Europe's Car Industry Faces Headwinds Amidst Economic Crisis
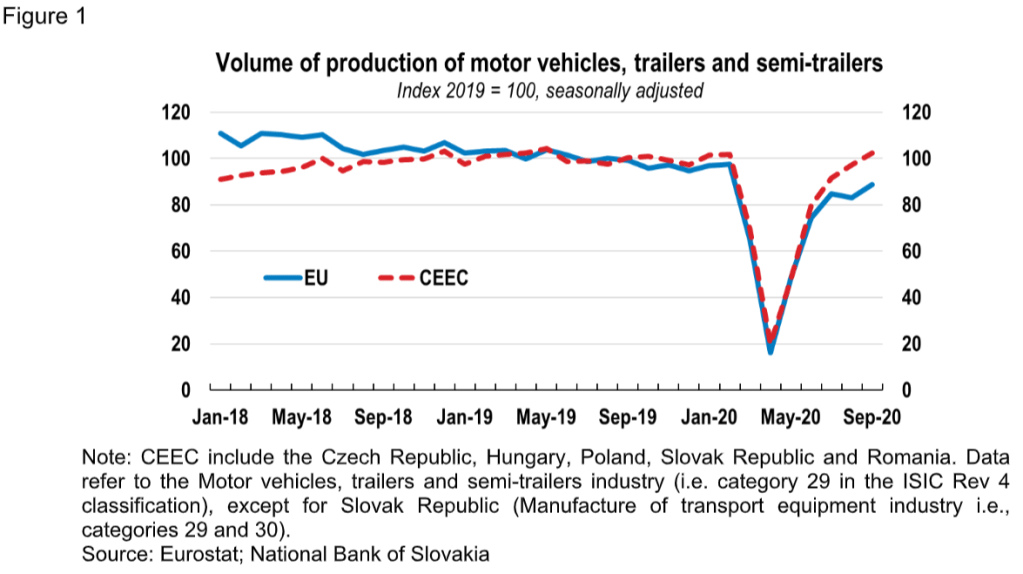
Table of Contents
Declining Consumer Demand and Purchasing Power
The economic downturn is directly impacting consumer purchasing power, leading to a substantial reduction in demand for new cars. Rising inflation and interest rates are making car loans more expensive, while the increased cost of living forces consumers to prioritize essential spending over discretionary purchases like new vehicles. This is reflected in a clear shift in consumer preferences towards the used car market, as buyers seek more affordable options.
- Rising inflation and interest rates: The Eurozone's inflation rate remains stubbornly high, eroding purchasing power and making borrowing more costly.
- Reduced consumer confidence: Uncertainty about the future and concerns about job security are dampening consumer spending across the board, including the automotive sector.
- Increased cost of living impacting discretionary spending: Essential expenses like food and energy are consuming a larger portion of household budgets, leaving less room for non-essential items like new cars.
- Shift in consumer preferences towards used cars: The used car market is booming as consumers seek more affordable alternatives to new vehicles.
Recent statistics reveal a worrying trend. For example, new car registrations in Germany, Europe's largest car market, fell by X% in [Insert Year], while similar declines have been observed across other major European markets. This decline in consumer demand represents a significant challenge for the European car industry.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Material Shortages
Beyond weakening consumer demand, the European car industry is grappling with persistent supply chain disruptions and material shortages. The ongoing semiconductor shortage, exacerbated by geopolitical instability and increased transportation costs, continues to hinder car production. This lack of crucial components leads to production delays, impacting manufacturing timelines and vehicle deliveries.
- Geopolitical instability and its effect on global trade: The war in Ukraine, among other geopolitical factors, has disrupted global supply chains, impacting the availability of key components.
- Increased transportation costs: Fuel price increases and logistical bottlenecks have driven up the cost of transporting goods, adding to the overall production cost.
- Lack of crucial components hindering manufacturing: The semiconductor shortage, in particular, is a major bottleneck, impacting the production of various car models.
- Impact on production timelines and delivery delays: Manufacturers are facing significant delays in getting vehicles to market, impacting sales and revenue.
These supply chain issues are compounding the challenges faced by the industry, further hindering its ability to meet existing and anticipated demand.
