Fewer Excessive Heat Warnings: Explaining The Recent Decrease
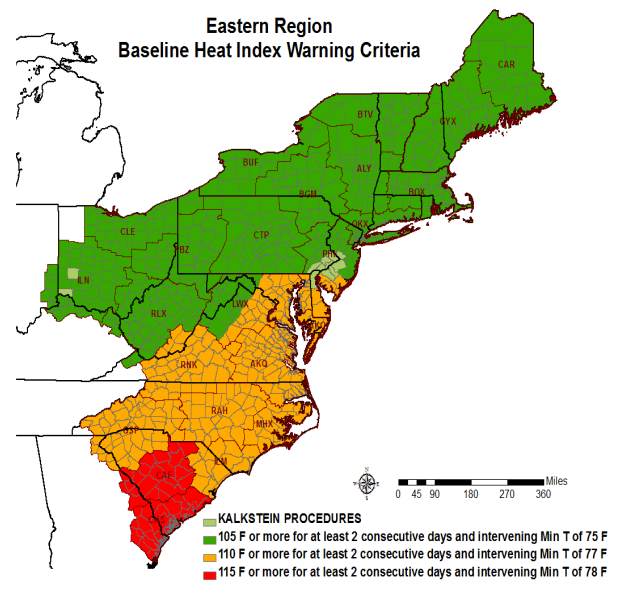
Table of Contents
Improved Weather Forecasting and Early Warning Systems
One potential explanation for fewer excessive heat warnings lies in the significant advancements made in weather forecasting and early warning systems. Improved accuracy in meteorological models allows for more precise predictions of temperature fluctuations, heatwave intensity, and duration. This translates to more effective warnings, potentially reducing the number of excessive heat warnings issued if less severe heat events are predicted accurately.
- Enhanced satellite technology: Modern satellites provide higher-resolution temperature data, allowing for more granular monitoring of heatwaves across wider geographical areas.
- Advanced data analysis and predictive algorithms: Sophisticated algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and predict extreme heat events with greater accuracy and lead time.
- Increased investment in weather infrastructure: Increased funding in weather stations, radar systems, and computational resources has significantly enhanced the quality and timeliness of weather information.
These improvements mean that we can now more accurately predict the severity and extent of heatwaves. A more precise forecast may mean that fewer warnings are needed, as less severe heat events can be anticipated and managed effectively without needing an official warning. However, it's crucial to note that this does not necessarily translate to fewer actual heat events.
Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation Efforts
Climate change adaptation and mitigation efforts also play a role in potentially reducing the frequency and intensity of heatwaves, thereby indirectly decreasing the need for excessive heat warnings. Measures such as urban greening, improved building design (incorporating features to enhance cooling), and widespread public awareness campaigns can significantly reduce the impact of extreme heat.
- Increased public awareness and heat safety campaigns: Education initiatives focusing on heat safety practices, including staying hydrated and avoiding strenuous activity during peak heat times, help individuals mitigate the risks of extreme heat.
- Government policies promoting energy efficiency and reducing carbon emissions: Policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions can contribute to slowing the rate of global warming and potentially reducing the frequency and intensity of heatwaves in the long term.
- Examples of successful adaptation strategies: Cities incorporating green spaces, such as parks and green roofs, have demonstrated lower temperatures than those with limited vegetation. Similarly, improved building insulation and cooling systems have proven effective in mitigating heat stress indoors.
While these are positive developments, we must be cautious not to equate reduced warnings with a decrease in extreme heat events.
Changes in Data Collection and Warning Thresholds
The apparent decrease in excessive heat warnings could also be partially attributed to changes in data collection methods and the criteria used to issue warnings. This is a crucial point to consider when analyzing this trend.
- Shifting criteria for issuing heat warnings: Changes in the thresholds used to define an "excessive heat warning" could lead to fewer warnings being issued, even if the actual number of extreme heat events remains the same or even increases.
- Differences in data reporting across regions: Inconsistent reporting methods across different geographical regions can lead to variations in the number of heat warnings reported, making direct comparisons challenging.
