Economic Pressures Mount: The Federal Reserve's Next Move On Interest Rates
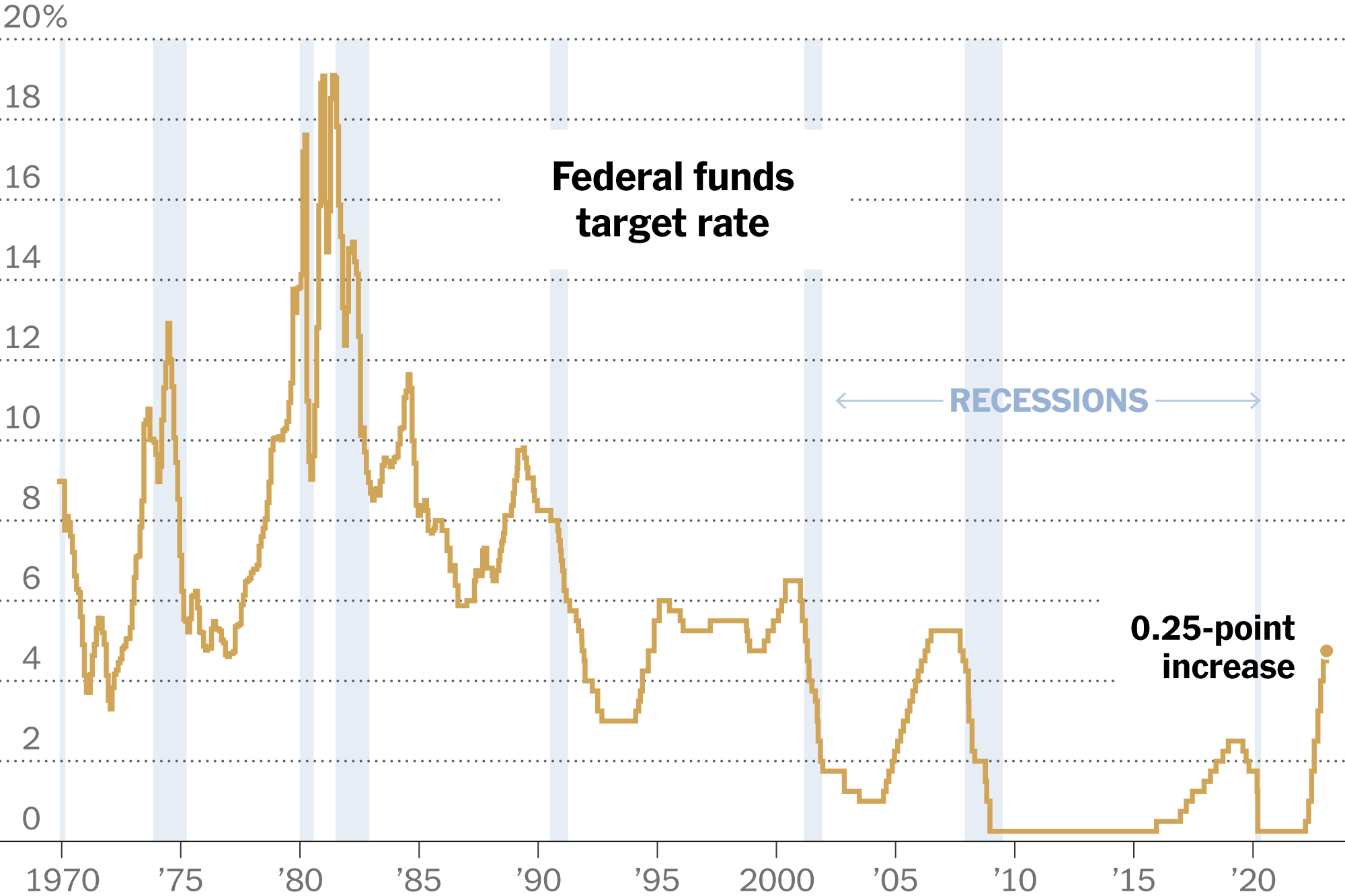
Table of Contents
Current Economic Indicators and Inflation
This section analyzes the current state of the US economy, focusing on key indicators that heavily influence the Fed's decisions regarding interest rates.
Inflation Rates and Trends
The persistence of inflation remains a primary concern. Recent Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) data reveal a complex picture. While headline inflation may show some signs of cooling, core inflation (excluding volatile food and energy prices) remains stubbornly high.
- CPI: [Insert latest CPI data and percentage change]. This indicates [Interpretation of the data and its implications for inflation].
- PPI: [Insert latest PPI data and percentage change]. This suggests [Interpretation of the data and its relation to consumer prices].
- Core Inflation: The persistence of core inflation suggests that inflationary pressures are deeply embedded in the economy, requiring sustained efforts to bring it under control.
- Market Expectations: Market participants are currently anticipating [Insert market consensus on future inflation based on surveys or market indicators].
Employment Data and Wage Growth
The labor market continues to be a key factor in the inflation debate. While unemployment remains relatively low, strong wage growth contributes to inflationary pressures.
- Unemployment Rate: [Insert latest unemployment rate]. A low unemployment rate indicates a tight labor market, putting upward pressure on wages.
- Job Creation: [Insert latest job creation figures]. Sustained job growth suggests robust economic activity, but also fuels demand-pull inflation.
- Wage Growth: [Insert latest wage growth data]. Rapid wage growth, while positive for workers, can lead to a wage-price spiral if businesses pass increased labor costs onto consumers.
