Electric Bus Technology In Europe: Hydrogen Vs. Battery Power
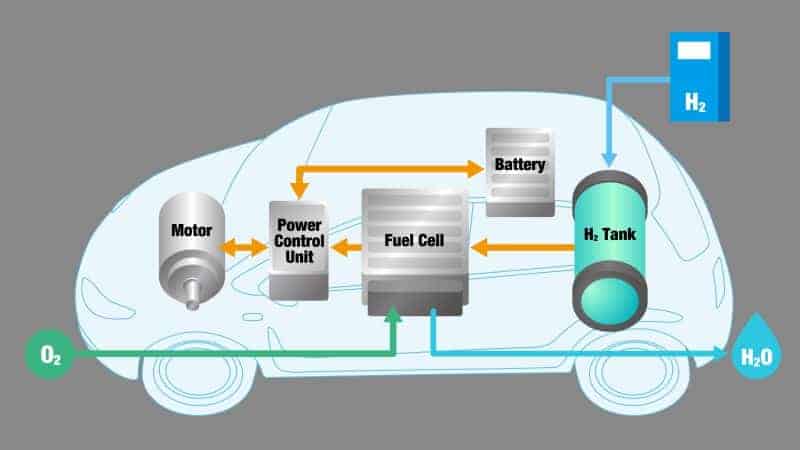
Table of Contents
Battery Electric Buses (BEBs): A Current Market Leader
Battery electric buses are currently the dominant force in the European electric bus market. Their widespread adoption is driven by several key advantages.
Advantages of BEBs:
- Lower Initial Cost: BEBs generally have a significantly lower upfront cost compared to hydrogen buses, making them a more accessible option for many municipalities and transport operators. This lower barrier to entry has fueled their rapid deployment.
- Established Infrastructure: A relatively mature charging infrastructure is already in place across many European cities. This reduces the significant upfront investment required for hydrogen refueling stations.
- Proven Technology: BEBs have a proven track record, with numerous successful deployments across Europe demonstrating their reliability and operational efficiency. This established technology translates to lower risks and easier maintenance.
- Lower Maintenance: Compared to the complex fuel cell systems in hydrogen buses, BEBs generally require less maintenance, leading to reduced operational costs over the vehicle's lifespan.
- Silent Operation: The quiet operation of BEBs significantly reduces noise pollution in urban areas, contributing to a more pleasant environment for both residents and passengers. This is a key advantage in densely populated cities.
- Faster Refueling (Charging): While charging times can vary, BEBs typically offer significantly shorter refueling times compared to hydrogen buses, minimizing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency.
Disadvantages of BEBs:
- Limited Range: BEBs have a shorter range than hydrogen buses, limiting their suitability for longer routes and rural areas. Range anxiety remains a concern, particularly in regions with less dense charging infrastructure.
- Battery Lifespan and Replacement: The lifespan of batteries is a significant factor influencing the long-term cost of BEBs. Battery replacement can be expensive and environmentally impactful.
- Environmental Impact of Battery Production: The production of batteries requires significant resources and energy, raising environmental concerns related to mining, manufacturing, and disposal. Recycling efforts are crucial to mitigating this impact.
- Charging Infrastructure Investment: Although existing, the charging infrastructure still requires substantial investment to support the widespread adoption of BEBs, especially for large fleets. This investment needs to consider grid capacity and potential strain.
- Potential Grid Strain: Widespread charging of BEB fleets can put significant strain on existing electricity grids, requiring upgrades and smart charging solutions to manage energy demand effectively.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Buses (HFCBs): The Emerging Contender
Hydrogen fuel cell buses represent a promising alternative to battery electric buses, particularly for longer routes and areas with limited charging infrastructure. However, several challenges remain.
Advantages of HFCBs:
- Longer Range: HFCBs offer a significantly longer range than BEBs, making them ideal for longer routes, rural areas, and regions with less developed charging networks. This extended range addresses the range anxiety associated with BEBs.
- Faster Refueling: Refueling hydrogen buses is significantly faster than charging BEBs, minimizing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency. This is a major advantage for high-frequency bus routes.
- Zero Tailpipe Emissions (Potentially): HFCBs offer the potential for zero tailpipe emissions, provided the hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources (green hydrogen). This is crucial for achieving true zero-emission goals.
- Energy Diversification: The development of hydrogen infrastructure could contribute to energy diversification, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting energy security.
Disadvantages of HFCBs:
- High Initial Cost: HFCBs have a significantly higher initial purchase price compared to BEBs, presenting a significant barrier to entry for many operators.
