Japan's Economic Performance Q1 2018: Before The Tariff Shock
Table of Contents
GDP Growth and its Drivers
Japan's GDP growth in Q1 2018 showed a modest expansion, though the exact figures require referencing specific data sources from that period (e.g., Cabinet Office, Japan). This growth, while positive, was less robust than in previous quarters. Analyzing the contributing factors reveals a mixed picture:
- Private Consumption: Consumer spending, a significant driver of Japan's GDP, showed [insert data on consumer spending growth rate for Q1 2018, e.g., a moderate increase of X%]. This was influenced by [insert factors impacting consumer spending, e.g., stable employment rates, but subdued wage growth]. <br> Image: Chart showing private consumption trends in Q1 2018. Alt text: "Japan Private Consumption Q1 2018 Chart showing modest growth."
- Government Spending: Government initiatives focused on [mention specific policy areas, e.g., infrastructure investment and stimulus packages]. The effectiveness of these measures in boosting GDP growth needs further analysis, considering their impact on national debt.
- Infrastructure Investment: Investment in infrastructure projects contributed to economic activity, particularly in specific sectors such as [mention sectors, e.g., construction and related industries]. However, the long-term impact on overall GDP growth requires assessing project completion rates and their broader economic ripple effects.
- Net Exports: Net exports (exports minus imports) played a [positive/negative] role in Q1 2018 GDP growth. [Insert data on export and import figures for Q1 2018 and calculate the net contribution. Include reasons for the positive or negative contribution, for example: strong global demand for certain Japanese goods, or a weaker Yen, which would boost exports]. <br> Image: Chart showing net export contribution to GDP in Q1 2018. Alt Text: "Japan Net Exports Contribution to GDP Q1 2018."
Inflation and Monetary Policy
Inflation in Q1 2018 remained stubbornly low, [insert specific inflation rate data for Q1 2018]. This failed to meet the Bank of Japan's (BOJ) target of [insert BOJ's inflation target]. The BOJ maintained its quantitative easing (QE) policy throughout this period, aiming to stimulate inflation and economic growth.
- BOJ's Policy: The BOJ continued its policy of near-zero interest rates and asset purchases (QE) to encourage borrowing and investment.
- Effectiveness: The effectiveness of this monetary policy in stimulating growth was debated, with some arguing that QE's impact was diminishing. The low inflation rate suggests limited success in achieving the BOJ's objectives.
- Impact on Lending: Low interest rates led to [discuss impact on lending rates and business investment in Q1 2018, and whether this was sufficient to stimulate the economy].
External Factors and Global Economic Conditions
The global economic environment in Q1 2018 was characterized by [describe the overall global economic climate, e.g., moderate growth in many developed economies, but uncertainties in emerging markets].
- Global GDP Growth: Global GDP growth forecasts for Q1 2018 were [insert data].
- Oil Prices: Oil prices [insert data on oil price trends in Q1 2018]. This [positively/negatively] impacted Japanese businesses and consumers, as Japan is a significant net importer of oil.
- Trade Tensions: While not yet fully manifested in Q1 2018, the early signs of rising trade tensions between major economies [mention specific examples] presented a significant risk to Japan's export-oriented economy.
Key Economic Indicators
Other key economic indicators for Japan in Q1 2018 included:
- Unemployment Rate: [Insert unemployment rate data for Q1 2018]. This indicates [interpret the data in terms of its impact on the economy and consumer confidence].
- Industrial Production: [Insert industrial production data for Q1 2018]. This reflected [interpret the data and its relation to overall economic performance].
- Consumer Confidence Index: [Insert consumer confidence index data for Q1 2018]. This suggests [interpret the data and its significance for consumer spending].
Conclusion
Japan's economic performance in Q1 2018 showed moderate growth, driven primarily by private consumption and government spending, though facing headwinds from subdued inflation and a reliance on net exports. While the economy displayed relative stability, the low inflation rate underscored the challenges facing the BOJ's monetary policy. The looming shadow of escalating trade disputes posed a significant uncertainty to Japan's future economic prospects. Understanding Japan's economic performance in Q1 2018 provides valuable context for analyzing subsequent economic shifts. For further insights into Japan's economic trajectory and the impact of global trade dynamics, continue exploring resources on Japan's Economic Performance Q1 2018 and related economic indicators.

