Is Uber Recession-Proof? Analyst Insights On Stock Performance
Table of Contents
Uber's Business Model and its Vulnerability to Recessions
Uber's success hinges on its two-sided marketplace connecting riders and drivers. This model, however, presents inherent vulnerabilities during economic downturns.
The Two-Sided Marketplace
Uber operates a classic two-sided marketplace. This means its success depends on a healthy balance between supply (drivers) and demand (riders). During recessions, this delicate balance can be disrupted.
- Decreased rider demand during recessions: As disposable income shrinks, people may cut back on non-essential spending, including ride-sharing services. This directly impacts Uber's revenue.
- Potential driver shortages due to reduced income opportunities: With fewer riders, drivers may earn less, potentially leading some to seek alternative employment. This can create supply issues, further impacting service quality and availability.
- Impact on pricing strategies: Uber might attempt to offset reduced demand by adjusting pricing. However, aggressive price increases could further deter riders already hesitant to spend.
Diversification Strategy and its Impact
Uber's diversification beyond ride-sharing, including Uber Eats (food delivery), Uber Freight (logistics), and other initiatives, is a key factor in assessing its recession resistance.
- Relative resilience of food delivery services during economic downturns: While discretionary spending falls, the demand for essential goods and convenient food delivery often remains relatively stable, even during recessions.
- Potential for growth in freight services: The freight sector can be less sensitive to economic fluctuations than passenger transportation, offering a degree of insulation during downturns.
- Interdependency between different business units: Although diversification helps, the various Uber business units aren't entirely independent. A severe recession could still negatively impact all segments.
Pricing Power and Elasticity of Demand
Uber's ability to adjust prices to maintain profitability is crucial during economic slowdowns. Understanding price elasticity of demand—how much demand changes in response to price changes—is critical.
- Impact of price increases on rider behavior: Raising prices could lead riders to switch to cheaper alternatives like public transport or carpooling, impacting revenue.
- Competition from other ride-sharing and food delivery services: Intense competition from Lyft, DoorDash, and others limits Uber's pricing power. Raising prices too much risks losing market share.
- Analysis of historical price adjustments during previous economic slowdowns: Examining how Uber reacted to previous economic downturns can offer valuable insights into its current strategies and vulnerabilities.
Analyst Sentiment and Stock Performance
Analyzing Uber's stock performance and analyst sentiment provides crucial insights into its recession resilience.
Recent Stock Performance and Analyst Ratings
Uber's stock price, earnings reports, and analyst ratings reflect investor confidence and future expectations. Tracking these indicators alongside macroeconomic data offers a holistic view.
- Stock price trends: Analyzing recent stock price movements helps gauge investor sentiment towards Uber's prospects.
- Earnings reports: Quarterly and annual earnings reports reveal the company's financial health and profitability.
- Analyst target prices: Analyst target prices indicate their projected future stock prices, reflecting their assessments of Uber's growth potential.
- Buy/sell/hold recommendations: Analyst ratings (buy, sell, or hold) summarize their overall opinion on the stock's investment value.
- Impact of macroeconomic factors on stock valuation: External economic factors significantly influence Uber's stock valuation, highlighting its sensitivity to the overall economy.
Comparison with Competitors
Comparing Uber's performance to competitors like Lyft and DoorDash provides a benchmark for assessing its relative resilience.
- Performance of Lyft, DoorDash, etc. during economic downturns: Analyzing how competing companies fared during previous recessions reveals industry-specific vulnerabilities.
- Market share analysis: Tracking market share changes helps gauge Uber's competitive position and its ability to withstand economic pressure.
- Competitive advantages and disadvantages: Identifying Uber's unique strengths and weaknesses compared to its competitors helps determine its vulnerability to economic shocks.
- Relative vulnerability to economic cycles: Comparing the sensitivity of Uber's stock to economic cycles with its competitors helps assess its relative resilience.
Long-Term Growth Potential and Recession Resilience
Uber's long-term growth prospects and its ability to weather future economic downturns depend on several factors.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Uber's investments in autonomous vehicle technology and other innovations could significantly impact its long-term profitability and resilience.
- Potential for cost reductions through automation: Self-driving cars could reduce labor costs, a major expense for Uber.
- Impact on driver costs: Automation could drastically alter the driver-related cost structure, affecting profitability.
- Long-term competitive advantages: Technological leadership could give Uber a significant edge over competitors.
- Risks associated with technological investments: Significant upfront investment carries inherent risks, and technological advancements don't guarantee success.
Expanding into New Markets and Services
Expansion into new geographical markets and service offerings can diversify revenue streams and mitigate risks associated with economic downturns.
- Growth opportunities in emerging markets: Expanding into rapidly growing economies can offset slower growth in mature markets.
- Diversification into new service areas: Offering additional services beyond ride-sharing and food delivery can broaden Uber's appeal and reduce dependence on any single sector.
- Geographic diversification mitigating regional economic risks: Operating in multiple countries reduces the impact of economic downturns in any single region.
Conclusion
This analysis of Uber's business model, stock performance, and analyst sentiment reveals a complex picture regarding its recession-proofness. While diversification and technological advancements offer potential for long-term resilience, the company remains vulnerable to economic downturns due to its dependence on consumer spending. Investors should carefully consider these factors and monitor Uber's performance alongside broader macroeconomic indicators. Further research into Uber's future strategies and the evolving competitive landscape is crucial for accurately assessing its long-term viability and whether it truly represents a recession-proof investment. Conduct thorough due diligence before making any investment decisions related to Uber stock.