- Limited Refueling Infrastructure: The lack of widespread hydrogen refueling infrastructure across Europe is a major constraint on the adoption of HFCBs. This requires substantial investment in infrastructure development.
- Hydrogen Production Challenges: The production and storage of hydrogen present logistical and environmental challenges. The energy intensity of traditional hydrogen production methods needs to be addressed through the adoption of green hydrogen production.
- Higher Maintenance Costs: The complexity of fuel cell technology can lead to higher maintenance costs compared to BEBs, impacting long-term operational expenses.
- Safety Concerns: Safety concerns surrounding the storage and handling of hydrogen require careful consideration and the implementation of robust safety protocols.
The European Landscape: Policy, Infrastructure, and Market Trends
The future of electric bus technology in Europe depends heavily on several key factors:
- Government Incentives and Subsidies: Different European countries offer varying levels of financial support for electric bus adoption, significantly influencing the market dynamics.
- Charging and Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure: The availability and accessibility of both charging stations for BEBs and hydrogen refueling stations for HFCBs are crucial determinants of market penetration.
- Market Share of BEBs and HFCBs: The current market share of BEBs significantly outweighs that of HFCBs, reflecting the current advantages of lower cost and established infrastructure.
- Influencing Factors in Technology Choice: The choice between BEBs and HFCBs is influenced by factors such as geography, route length, budget constraints, and local environmental regulations.
- Technological Advancements and Future Projections: Ongoing technological advancements in both battery and hydrogen fuel cell technologies are constantly reshaping the landscape and influencing future projections.
Conclusion
The choice between battery electric and hydrogen fuel cell buses for Europe's sustainable transport future is complex, with each technology presenting distinct advantages and drawbacks. While BEBs currently dominate the market due to lower costs and established infrastructure, HFCBs offer a compelling alternative for longer routes and scenarios where extensive charging infrastructure is impractical. Ultimately, a balanced approach leveraging the strengths of both technologies, coupled with significant investment in both charging and hydrogen infrastructure, is likely needed to achieve a truly green and efficient public transport system across Europe. The future of electric bus technology in Europe will depend on continued innovation, supportive policies, and strategic infrastructure development. Learn more about the exciting advancements in electric bus technology and the ongoing hydrogen vs. battery power debate to stay informed about this critical sector.

Featured Posts
-
 Find The Winning Lotto Numbers Saturday April 12th Results
May 07, 2025
Find The Winning Lotto Numbers Saturday April 12th Results
May 07, 2025 -
 Lotto Jackpot Numbers Wednesday April 9th Winning Numbers Revealed
May 07, 2025
Lotto Jackpot Numbers Wednesday April 9th Winning Numbers Revealed
May 07, 2025 -
 Anchor Brewing Shuttering 127 Years Of Brewing History Conclude
May 07, 2025
Anchor Brewing Shuttering 127 Years Of Brewing History Conclude
May 07, 2025 -
 Charles Barkley On The Cavaliers A Frank Assessment
May 07, 2025
Charles Barkley On The Cavaliers A Frank Assessment
May 07, 2025 -
 Cem Karaca Bati Ve Anadolu Mueziginin Essiz Bulusmasi
May 07, 2025
Cem Karaca Bati Ve Anadolu Mueziginin Essiz Bulusmasi
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Brezilya Bitcoin Maas Oedemelerini Yasallastiriyor Detaylar Ve Etkileri
May 08, 2025
Brezilya Bitcoin Maas Oedemelerini Yasallastiriyor Detaylar Ve Etkileri
May 08, 2025 -
 Sifrenizi Unuttunuz Mu Kripto Mirasiniz Tehlikede
May 08, 2025
Sifrenizi Unuttunuz Mu Kripto Mirasiniz Tehlikede
May 08, 2025 -
 Bakan Simsek Ten Kripto Para Piyasasina Uyari Riskler Ve Oenlemler
May 08, 2025
Bakan Simsek Ten Kripto Para Piyasasina Uyari Riskler Ve Oenlemler
May 08, 2025 -
 Brezilya Da Bitcoin Maas Oedemeleri Yasal Olarak Kabul Ediliyor Mu
May 08, 2025
Brezilya Da Bitcoin Maas Oedemeleri Yasal Olarak Kabul Ediliyor Mu
May 08, 2025 -
 Kripto Varliklarda Miras Sifresiz Kalanlar Ne Yapmali
May 08, 2025
Kripto Varliklarda Miras Sifresiz Kalanlar Ne Yapmali
May 08, 2025