- Labor Market Softening: Some economists predict a potential softening in the labor market in the coming months, which could ease inflationary pressures.
GDP Growth and Economic Outlook
GDP growth has [Insert latest GDP growth figures]. Forecasts for future growth vary significantly among economists, with some predicting a mild recession and others anticipating a soft landing.
- Recent GDP Growth: [Insert GDP growth rates for the last few quarters]. This reflects [Interpretation of GDP growth and its implications for the economy].
- Economic Forecasts: Leading economic institutions like the IMF and the Congressional Budget Office project [Summarize major economic forecasts, highlighting the range of predictions].
- Recessionary Risks: The possibility of a recession remains a significant concern, with factors like [Mention potential recessionary factors: high interest rates, geopolitical uncertainty, supply chain disruptions].
The Federal Reserve's Current Monetary Policy Stance
The Fed's current monetary policy is aimed at curbing inflation while minimizing the risk of a recession.
The Federal Funds Rate and Future Projections
The current federal funds rate is [Insert current federal funds rate]. Future projections, as indicated by the "dot plot" (a chart showing individual Federal Open Market Committee members' projections for the federal funds rate), suggest [Summarize the dot plot and interpret its implications]. Fed Chair Powell's recent statements indicate [Summarize Powell's recent statements on interest rates].
- Projected Rate Hikes/Cuts: Market analysts predict [Insert market predictions for future rate hikes or cuts].
- Fed Communication: The Fed's communication strategy, aiming for transparency, plays a crucial role in influencing market expectations and guiding economic activity.
- Impact of Rate Hikes: Further rate hikes would increase borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, potentially slowing economic growth.
Quantitative Tightening (QT) and its Effects
Quantitative tightening (QT) involves the Fed reducing its balance sheet by allowing Treasury bonds and mortgage-backed securities to mature without reinvestment. This reduces the money supply and aims to curb inflation.
- Mechanics of QT: QT involves [Explain how QT works and its effects on the money supply].
- Effectiveness of QT: The effectiveness of QT in combating inflation is still being debated among economists.
- Side Effects of QT: QT can lead to increased bond yields and potentially higher borrowing costs for businesses and consumers.
Potential Impacts of the Fed's Decision on Interest Rates
The Fed's decision on interest rates will have significant ripple effects across the economy.
Impact on Consumer Spending and Borrowing
Changes in interest rates directly impact consumer spending and borrowing. Higher rates lead to increased borrowing costs, potentially dampening consumer demand.
- Effects on Consumer Spending: Higher interest rates can significantly reduce consumer spending on durable goods like cars and houses.
- Sensitivity to Interest Rates: The sensitivity of consumer spending to interest rate changes varies across different income groups and types of goods.
- Impact on Consumer Confidence: Uncertainty regarding future interest rates can negatively impact consumer confidence and willingness to spend.
Effects on Businesses and Investment
Businesses are highly sensitive to interest rate changes. Higher rates increase borrowing costs, potentially discouraging investment and hiring.
- Impact on Business Investment: Higher interest rates increase the cost of capital, making it more expensive for businesses to invest in new equipment and expand operations.
- Impact on Capital Expenditure: Businesses may postpone capital expenditure plans in response to higher interest rates.
- Impact on Job Creation: Reduced business investment can lead to slower job creation.
Global Market Implications
The Fed's decisions have global implications, affecting the US dollar and international capital flows.
- Impact on Exchange Rates: Changes in US interest rates affect the value of the US dollar relative to other currencies.
- Spillover Effects: Changes in US interest rates can have significant spillover effects on other economies, particularly emerging markets.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve's next move on interest rates is a critical decision with far-reaching consequences. Balancing the need to control inflation with the risk of triggering a recession requires a delicate balancing act. The current economic indicators, coupled with the Fed’s monetary policy tools, suggest several potential scenarios, each with distinct impacts on consumers, businesses, and global markets. Staying informed about the latest developments regarding Federal Reserve interest rates is crucial for individuals and businesses alike to make informed financial decisions. Continuously monitor economic news and analysis to effectively navigate this period of economic uncertainty. Understanding the complexities surrounding Federal Reserve interest rates and their implications for monetary policy will be key to mitigating risk and capitalizing on opportunities in the evolving economic landscape.

Featured Posts
-
 Muutokset Britannian Kruununperimysjaerjestyksessae Naein Se Toimii Nyt
May 10, 2025
Muutokset Britannian Kruununperimysjaerjestyksessae Naein Se Toimii Nyt
May 10, 2025 -
 Lynk Lee Chuyen Gioi Ngoai Hinh Xinh Dep Ban Trai Luon Sat Canh
May 10, 2025
Lynk Lee Chuyen Gioi Ngoai Hinh Xinh Dep Ban Trai Luon Sat Canh
May 10, 2025 -
 Is Apple Secretly Helping Google Maintain Its Market Share
May 10, 2025
Is Apple Secretly Helping Google Maintain Its Market Share
May 10, 2025 -
 Putins Victory Day Ceasefire Reactions From Ukraine And The International Community
May 10, 2025
Putins Victory Day Ceasefire Reactions From Ukraine And The International Community
May 10, 2025 -
 Increased Danish Influence In Greenland The Legacy Of Trumps Actions
May 10, 2025
Increased Danish Influence In Greenland The Legacy Of Trumps Actions
May 10, 2025
