End Of An Era: Justice Department Ends Decades-Long School Desegregation Order
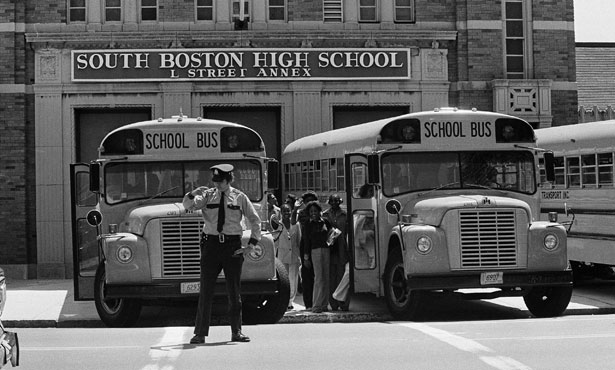
Table of Contents
After decades of oversight, the Justice Department has officially ended its involvement in a landmark school desegregation case. This decision, announced [Insert Date], closes a chapter in American history marked by both progress and persistent challenges in achieving racial equality in education. This article will explore the implications of this momentous shift and examine the ongoing fight for school desegregation.
The History of the School Desegregation Order
This decision pertains to [Insert Name of School District/Specific Case Name], a long-standing school desegregation case originating in [City, State] in [Year]. The initial lawsuit, [Insert Original Case Name], challenged the discriminatory practices of the school system, which included [Mention specific discriminatory practices, e.g., segregated schools, unequal resource allocation]. The subsequent decades witnessed numerous legal battles, appeals, and court-ordered mandates aimed at achieving meaningful racial integration within the school district.
- Key figures involved: [List key figures, including lawyers, judges, and community activists].
- Significant court rulings: [List key court rulings and their impact on school desegregation efforts]. For example, the [Name of Ruling] decision in [Year] mandated [Specific mandate, e.g., busing, redrawing school district lines].
- Key achievements: [List significant achievements in school integration, e.g., increased enrollment of minority students in previously all-white schools, improved access to educational resources].
The Justice Department's Rationale for Ending the Order
The Justice Department's official statement cited [Summarize the official statement's main points]. The arguments presented suggest that [Analyze the arguments – were goals met, were there budgetary constraints, etc.]. While the department claims [Specific claim from DOJ statement], critics argue that [Counterarguments].
- Specific claims by the Justice Department: [List specific claims made by the DOJ to justify their decision].
- Potential criticisms: [List potential criticisms of the DOJ’s rationale, highlighting inconsistencies or lack of evidence].
- Counterarguments: [Include counterarguments from advocacy groups, affected communities, or legal experts]. For instance, [Mention specific counterarguments and supporting evidence].
Implications and Consequences of the Decision
The termination of this decades-long order carries significant implications for the affected schools and communities. The most immediate concern is the potential for increased racial segregation. Without continued federal oversight, the school district may revert to patterns of segregation, impacting not only the racial makeup of schools but also the quality of education available to minority students.
- Potential for increased segregation: [Explain the potential for increased segregation, citing relevant statistics or examples].
- Impact on student achievement: [Discuss the potential negative impact on academic performance and access to quality education for minority students].
- Long-term consequences: [Explore the long-term effects on educational equity, social mobility, and racial harmony within the community].
The Ongoing Fight for School Desegregation
While this specific order has ended, the fight for school desegregation continues on multiple fronts. Community organizations and advocacy groups remain committed to achieving racial integration and educational equity through various strategies, including legislative action and grassroots mobilization.
- Current legislative efforts: [Highlight current state and federal legislative efforts aimed at addressing school segregation].
- Community activism: [Discuss the role of community organizations and their strategies for promoting racial integration]. Examples include [Mention specific examples of community initiatives].
- Strategies for achieving equity: [Discuss potential strategies, such as promoting diverse school choice options, addressing housing segregation, and investing in under-resourced schools].
