Germany's Klingbeil Rejects Renewed Russian Gas Imports

Table of Contents
Klingbeil's Rationale: Why No Russian Gas?
Klingbeil's rejection of renewed Russian gas imports stems from a multifaceted rationale deeply rooted in morality, geopolitical strategy, and the pursuit of long-term energy independence. His decision reflects a growing consensus within Germany and parts of the EU.
-
Moral Opposition: Klingbeil firmly opposes financially supporting the Russian regime, especially given the ongoing brutal war in Ukraine. Further funding of the war machine through gas purchases is seen as morally unacceptable.
-
Reliability Concerns: Russia's history of using energy as a geopolitical weapon, including past instances of gas supply disruptions and manipulation, raises significant concerns about its reliability as a long-term energy supplier. This unreliability necessitates a shift away from dependence.
-
Sanctions Reinforcement: Maintaining and strengthening sanctions against Russia is crucial to pressuring it to end the war and respect international law. Renewed gas imports would undermine these sanctions and weaken the international pressure on the Kremlin.
-
Energy Diversification: Klingbeil's stance underlines Germany's commitment to long-term energy independence and diversification away from Russian energy sources. This strategy reduces vulnerability to future disruptions and strengthens Germany's energy security. This is a key element of Germany's Energiewende (energy transition).
Supporting Klingbeil's position, many experts argue that continued reliance on Russian gas jeopardizes Europe's security and undermines efforts to hold Russia accountable for its actions. The financial support implicitly given by energy imports directly fuels the war effort. This directly contradicts the stated aims of the EU's sanctions policy.
Implications for Germany's Energy Security
Germany's rejection of Russian gas has profound implications for its energy security, demanding a rapid acceleration of its energy transition and investment in alternative sources.
-
Current Energy Mix: While Germany has made progress in reducing its reliance on Russian gas, it still faces challenges. Diversification efforts are underway, focusing on LNG imports from other countries and bolstering domestic gas storage capacities.
-
Economic Consequences: Rejecting Russian gas will likely lead to further price increases in the short term. However, the long-term benefits of energy independence outweigh these costs. Government support packages and energy efficiency measures aim to mitigate the impact on consumers and businesses.
-
Energy Transition Acceleration: The decision underscores the urgency of Germany's energy transition, accelerating investments in renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal. Modernization of the electricity grid and expansion of renewable energy infrastructure are critical.
-
Mitigation Measures: Germany is implementing various strategies to cope with the reduced supply of Russian gas. These include filling gas storage facilities to maximum capacity, investing in energy efficiency improvements, and promoting energy conservation among citizens and businesses.
The Broader European Context: EU Energy Policy
Klingbeil's statement resonates with the broader EU context, highlighting the ongoing debate within the bloc about energy independence and its reliance on Russia.
-
EU Strategy: The European Union has been actively pursuing a strategy to reduce its dependence on Russian gas, implementing sanctions, and seeking alternative energy partnerships. However, the bloc's response has been uneven, with varying levels of reliance on Russian gas across member states.
-
Varying Opinions: Member states hold differing views on the speed and intensity of sanctions against Russia, reflecting different levels of dependence on Russian energy and economic priorities.
-
EU Energy Security: Klingbeil's decision underscores the vulnerabilities within the EU’s energy system and highlights the need for greater energy cooperation and solidarity among member states to achieve collective energy independence.
-
Alternative Partnerships: The EU is actively exploring alternative gas supplies from Norway, the US, and other countries, as well as increasing investment in renewable energy and energy efficiency measures. These partnerships are crucial in securing Europe’s long-term energy independence.
Conclusion
Lars Klingbeil's unequivocal rejection of renewed Russian gas imports represents a crucial turning point in Germany's and Europe’s energy policies. Driven by moral concerns, geopolitical realities, and the pursuit of long-term energy security, this decision necessitates a rapid acceleration of the energy transition, fostering energy independence and resilience. The short-term economic challenges must be addressed through targeted support measures and energy efficiency improvements. However, the long-term benefits of breaking free from Russian energy dominance far outweigh the immediate costs. Germany's commitment to energy independence and its rejection of Russian gas serves as a model for the rest of Europe. Stay informed on developments regarding Germany’s energy security and the ongoing debate about Germany's and Europe's future relationship with Russian gas imports.