Featured Posts
-
 Fortnite Music Change Sparks Player Backlash
May 17, 2025
Fortnite Music Change Sparks Player Backlash
May 17, 2025 -
 Investigation Uncovers Final Moments Before Bayesian Superyacht Tragedy
May 17, 2025
Investigation Uncovers Final Moments Before Bayesian Superyacht Tragedy
May 17, 2025 -
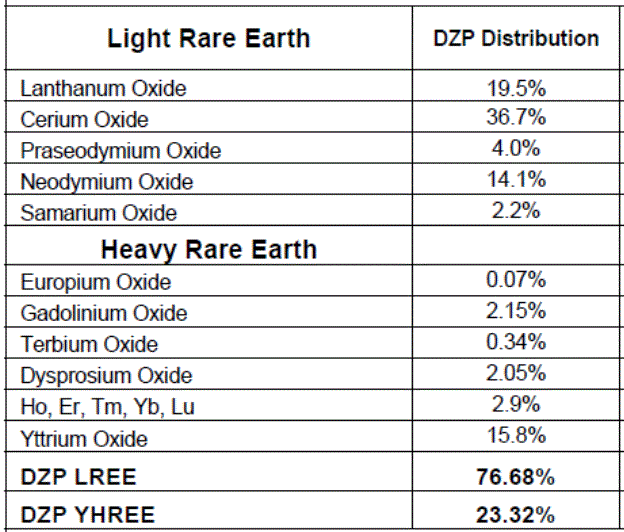 Lynas Breaks Chinese Monopoly Leading Heavy Rare Earths Production Globally
May 17, 2025
Lynas Breaks Chinese Monopoly Leading Heavy Rare Earths Production Globally
May 17, 2025 -
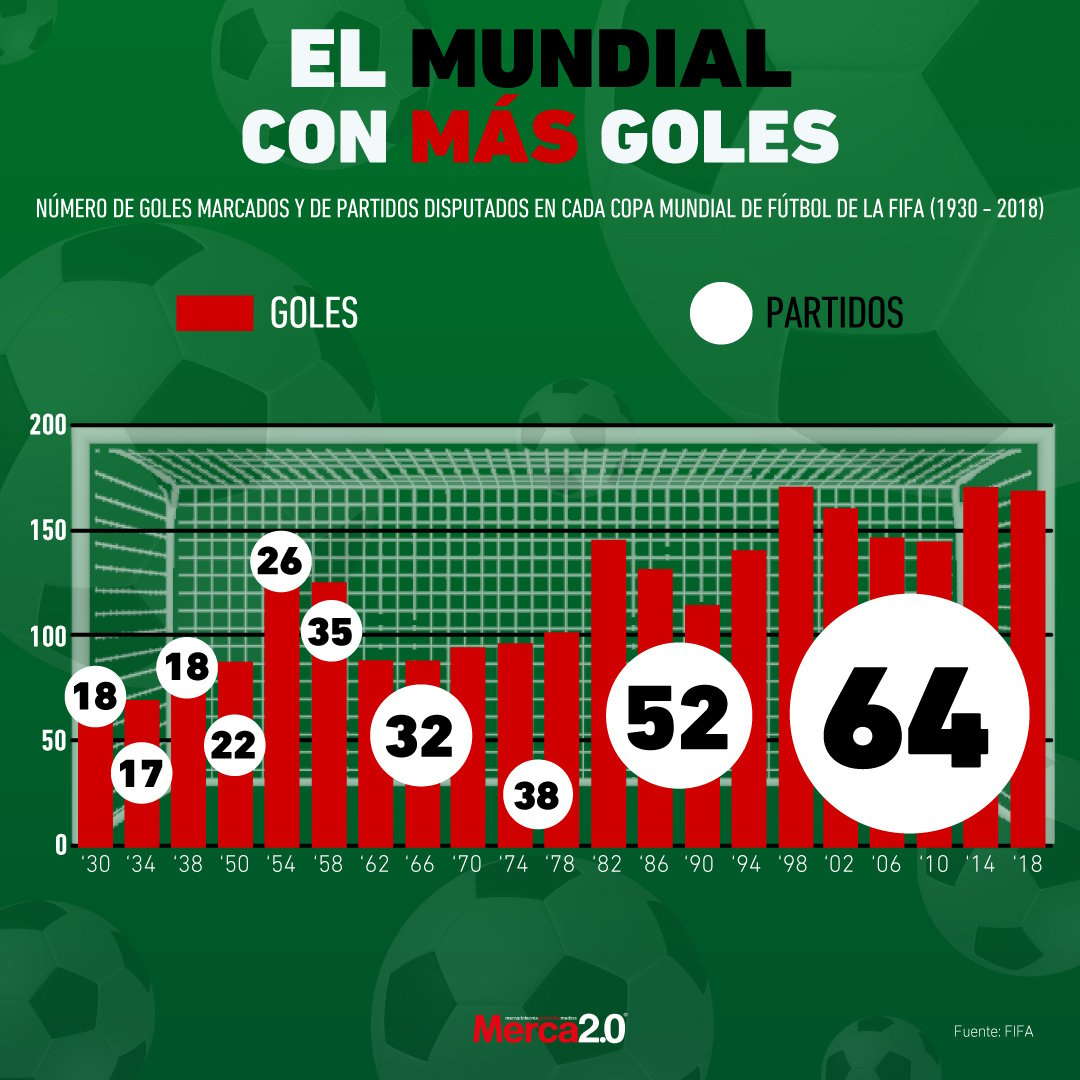 Penarol 0 Olimpia 2 Cronica Goles Y Resumen Del Partido
May 17, 2025
Penarol 0 Olimpia 2 Cronica Goles Y Resumen Del Partido
May 17, 2025 -
 Top 16 Black Wnba Players A Historical Look
May 17, 2025
Top 16 Black Wnba Players A Historical Look
May 17, 2025
