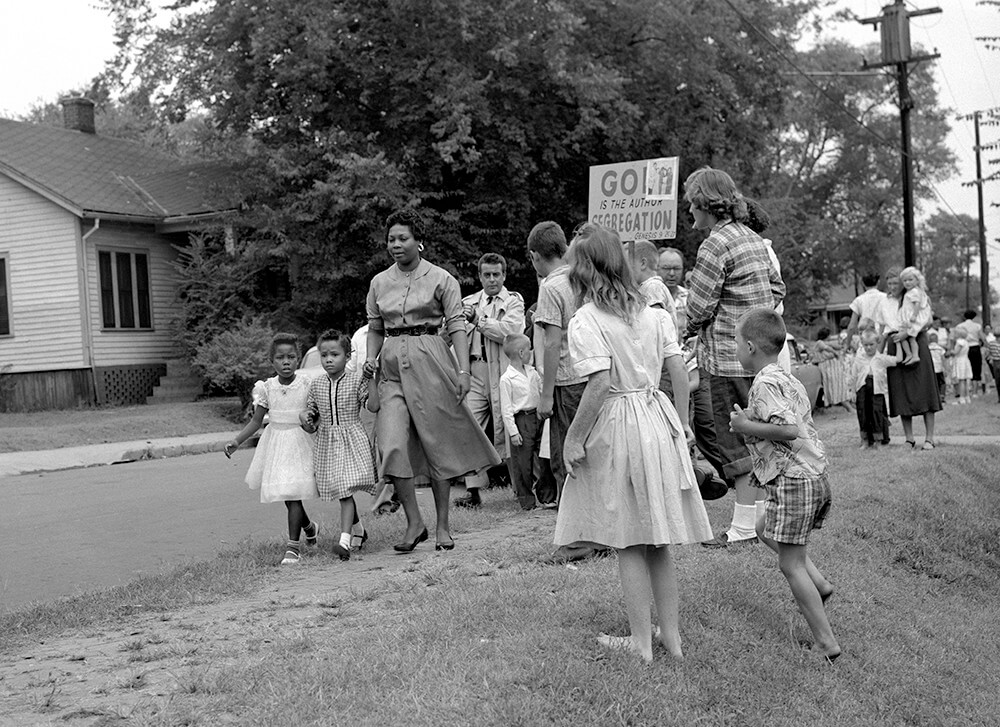
Table of Contents
The History of the Desegregation Order
Origins and Initial Impact
The desegregation order in question, like many others across the United States, stemmed from the landmark 1954 Supreme Court case, Brown v. Board of Education. This ruling declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students unconstitutional, overturning the "separate but equal" doctrine that had underpinned racial segregation for decades. However, the implementation of Brown v. Board faced significant resistance, leading to protracted legal battles and the implementation of court-ordered desegregation plans in numerous school districts. The specific order in question was implemented in [Insert Year] in response to [Insert specific details about the legal case or situation that led to the order].
- 1954: Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court ruling.
- [Insert Year]: Implementation of the desegregation order in [Insert School District/State].
- [Insert Years]: Initial successes in integrating schools, often involving busing programs and other affirmative action initiatives.
- [Insert Years]: Growing challenges in maintaining integration, including white flight to suburban schools and resistance from some communities.
- [Insert Data]: Statistics illustrating racial demographics in the affected school districts before and after the implementation of the desegregation order (e.g., percentage of minority students in predominantly white schools).
This initial period saw a complex interplay of progress and setbacks in achieving school integration. While some districts made significant strides, others experienced continued resistance and limited success in meaningfully integrating their schools. The initial impact varied widely depending on local political and social dynamics.
Reasons for Termination of the Desegregation Order
Legal Arguments
The termination of the decades-old desegregation order followed years of legal challenges. Proponents of termination argued that the order had outlived its purpose, citing significant demographic shifts and the achievement of sufficient integration in the affected school districts. They contended that continued court oversight was unnecessary and potentially harmful, hindering local control over education. Conversely, opponents argued that the termination threatened to reverse decades of progress and lead to increased school segregation. They highlighted persistent racial disparities in educational outcomes and argued that continued monitoring was crucial to ensure equal educational opportunities for all students.
- Arguments for Termination: Achieved sufficient integration; changed demographics; unnecessary court oversight; local control arguments.
- Arguments Against Termination: Persistent racial disparities; risk of re-segregation; need for continued monitoring; failure to achieve true educational equity.
- Relevant Supreme Court Cases/Precedents: [Mention any relevant Supreme Court cases or precedents, such as Parents Involved in Community Schools v. Seattle School District].
The legal arguments presented before the court reflected a deeply divided society grappling with the complexities of racial equality and the role of the judiciary in achieving it. The court’s decision ultimately hinged on interpreting the existing legal framework and the specific circumstances of the case.