- Potential for underreporting of extreme heat events: In some areas, underreporting of extreme heat events might occur due to limitations in data collection or reporting infrastructure, leading to an artificially lower number of reported excessive heat warnings.
These methodological variations highlight the complexity of interpreting the trend of fewer excessive heat warnings. The data needs careful consideration and validation before conclusions can be drawn about the actual frequency of extreme heat events.
Potential Concerns and Unanswered Questions
While advancements in forecasting and adaptation efforts are encouraging, it is vital to acknowledge potential limitations and unanswered questions. The observed decrease in excessive heat warnings does not necessarily indicate a reduction in the occurrence of extreme heat events.
- Limitations of current forecasting models: Current models may not fully capture the complexity of local climate conditions and microclimates, leading to inaccuracies in predicting extreme heat in specific areas.
- Potential for future increases in extreme heat events: Despite the current trend, climate change projections indicate a likely increase in the frequency and intensity of heatwaves in the future.
- The need for continued monitoring and research: Continuous monitoring, research, and improvements in data collection and analysis are essential to ensure accurate assessment of extreme heat events and effective early warning systems.
The reduction in excessive heat warnings warrants further investigation to determine if it reflects a true decrease in extreme heat events or is a consequence of methodological changes.
Conclusion: Understanding the Shift in Fewer Excessive Heat Warnings
The decrease in excessive heat warnings is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. Improvements in weather forecasting, climate change adaptation efforts, and changes in data collection methodologies all play a role. However, it's crucial to acknowledge the potential for underreporting and the limitations of current forecasting models. The decrease in warnings should not be interpreted as a sign that extreme heat is no longer a threat.
While the decrease in excessive heat warnings is noteworthy, it's crucial to remain vigilant. Stay informed about local weather forecasts and take necessary precautions to protect yourself and your family from extreme heat. Understanding the nuances of fewer excessive heat warnings is critical for community safety and preparedness. Continued research and investment in early warning systems are essential to ensure accurate and timely warnings are issued to safeguard public health against the dangers of extreme heat.

Featured Posts
-
 Spesifikasi Dan Harga Kawasaki W175 Cafe Pilihan Motor Retro Klasik
May 30, 2025
Spesifikasi Dan Harga Kawasaki W175 Cafe Pilihan Motor Retro Klasik
May 30, 2025 -
 Fan Favorite Avenger Snubbed No Endgame Return Invite
May 30, 2025
Fan Favorite Avenger Snubbed No Endgame Return Invite
May 30, 2025 -
 Valley High School Coach Receives Regional Coach Of The Year Award
May 30, 2025
Valley High School Coach Receives Regional Coach Of The Year Award
May 30, 2025 -
 Indias Solar Energy Exports To Southeast Asia Navigating The Impact Of Trump Tariffs
May 30, 2025
Indias Solar Energy Exports To Southeast Asia Navigating The Impact Of Trump Tariffs
May 30, 2025 -
 Zheng Qinwens Madrid Open Upset Loss To Potapova
May 30, 2025
Zheng Qinwens Madrid Open Upset Loss To Potapova
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Alcaraz Cruises To Straight Sets Win At Barcelona Open
May 31, 2025
Alcaraz Cruises To Straight Sets Win At Barcelona Open
May 31, 2025 -
 Sage Hill Volleyball Cif Ss Finals Bound Following Victory Over Crean Lutheran
May 31, 2025
Sage Hill Volleyball Cif Ss Finals Bound Following Victory Over Crean Lutheran
May 31, 2025 -
 Beatles Biopic Cast Announced Whos Playing Who
May 31, 2025
Beatles Biopic Cast Announced Whos Playing Who
May 31, 2025 -
 The Beatles Cast Revealed A Look At The Actors
May 31, 2025
The Beatles Cast Revealed A Look At The Actors
May 31, 2025 -
 Star Trek Strange New Worlds Season 3 Teaser A Deeper Dive Into The New Season
May 31, 2025
Star Trek Strange New Worlds Season 3 Teaser A Deeper Dive Into The New Season
May 31, 2025
