India And The US: Differing Approaches To Conflict Resolution
Table of Contents
Keyword: Conflict Resolution, India-US relations, Diplomacy, Negotiation, International Relations
The United States and India, two global powers with vastly different historical and cultural contexts, approach conflict resolution in distinct ways. While both nations prioritize peace and stability, their methods, stemming from unique geopolitical realities and domestic policies, often diverge significantly. This analysis explores these differing approaches, examining their strengths, weaknesses, and implications for international relations. Understanding these contrasting strategies is crucial for comprehending the complexities of modern conflict resolution and international diplomacy.
<h2>India's Approach to Conflict Resolution</h2>
<h3>Emphasis on Diplomacy and Non-Alignment</h3>
India's approach to conflict resolution is deeply rooted in its historical commitment to non-alignment and peaceful coexistence. This philosophy emphasizes dialogue, negotiation, and multilateralism as primary tools for conflict management.
- Focus on multilateralism: India actively participates in international organizations like the United Nations and the Non-Aligned Movement, advocating for peaceful resolutions through collaborative efforts.
- Prioritizing dialogue and negotiation: India consistently seeks diplomatic solutions, prioritizing discussions and negotiations before resorting to more forceful measures.
- Historical commitment to non-alignment: This policy, adopted during the Cold War, continues to shape India's approach, promoting independent foreign policy decisions and avoiding entanglements in major power rivalries.
- Utilizing regional organizations like SAARC: India actively engages with regional organizations like the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) to address regional conflicts and foster cooperation.
- Strong emphasis on cultural diplomacy: India leverages its rich cultural heritage and soft power to build relationships and foster understanding with other nations, promoting peace through cultural exchange.
India's preference for avoiding direct confrontation stems from its belief in peaceful coexistence and its experience with managing internal diversity. This approach, while often successful in de-escalating tensions, can be perceived as slow or ineffective in addressing immediate threats.
<h3>The Role of Mediation and Arbitration</h3>
India has actively participated in numerous international mediation efforts, leveraging its soft power and diplomatic expertise to de-escalate conflicts and facilitate peaceful settlements.
- Active participation in international mediation efforts: India has played a significant role in mediating disputes between various nations, offering its services as a neutral and respected mediator.
- Willingness to engage in arbitration processes: India has shown a willingness to participate in international arbitration processes, adhering to established legal frameworks for conflict resolution.
- Leveraging its soft power for conflict de-escalation: India's cultural influence and diplomatic standing provide it with leverage in promoting peaceful resolutions.
- Examples of successful mediation initiatives undertaken by India: Specific examples, such as India's role in mediating disputes between neighboring countries, should be highlighted here to demonstrate its success in this area. (Further research is needed to provide specific examples.)
This proactive approach to mediation and arbitration highlights India’s commitment to a rules-based international order and its willingness to engage constructively in resolving global challenges.
<h3>Internal Conflict Management</h3>
India's approach to internal conflict management is complex, reflecting its diverse population and multifaceted challenges. Balancing competing interests within its vast and varied society presents ongoing difficulties.
- Strategies for managing internal conflicts (e.g., Kashmir): India employs a range of strategies to manage internal disputes, balancing security concerns with the need for political reconciliation and economic development. (Further detail is needed on specific strategies used in Kashmir and other regions.)
- Balancing competing interests within a diverse population: India's approach acknowledges the need to address the diverse needs and aspirations of its various communities.
- Challenges in maintaining internal peace and stability: The country faces significant challenges in maintaining internal peace and stability, requiring ongoing efforts to address underlying grievances and promote inclusive governance.
- The role of federalism in conflict resolution: India's federal structure plays a critical role in conflict management, allowing for regional autonomy and the devolution of power.
Managing internal conflicts within a diverse nation presents ongoing challenges, requiring a delicate balance between security and reconciliation. Success often involves addressing root causes, promoting inclusive development, and fostering dialogue among conflicting groups.
<h2>The US Approach to Conflict Resolution</h2>
<h3>Military Intervention and Hard Power</h3>
The United States has a history of employing military intervention as a tool for conflict resolution, often relying on its significant hard power capabilities.
- A history of military intervention in international conflicts: The US has intervened militarily in numerous international conflicts, sometimes with success, sometimes with criticism and unintended consequences.
- Reliance on hard power projection: The US military's global reach and technological superiority allow for the projection of considerable force.
- Robust military alliances (NATO): Alliances like NATO provide a framework for collective security and coordinated military action.
- Emphasis on national security interests: US foreign policy decisions are often driven by considerations of national security interests, sometimes leading to direct military engagement.
The reliance on military intervention, while effective in certain contexts, often raises ethical and political questions about its long-term consequences and the potential for escalating conflicts.
<h3>Economic Sanctions and Diplomatic Pressure</h3>
The US frequently uses economic sanctions and diplomatic pressure to influence international conflicts and encourage desired outcomes.
