Interest Rates Unchanged: Fed's Assessment Of Inflation And Unemployment
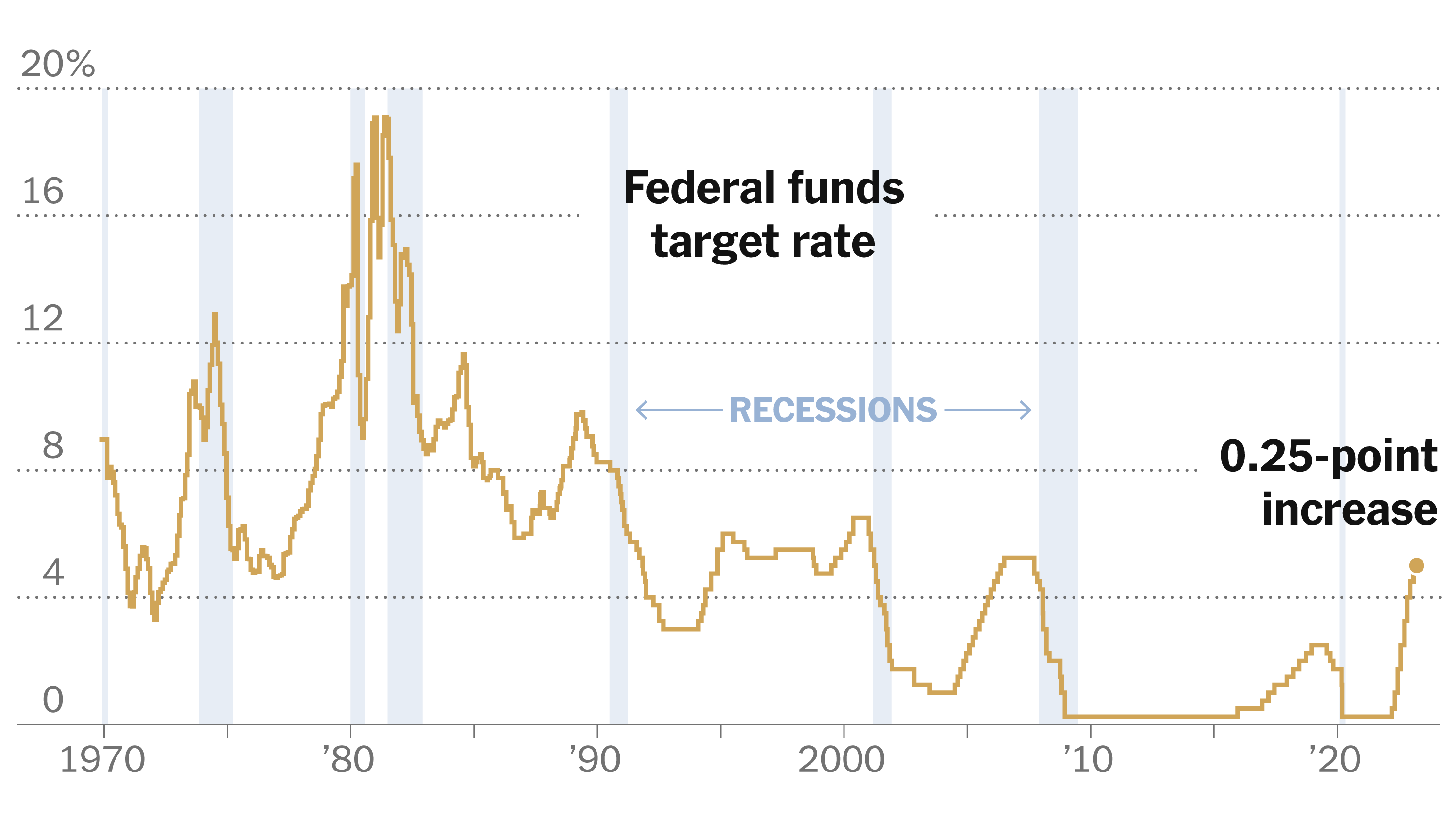
Table of Contents
The Federal Reserve's decision to leave interest rates unchanged has sent ripples through the financial markets. This decision comes amidst a complex economic landscape marked by persistent inflation and fluctuating unemployment figures. This article delves into the Fed's rationale, examining their assessment of inflation, the unemployment situation, and the implications for consumers and businesses. Understanding the nuances of this decision is crucial for navigating the current economic climate.
Persistent Inflation Remains a Key Concern
While recent data shows some easing of price pressures, persistent inflation remains a primary concern for the Federal Reserve. The Fed's mandate is to maintain price stability and maximum employment. Achieving both simultaneously presents a significant challenge.
Core Inflation Metrics
- CPI (Consumer Price Index): The latest CPI figures show a slight decrease in the rate of inflation, but core inflation (excluding volatile food and energy prices) remains stubbornly high. This indicates that inflationary pressures are entrenched within the economy.
- PCE (Personal Consumption Expenditures): The PCE index, the Fed's preferred inflation measure, also reflects a similar trend, with core PCE still above the Fed's 2% target. The persistence of these elevated core inflation metrics is a major factor in the Fed's decision to hold interest rates steady for now.
- Comparison to Target: The current inflation rate significantly exceeds the Fed's 2% target. The gap remains a source of concern and highlights the ongoing challenge in bringing inflation back down to a sustainable level.
The Fed is concerned about the "stickiness" of inflation – the tendency for prices to remain elevated even as other economic indicators soften. This stickiness suggests that inflationary pressures are deeply embedded in the economy and will require a sustained effort to mitigate.