Potential Implications of the Termination
Educational Outcomes
The termination of the desegregation order raises significant concerns about the potential for re-segregation and its impact on educational outcomes. Studies have consistently shown a strong correlation between school segregation and disparities in academic achievement, resource allocation, and access to advanced courses. A return to racially segregated schools could exacerbate existing inequalities and disproportionately affect minority students.
Social and Political Ramifications
Beyond educational impacts, the termination could have broader social and political ramifications. It could lead to increased racial tension within communities, fuel political polarization, and potentially inspire further legal challenges related to school segregation. The decision serves as a reminder of the ongoing struggle for racial justice and the fragility of progress made in desegregating schools.
- Potential for re-segregation: Increased racial isolation in schools.
- Impact on student achievement: Exacerbation of existing achievement gaps.
- Potential for increased racial tension: Heightened social divisions within communities.
- Impact on future legislative efforts: Setback to ongoing efforts to promote educational equity.
Moving Forward: Ensuring Equal Educational Opportunities
Policy Recommendations
To mitigate the potential negative consequences of the desegregation order's termination, policymakers must prioritize proactive measures to ensure equitable access to quality education for all students. This requires a multi-pronged approach that includes:
- Increased funding for under-resourced schools, particularly those serving predominantly minority populations.
- Implementation of robust diversity initiatives to promote integration and inclusivity.
- Targeted programs to address achievement gaps and provide support for students from disadvantaged backgrounds.
- Strengthening of anti-discrimination laws and enforcement mechanisms.
Community Engagement
Effective strategies for addressing school segregation must go beyond policy changes and involve active community engagement. Open dialogue, collaboration among diverse stakeholders (including parents, educators, community leaders, and policymakers), and a commitment to building inclusive school environments are essential.
- Promoting diverse school cultures that celebrate the strengths of all students.
- Fostering open communication between schools, families, and the wider community.
- Empowering parents and communities to advocate for equitable educational resources and opportunities for their children.
The ongoing struggle for equal educational opportunities requires sustained effort and commitment from all stakeholders.
Conclusion
The termination of this decades-old school desegregation order marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing fight for racial equality in education. While the legal battle may be over, the struggle to achieve truly equitable educational opportunities for all students continues. The potential implications of this decision are far-reaching, impacting not only the educational prospects of countless children but also the social fabric of our communities. Understanding the history of school desegregation, the reasons behind the order's termination, and the potential consequences is crucial for informed discussion and effective action. Let's continue the conversation on school desegregation and advocate for meaningful change, ensuring that all students have access to a quality education, regardless of race or background. We must work tirelessly to dismantle systemic barriers to equal education and build a more just and equitable future.
Featured Posts
-
 Bbc Faces Unprecedented Difficulties Following 1bn Revenue Plunge
May 03, 2025
Bbc Faces Unprecedented Difficulties Following 1bn Revenue Plunge
May 03, 2025 -
 Data Breach Exposes Executive Vulnerability Millions Lost Through Office 365
May 03, 2025
Data Breach Exposes Executive Vulnerability Millions Lost Through Office 365
May 03, 2025 -
 Programme La Seine Musicale 2025 2026 Concerts Spectacles Et Cinema
May 03, 2025
Programme La Seine Musicale 2025 2026 Concerts Spectacles Et Cinema
May 03, 2025 -
 Confirmed Lara Croft Returns To Fortnite Soon
May 03, 2025
Confirmed Lara Croft Returns To Fortnite Soon
May 03, 2025 -
 Client Outflows Drive Schroders Asset Reduction In First Quarter
May 03, 2025
Client Outflows Drive Schroders Asset Reduction In First Quarter
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Le Role Presume De Macron Dans Le Choix Du Prochain Pape L Echo A Rome
May 03, 2025
Le Role Presume De Macron Dans Le Choix Du Prochain Pape L Echo A Rome
May 03, 2025 -
 Discours De Macron Au Gabon La Francafrique Un Heritage Revolu
May 03, 2025
Discours De Macron Au Gabon La Francafrique Un Heritage Revolu
May 03, 2025 -
 Affaire Rome Rumeurs De Manipulation Par Emmanuel Macron Concernant Le Successeur De Francois
May 03, 2025
Affaire Rome Rumeurs De Manipulation Par Emmanuel Macron Concernant Le Successeur De Francois
May 03, 2025 -
 Finding The Perfect Place In The Sun Location Location Location
May 03, 2025
Finding The Perfect Place In The Sun Location Location Location
May 03, 2025 -
 Emmanuel Macron Evoque Son Intimite Avec Brigitte Des Annees Apres Leur Mariage
May 03, 2025
Emmanuel Macron Evoque Son Intimite Avec Brigitte Des Annees Apres Leur Mariage
May 03, 2025
