INSACOG's Report On BA.1 And LF.7 COVID-19 Variants In India: Assessing The Risk
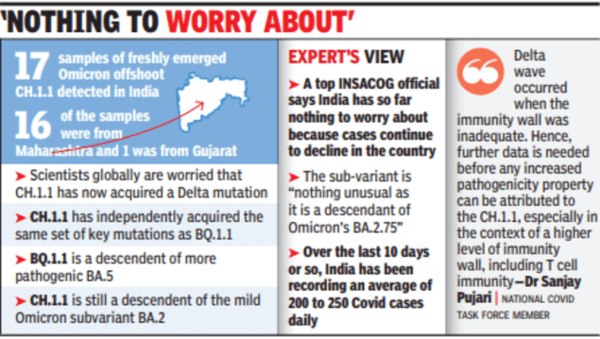
Table of Contents
Prevalence and Geographic Distribution of BA.1 and LF.7 in India
Understanding the spread of BA.1 and LF.7 is crucial for effective public health interventions. INSACOG's reports (insert citation if available) detail the prevalence and geographic distribution of these variants across India. While precise figures vary depending on the reporting period, initial data suggests [insert data on prevalence rates if available from INSACOG reports, perhaps as percentages or a graph]. This data highlights [insert analysis of geographic distribution, e.g., concentration in certain regions, patterns of spread].
- BA.1 Prevalence: [Insert specific data and regional distribution details if available from INSACOG reports]
- LF.7 Prevalence: [Insert specific data and regional distribution details if available from INSACOG reports]
- Geographic Patterns: [Analyze observed patterns of spread. Did it spread from a specific region? Were there correlations with population density or travel patterns?]
Visual representation of this data, such as maps illustrating the spread of BA.1 and LF.7 across different states, would provide a clearer picture. Keywords: BA.1 prevalence, LF.7 prevalence, India COVID-19 map, geographic distribution, variant spread.
Clinical Characteristics Associated with BA.1 and LF.7 Infections
Analyzing the clinical characteristics of BA.1 and LF.7 infections is vital for assessing their severity. INSACOG's data (if available, cite the report) should provide insights into:
- Severity of Illness: [Insert information on the severity of illness associated with BA.1 and LF.7 infections, e.g., were they generally mild, moderate, or severe? Were there any significant differences observed compared to previous variants?]
- Symptoms: [Describe the common symptoms associated with each variant. Were there any unique or distinguishing symptoms?]
- Hospitalization and Mortality Rates: [Present data on hospitalization and mortality rates associated with infections caused by BA.1 and LF.7. Compare these rates to those seen with previous variants].
This information helps healthcare systems prepare for potential surges in cases and allocate resources effectively. Keywords: BA.1 symptoms, LF.7 symptoms, COVID-19 severity, hospitalization rates, mortality rates, clinical characteristics.
Comparison of BA.1 and LF.7 with other circulating Variants
Comparing BA.1 and LF.7 with other circulating variants in India provides a crucial context for risk assessment. Key factors to consider include:
- Transmissibility: [Compare the transmissibility rates of BA.1 and LF.7 with other variants prevalent in India. Which variant is more contagious?]
- Immune Evasion: [Discuss the ability of BA.1 and LF.7 to evade the immune response generated by vaccination or prior infection. How effectively do existing antibodies neutralize these variants?]
- Competitive Advantage: [Analyze the potential for BA.1 and LF.7 to outcompete other circulating variants. What factors contribute to their ability to spread and dominate?]
This comparative analysis is essential for predicting the future trajectory of the pandemic in India. Keywords: variant comparison, transmissibility, immune evasion, competitive advantage, COVID-19 variant evolution.
INSACOG's Genomic Surveillance and its Implications for Public Health
INSACOG's genomic surveillance program is a cornerstone of India's COVID-19 response. Its continuous monitoring of circulating variants allows for:
- Early Warning System: [Explain how genomic sequencing helps detect new variants early, enabling proactive public health interventions.]
- Informing Public Health Strategies: [Describe how data from INSACOG informs decisions about vaccination strategies, testing protocols, and public health messaging.]
- Limitations and Improvements: [Acknowledge the limitations of genomic surveillance, such as potential biases in sampling and the need for improved data sharing and analysis.]
Strengthening genomic surveillance is vital for effective pandemic preparedness. Keywords: genomic surveillance, public health response, data analysis, COVID-19 monitoring, variant tracking.
Risk Assessment and Future Outlook for BA.1 and LF.7 in India
Based on the available data from INSACOG, the overall risk posed by BA.1 and LF.7 to the Indian population can be assessed. Key considerations include:
- Potential Impact on Healthcare Systems: [Analyze the potential strain on healthcare systems if there is a significant surge in cases due to these variants.]
- Economic Impact: [Discuss the potential economic consequences, such as disruptions to businesses and industries.]
- Future Scenarios: [Outline potential future scenarios based on the observed characteristics of BA.1 and LF.7 and the current epidemiological situation.]
- Preparedness: [Highlight the importance of maintaining a high level of public health preparedness and the need for continued monitoring.]
Continuous monitoring and adaptation are essential to effectively manage the evolving threat posed by new COVID-19 variants. Keywords: risk assessment, public health preparedness, COVID-19 future predictions, healthcare impact, economic impact.
Conclusion: Staying Informed about INSACOG's Findings on COVID-19 Variants in India
INSACOG's reports on the BA.1 and LF.7 variants provide valuable insights into the evolving COVID-19 landscape in India. While the immediate risk may vary, ongoing monitoring and genomic surveillance are crucial. Continued public health measures, including vaccination, testing, and adherence to safety guidelines, remain essential. Stay informed about INSACOG's updates on emerging COVID-19 variants by regularly checking their website and following public health advisories. Understanding the risk of new COVID-19 variants and monitoring INSACOG's reports on COVID-19 variants are critical for protecting the health of the Indian population.

Featured Posts
-
 Duncan Bannatyne On Supreme Court Ruling Protecting Womens Safety In Changing Rooms
May 31, 2025
Duncan Bannatyne On Supreme Court Ruling Protecting Womens Safety In Changing Rooms
May 31, 2025 -
 Communique De Presse Developpement De Sanofi En France Inauguration D Un Nouveau Site
May 31, 2025
Communique De Presse Developpement De Sanofi En France Inauguration D Un Nouveau Site
May 31, 2025 -
 Banksys Identity Unmasking The Artist Behind The Mystery
May 31, 2025
Banksys Identity Unmasking The Artist Behind The Mystery
May 31, 2025 -
 The Terrain Of Northern Arkansas And Evasion Techniques
May 31, 2025
The Terrain Of Northern Arkansas And Evasion Techniques
May 31, 2025 -
 Authenticating The Westcliff Bournemouth Banksy A Guide For Art Enthusiasts
May 31, 2025
Authenticating The Westcliff Bournemouth Banksy A Guide For Art Enthusiasts
May 31, 2025