The Energy Transition and its Impact
The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) presents both opportunities and challenges. While the transition to a greener automotive sector is crucial, the high initial cost of EVs compared to gasoline-powered cars remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption, particularly amidst an economic crisis. Furthermore, the lack of comprehensive charging infrastructure in some regions poses another hurdle.
- High initial cost of EVs compared to gasoline-powered cars: The higher price point of EVs makes them less accessible to many consumers, especially during a period of economic hardship.
- Limited charging infrastructure in some regions: A lack of readily available charging stations hinders the adoption of EVs, particularly in rural areas.
- Government support and incentives for EV adoption: Government policies play a crucial role in incentivizing EV adoption, but the effectiveness of these measures varies across Europe.
- Competition from Asian EV manufacturers: The European car industry faces stiff competition from established Asian EV manufacturers who are rapidly expanding their market share.
Successfully navigating the energy transition requires a concerted effort involving government support, technological innovation, and investment in charging infrastructure.
Government Regulations and Policies
Government regulations, particularly concerning emissions standards, play a crucial role in shaping the industry's landscape. Stricter emission standards, while essential for environmental protection, increase production costs for manufacturers. This is particularly challenging during an economic downturn. However, government support packages and subsidies can help mitigate some of these pressures. The variations in automotive policy across different European countries further complicate the situation.
- Impact of stricter emission standards on production costs: Meeting increasingly stringent emission regulations requires significant investment in new technologies and manufacturing processes, increasing costs.
- Government support packages for the automotive sector: Some governments are offering financial support and incentives to help the automotive sector navigate the current challenges.
- Potential for new regulations impacting future production: Future regulations could further impact production costs and investment strategies for the industry.
- Variations in government policies across different European countries: The fragmented nature of European automotive policy creates challenges for manufacturers operating across multiple markets.
Conclusion: Navigating the Headwinds for Europe's Car Industry
Europe's car industry is facing a confluence of unprecedented challenges: declining consumer demand fueled by the economic crisis, persistent supply chain disruptions, the complexities of the energy transition to EVs, and the evolving regulatory landscape. These headwinds require innovative solutions, strategic adaptations, and significant collaboration between manufacturers, governments, and other stakeholders. The future of the European car industry hinges on its ability to navigate these obstacles and seize emerging opportunities. To learn more about the specific challenges and opportunities facing the European car industry, explore further resources on the impact of the economic crisis on the automotive sector. Share your thoughts and insights in the comments below. Let's discuss how the European car industry can best overcome these significant headwinds.

Featured Posts
-
 Mlb Prediction Dodgers Vs Diamondbacks Who Will Win
May 28, 2025
Mlb Prediction Dodgers Vs Diamondbacks Who Will Win
May 28, 2025 -
 Padres On Deck 2025 Home Opener At Wrigley Field
May 28, 2025
Padres On Deck 2025 Home Opener At Wrigley Field
May 28, 2025 -
 Knicks Vs Pacers Game 3 Tyrese Haliburton Prop Bets And Analysis
May 28, 2025
Knicks Vs Pacers Game 3 Tyrese Haliburton Prop Bets And Analysis
May 28, 2025 -
 Rezhisser Ues Anderson Noviy Film V Razrabotke
May 28, 2025
Rezhisser Ues Anderson Noviy Film V Razrabotke
May 28, 2025 -
 Googles Veo 3 Ai Video Generator A Slippery Slope
May 28, 2025
Googles Veo 3 Ai Video Generator A Slippery Slope
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ticketmaster Ofrece Mayor Transparencia En El Precio De Las Entradas
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Ofrece Mayor Transparencia En El Precio De Las Entradas
May 30, 2025 -
 Listen To Jacob Alons Hit Song Fairy In A Bottle
May 30, 2025
Listen To Jacob Alons Hit Song Fairy In A Bottle
May 30, 2025 -
 Cambios En La Politica De Precios De Ticketmaster Mas Claridad Para Los Compradores
May 30, 2025
Cambios En La Politica De Precios De Ticketmaster Mas Claridad Para Los Compradores
May 30, 2025 -
 Jacob Alons Fairy In A Bottle A Popular New Song
May 30, 2025
Jacob Alons Fairy In A Bottle A Popular New Song
May 30, 2025 -
 Ticketmaster Aclara Sus Precios De Boletos Lo Que Debes Saber
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Aclara Sus Precios De Boletos Lo Que Debes Saber
May 30, 2025