- Use of economic sanctions as a tool for conflict resolution: Sanctions can range from targeted measures against specific individuals or entities to broader restrictions on trade and finance.
- Leveraging diplomatic pressure through international organizations (UN): The US utilizes its influence within international organizations like the UN to exert diplomatic pressure.
- Engaging in bilateral negotiations: The US engages in extensive bilateral negotiations to resolve conflicts through diplomacy.
- Use of targeted sanctions: Targeted sanctions aim to exert pressure without harming civilian populations.
The effectiveness of economic sanctions and diplomatic pressure varies greatly depending on the context, the target's vulnerability, and the broader geopolitical environment.
<h3>Promotion of Democracy and Human Rights</h3>
The US promotes democracy and human rights as cornerstones of its foreign policy, often supporting democratic movements and providing aid to foster stability.
- Promoting democracy and human rights as a cornerstone of its foreign policy: This approach emphasizes the spread of democratic values and institutions globally.
- Using aid and development assistance to foster stability: Economic assistance is often tied to conditions related to good governance and human rights.
- Support for democratic movements globally: The US provides political and financial support to pro-democracy groups worldwide.
- Limitations and challenges: This approach faces limitations, including the difficulty of imposing democratic values on diverse cultures and the potential for unintended consequences.
The promotion of democracy and human rights is a complex endeavor, often facing challenges due to cultural differences, internal political dynamics, and the potential for unintended consequences.
<h2>Comparing and Contrasting Approaches</h2>
India and the US employ fundamentally different approaches to conflict resolution. India prioritizes diplomacy, mediation, and non-alignment, focusing on long-term relationships and de-escalation. The US, in contrast, often utilizes its hard power, economic sanctions, and the promotion of democracy, aiming for quicker, more decisive outcomes. The effectiveness of each approach varies greatly based on the nature of the conflict, the actors involved, and the broader geopolitical landscape.
| Feature | India's Approach | US Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Tool | Diplomacy, Mediation, Non-alignment | Hard Power, Economic Sanctions, Democracy Promotion |
| Emphasis | Long-term relationships, de-escalation | Quick resolutions, decisive action |
| Strengths | Reduced escalation, fosters cooperation | Swift action, significant influence |
| Weaknesses | Can be slow, less effective in immediate threats | Can be destabilizing, potential for unintended consequences |