Conclusion
The Justice Department's decision to end the decades-long school desegregation order represents a significant turning point, prompting reflection on progress made and the persistent challenges in achieving true racial equality in education. While the order's termination may signal a shift in legal strategy, the fight for desegregation continues through community activism and ongoing legislative efforts. The legacy of this case serves as a reminder of the ongoing struggle for educational equity and the crucial need for sustained commitment to dismantling systemic barriers to school desegregation.
Call to Action: The end of this specific order does not signal the end of the fight for school desegregation. Stay informed about the ongoing efforts to achieve educational equity and consider getting involved in promoting school desegregation in your community. Learn more about the continued fight for fair and equal access to education and how you can support initiatives dedicated to dismantling systemic barriers to school desegregation.
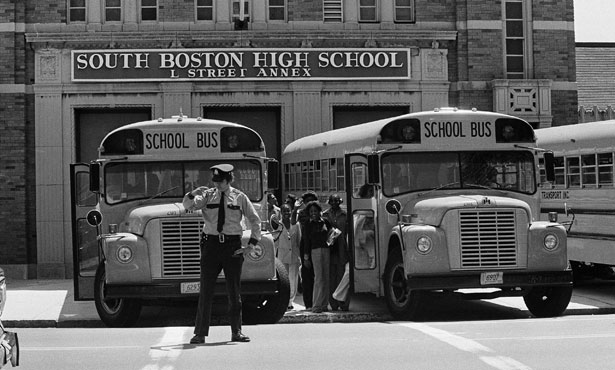
Featured Posts
-
 Play Station Plus Your Guide To The New Extra And Premium Games
May 02, 2025
Play Station Plus Your Guide To The New Extra And Premium Games
May 02, 2025 -
 Riot Fest 2025 Green Day Blink 182 And Weird Al Yankovic Headline
May 02, 2025
Riot Fest 2025 Green Day Blink 182 And Weird Al Yankovic Headline
May 02, 2025 -
 Broadcoms Proposed V Mware Price Hike A 1 050 Increase For At And T
May 02, 2025
Broadcoms Proposed V Mware Price Hike A 1 050 Increase For At And T
May 02, 2025 -
 Lotto 6aus49 Vom 19 April 2025 Lottozahlen Und Gewinnzahlen
May 02, 2025
Lotto 6aus49 Vom 19 April 2025 Lottozahlen Und Gewinnzahlen
May 02, 2025 -
 Check Daily Lotto Results For Wednesday 16th April 2025
May 02, 2025
Check Daily Lotto Results For Wednesday 16th April 2025
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Dari Sampah Menjadi Harta Potensi Cangkang Telur Sebagai Sumber Kalsium
May 03, 2025
Dari Sampah Menjadi Harta Potensi Cangkang Telur Sebagai Sumber Kalsium
May 03, 2025 -
 Daur Ulang Cangkang Telur Cara Mudah Mendapatkan Nutrisi Tambahan
May 03, 2025
Daur Ulang Cangkang Telur Cara Mudah Mendapatkan Nutrisi Tambahan
May 03, 2025 -
 Manfaatkan Cangkang Telur Pupuk Alami Untuk Tanaman Dan Pakan Hewan
May 03, 2025
Manfaatkan Cangkang Telur Pupuk Alami Untuk Tanaman Dan Pakan Hewan
May 03, 2025 -
 Kivinin Kabugu Tueketimi Faydalari Ve Riskleri Hakkinda Bilmeniz Gerekenler
May 03, 2025
Kivinin Kabugu Tueketimi Faydalari Ve Riskleri Hakkinda Bilmeniz Gerekenler
May 03, 2025 -
 Cangkang Telur Manfaat Kreatif Untuk Pertanian Dan Peternakan
May 03, 2025
Cangkang Telur Manfaat Kreatif Untuk Pertanian Dan Peternakan
May 03, 2025