Featured Posts
-
 Should Snl Embrace Stronger Language Bowen Yang Weighs In
May 18, 2025
Should Snl Embrace Stronger Language Bowen Yang Weighs In
May 18, 2025 -
 Instant Withdrawal Casinos No Kyc 7 Bit Casino Review And Player Experience
May 18, 2025
Instant Withdrawal Casinos No Kyc 7 Bit Casino Review And Player Experience
May 18, 2025 -
 Brooklyn Bridge Structural Analysis Strengths And Weaknesses
May 18, 2025
Brooklyn Bridge Structural Analysis Strengths And Weaknesses
May 18, 2025 -
 Las Vegas Sands Abandons Nassau Coliseum Casino Resort Project
May 18, 2025
Las Vegas Sands Abandons Nassau Coliseum Casino Resort Project
May 18, 2025 -
 Taylor Swift Sues Kanye West Over Explicit Lyrics A Legal Breakdown
May 18, 2025
Taylor Swift Sues Kanye West Over Explicit Lyrics A Legal Breakdown
May 18, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Daily Lotto Results Tuesday 22nd April 2025
May 18, 2025
Daily Lotto Results Tuesday 22nd April 2025
May 18, 2025 -
 Saturday Lotto Results April 12 2025 Lotto Plus Numbers
May 18, 2025
Saturday Lotto Results April 12 2025 Lotto Plus Numbers
May 18, 2025 -
 April 17 2025 Daily Lotto Results Find The Winning Numbers
May 18, 2025
April 17 2025 Daily Lotto Results Find The Winning Numbers
May 18, 2025 -
 Check Daily Lotto Results For Friday April 18 2025
May 18, 2025
Check Daily Lotto Results For Friday April 18 2025
May 18, 2025 -
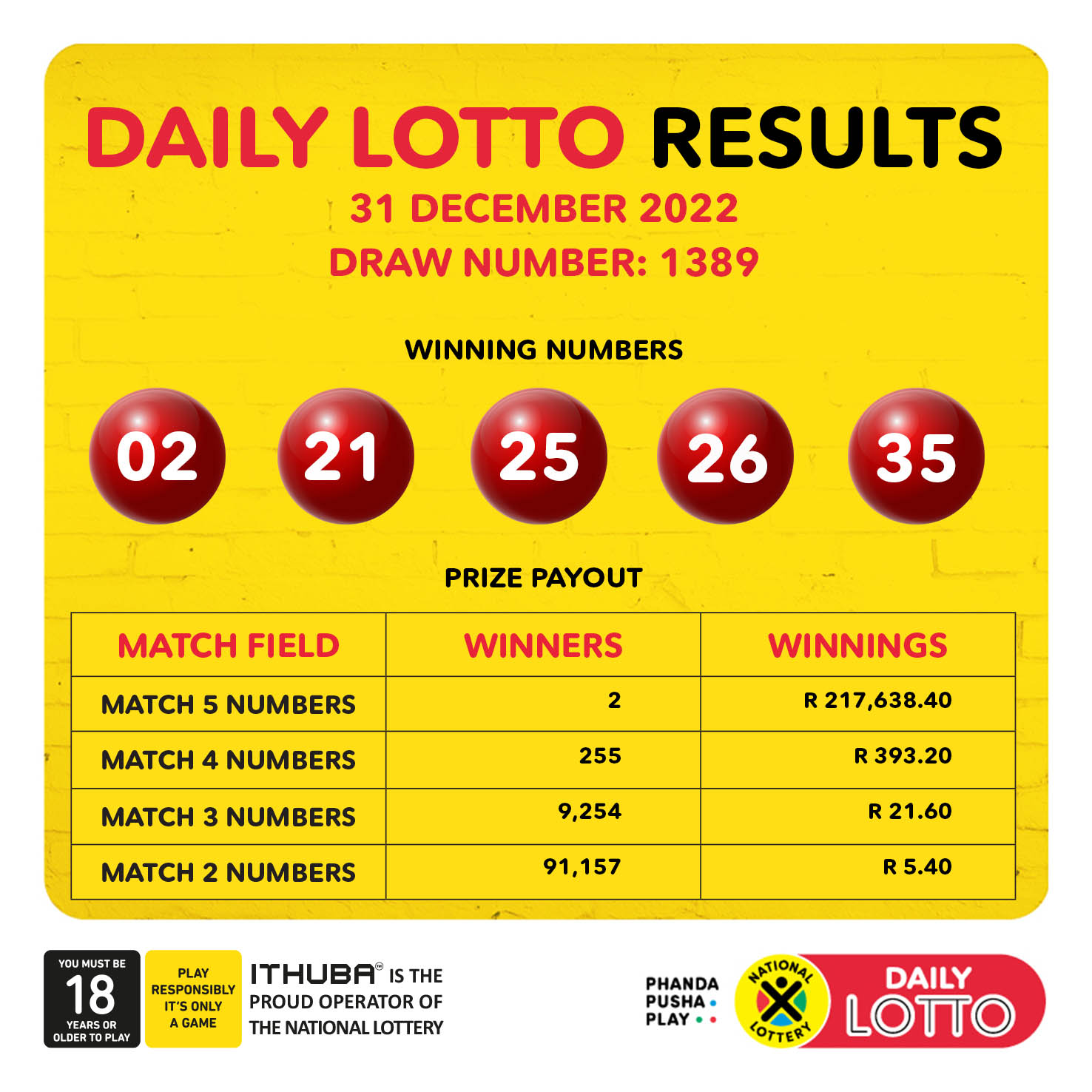 Daily Lotto Results Sunday April 20 2025
May 18, 2025
Daily Lotto Results Sunday April 20 2025
May 18, 2025