Factors Contributing to Inflation
Several factors contribute to the persistent inflation:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Lingering supply chain issues continue to impact the availability and cost of goods.
- Energy Prices: Volatile energy prices, driven partly by geopolitical factors, have significantly contributed to overall inflation.
- Wage Growth: Strong wage growth, while positive for workers, can contribute to inflationary pressures if it outpaces productivity gains, creating a wage-price spiral.
- Demand-Pull Inflation: Robust consumer demand, fueled by pent-up savings and government stimulus, has added to inflationary pressures.
- Cost-Push Inflation: Rising input costs for businesses, including energy and raw materials, are pushing up prices for consumers. Geopolitical instability exacerbates this issue.
Fed's Strategy to Combat Inflation
The Fed employs several monetary policy tools to combat inflation:
- Quantitative Tightening (QT): The Fed is reducing its balance sheet through QT, a process of gradually selling off the assets it accumulated during previous quantitative easing programs. This reduces the money supply and helps to curb inflation.
- Interest Rate Hikes (Potential): While rates remain unchanged currently, the possibility of future interest rate hikes remains on the table, depending on incoming economic data and the Fed's assessment of inflation and the labor market.
- Forward Guidance: The Fed uses communication to influence expectations and guide the markets. Clear and consistent messaging on its inflation targets and policy intentions is crucial in managing inflation expectations.
Unemployment Rate and Labor Market Dynamics
The labor market continues to exhibit strength, presenting another layer of complexity for the Fed's policy decisions.
Current Unemployment Figures
- Unemployment Rate: The unemployment rate remains relatively low, indicating a strong labor market. This is generally a positive sign, but also contributes to upward pressure on wages.
- Labor Force Participation Rate: The labor force participation rate reflects the percentage of the working-age population that is either employed or actively seeking employment. Its recent trends provide insights into labor market dynamics.
- Job Growth: Job growth in key sectors remains strong, further evidence of a robust labor market. However, this also fuels wage increases.
The Fed's Assessment of the Labor Market
The Fed views the strong labor market as a positive indicator of economic health. However, they also recognize the potential for a wage-price spiral – a situation where rising wages lead to higher prices, which in turn lead to further wage increases, creating a self-perpetuating cycle of inflation.
Balancing Inflation and Unemployment
The Fed faces the difficult task of balancing the need to control inflation with the need to avoid triggering a recession. This classic economic challenge is represented by the Phillips Curve, which illustrates the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. The Fed must carefully navigate this trade-off, striving for a "soft landing"—slowing inflation without causing significant job losses.
Implications for the Economy and Financial Markets
The Fed's decision to hold interest rates steady has wide-ranging implications for the economy and financial markets.
Impact on Consumer Spending
- Mortgage Rates: Interest rate decisions directly impact mortgage rates, influencing housing affordability and consumer spending.
- Consumer Confidence: The Fed's decisions affect consumer confidence, which in turn impacts spending habits.
- Retail Sales: Retail sales data provides insights into consumer spending patterns and their response to economic conditions.
Effect on Businesses and Investment
- Corporate Borrowing Costs: Interest rate decisions influence corporate borrowing costs, affecting businesses' investment plans and expansion strategies.
- Stock Market Reactions: The stock market often reacts to Fed announcements, reflecting investors' expectations about future economic conditions and corporate profitability.
- Business Sentiment: Business sentiment surveys provide indicators of confidence and willingness to invest.
Global Economic Context
The global economic climate significantly influences the Fed's decision-making.
- Global Inflation: Global inflationary pressures impact the US economy through increased import costs.
- Interest Rate Policies of Other Central Banks: The actions of other central banks around the world influence global interest rate levels and capital flows.
- Geopolitical Risks: Geopolitical events and uncertainty can disrupt global supply chains and contribute to inflation.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve's decision to maintain interest rates reflects their cautious approach to navigating the complex interplay between persistent inflation and a robust labor market. The Fed's ongoing concerns about core inflation, alongside their assessment of the strong labor market and its potential for a wage-price spiral, underscore the delicate balancing act they face. The implications for consumers, businesses, and the overall economy are significant and warrant close monitoring. Understanding the complexities of interest rate decisions and their impact is crucial for informed financial planning.
Call to Action: Stay informed about future decisions regarding interest rates by regularly checking our website for updates on the Fed's policy and its impact on the economy. Learn more about [link to relevant resource or next article on interest rates]. Understanding the complexities of interest rates is crucial for sound financial planning.

Featured Posts
-
 Kraujingos Plintos Nuotraukos Dakota Johnson Atskleidzia Tiesa
May 10, 2025
Kraujingos Plintos Nuotraukos Dakota Johnson Atskleidzia Tiesa
May 10, 2025 -
 Ohio Train Derailment The Long Term Impact Of Toxic Chemical Contamination On Buildings
May 10, 2025
Ohio Train Derailment The Long Term Impact Of Toxic Chemical Contamination On Buildings
May 10, 2025 -
 Nhl Playoffs Oilers Vs Kings Prediction Best Bets For Game 1 Tonight
May 10, 2025
Nhl Playoffs Oilers Vs Kings Prediction Best Bets For Game 1 Tonight
May 10, 2025 -
 Survival Of The Fittest Instagram Ceo On Competing With Tik Toks Explosive Growth
May 10, 2025
Survival Of The Fittest Instagram Ceo On Competing With Tik Toks Explosive Growth
May 10, 2025 -
 2025 Presidential Politics Retrospective On Trumps Day 109 May 8th
May 10, 2025
2025 Presidential Politics Retrospective On Trumps Day 109 May 8th
May 10, 2025