A comparative analysis reveals that while both nations strive for peace, their methods reflect distinct historical experiences and geopolitical priorities. Neither approach is universally superior; their effectiveness depends on the specific circumstances of each conflict.
<h2>Conclusion</h2>
This article explored the contrasting approaches of India and the US to conflict resolution. India emphasizes diplomacy, mediation, and non-alignment, while the US often employs military intervention, economic sanctions, and the promotion of democracy. Both approaches have their strengths and limitations depending on the specific conflict and circumstances. Understanding these differing approaches to conflict resolution is crucial for navigating an increasingly complex geopolitical landscape. Further research into India-US cooperation on conflict resolution and the potential for integrating these distinct strategies can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of effective peacebuilding initiatives. By analyzing both India’s and the US’s unique strategies for conflict resolution, we can develop more effective solutions for international disputes and improve global peace and security.

Featured Posts
-
 Watch England Vs Spain Tv Channel Kick Off Time And Live Streaming Options
May 02, 2025
Watch England Vs Spain Tv Channel Kick Off Time And Live Streaming Options
May 02, 2025 -
 The Calibri Ms 13 Tattoo Confusion Understanding Trumps Remarks
May 02, 2025
The Calibri Ms 13 Tattoo Confusion Understanding Trumps Remarks
May 02, 2025 -
 The Future Of Buy Canadian Loblaws Perspective And The Shifting Market
May 02, 2025
The Future Of Buy Canadian Loblaws Perspective And The Shifting Market
May 02, 2025 -
 Mqbwdh Kshmyr Agha Syd Rwh Allh Mhdy Ka Bharty Hkwmt Pr Tnqydy Byan
May 02, 2025
Mqbwdh Kshmyr Agha Syd Rwh Allh Mhdy Ka Bharty Hkwmt Pr Tnqydy Byan
May 02, 2025 -
 Daisy May Cooper Opens Up Weight Loss Lip Fillers And Body Image
May 02, 2025
Daisy May Cooper Opens Up Weight Loss Lip Fillers And Body Image
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Examining Maines Inaugural Post Election Audit
May 02, 2025
Examining Maines Inaugural Post Election Audit
May 02, 2025 -
 Post Election Audit Pilot Program Begins In Maine
May 02, 2025
Post Election Audit Pilot Program Begins In Maine
May 02, 2025 -
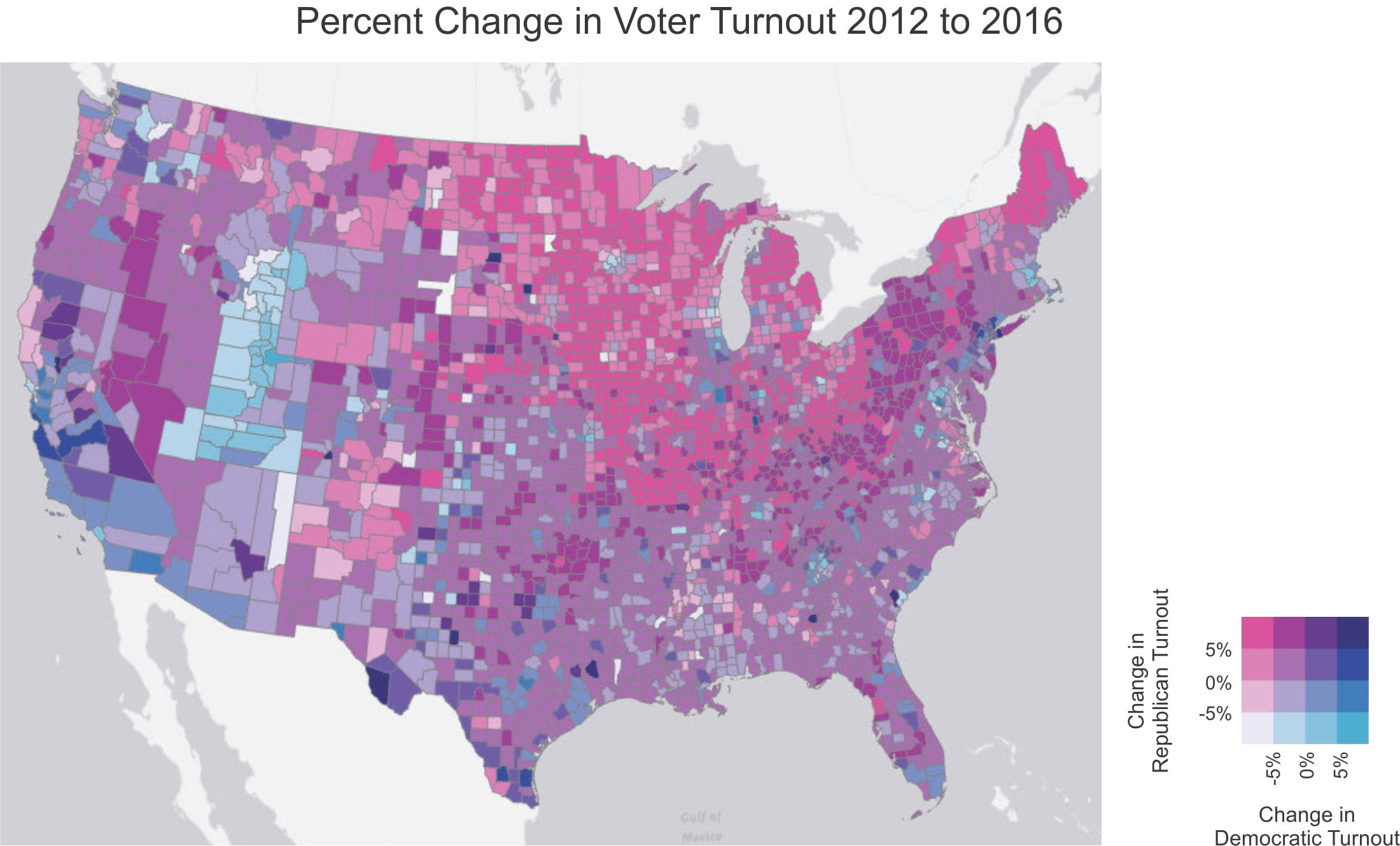 Florida And Wisconsin Voter Turnout Understanding The Shifting Political Dynamics
May 02, 2025
Florida And Wisconsin Voter Turnout Understanding The Shifting Political Dynamics
May 02, 2025 -
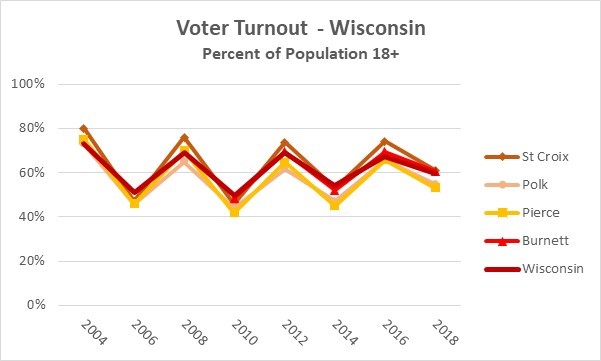 Analyzing Voter Turnout In Florida And Wisconsin Implications For The Current Political Moment
May 02, 2025
Analyzing Voter Turnout In Florida And Wisconsin Implications For The Current Political Moment
May 02, 2025 -
 High Voter Confidence In Sc Elections 93 Approval Rating
May 02, 2025
High Voter Confidence In Sc Elections 93 Approval Rating
May 02, 2025