Featured Posts
-
 Phipps Critiques Australian Rugbys Performance In Both Hemispheres
May 01, 2025
Phipps Critiques Australian Rugbys Performance In Both Hemispheres
May 01, 2025 -
 Campeonato Nacional De Boxeo 2025 Participacion De Claudia Sheinbaum Y Julio Cesar
May 01, 2025
Campeonato Nacional De Boxeo 2025 Participacion De Claudia Sheinbaum Y Julio Cesar
May 01, 2025 -
 Bio Based Scholen En De Noodzaak Van Generatoren
May 01, 2025
Bio Based Scholen En De Noodzaak Van Generatoren
May 01, 2025 -
 Yankees Early Lead Not Enough Bibee And Guardians Secure Victory
May 01, 2025
Yankees Early Lead Not Enough Bibee And Guardians Secure Victory
May 01, 2025 -
 Dragons Den Invests In Omnis Plant Based Dog Food
May 01, 2025
Dragons Den Invests In Omnis Plant Based Dog Food
May 01, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Aaj Ka Love Rashifal 14 March 2025
May 01, 2025
Aaj Ka Love Rashifal 14 March 2025
May 01, 2025 -
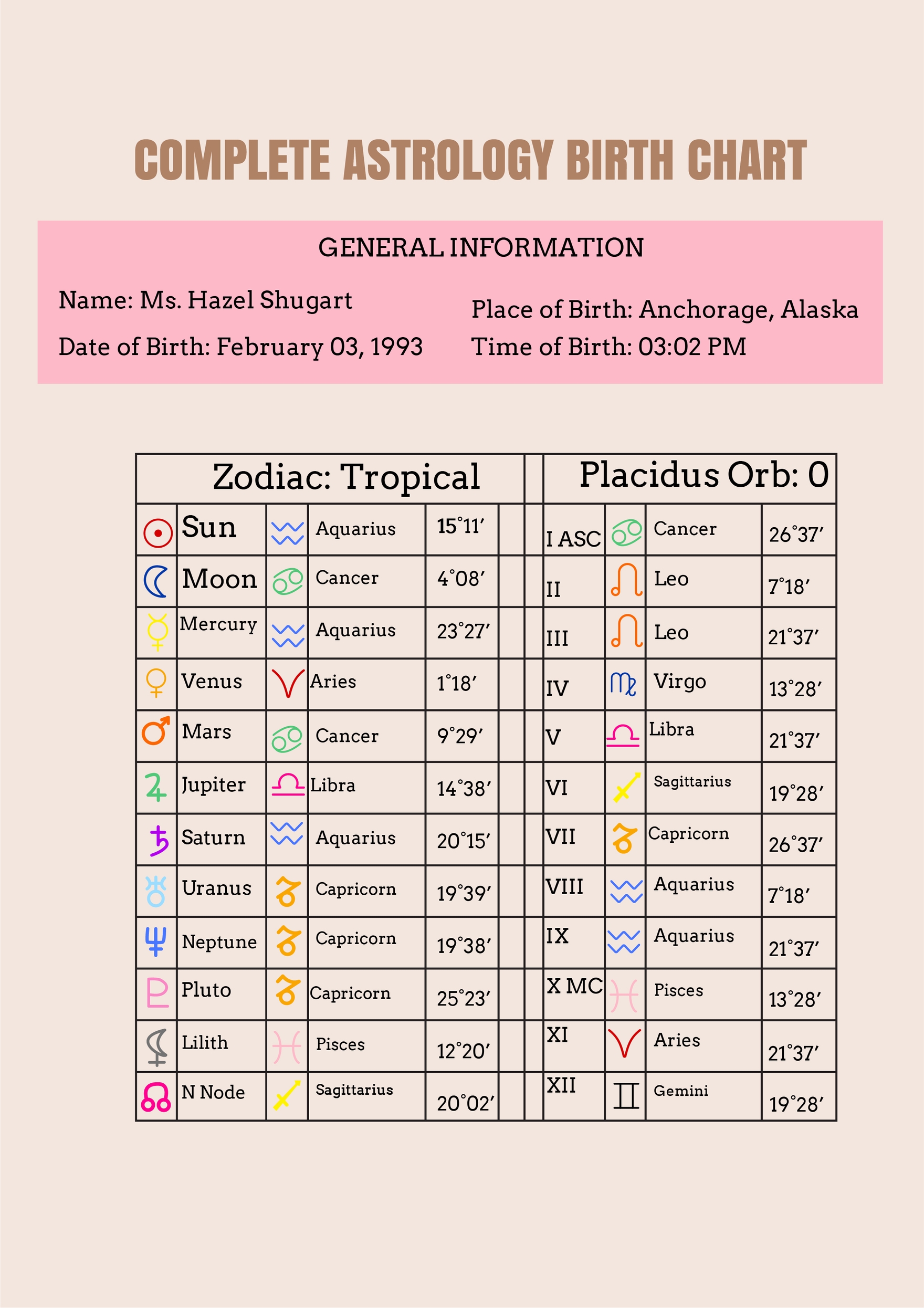 April 17 2025 Horoscope Astrological Readings For Every Sign
May 01, 2025
April 17 2025 Horoscope Astrological Readings For Every Sign
May 01, 2025 -
 The X Files Director Ryan Coogler On A Potential Reboot
May 01, 2025
The X Files Director Ryan Coogler On A Potential Reboot
May 01, 2025 -
 X Files Reboot Cooglers Conversation With Anderson
May 01, 2025
X Files Reboot Cooglers Conversation With Anderson
May 01, 2025 -
 Gillian Anderson And Ryan Coogler Discuss Future Of X Files
May 01, 2025
Gillian Anderson And Ryan Coogler Discuss Future Of X Files
May 01, 2025
