Japan's Economy Faces Headwinds: The Steepening Bond Yield Curve
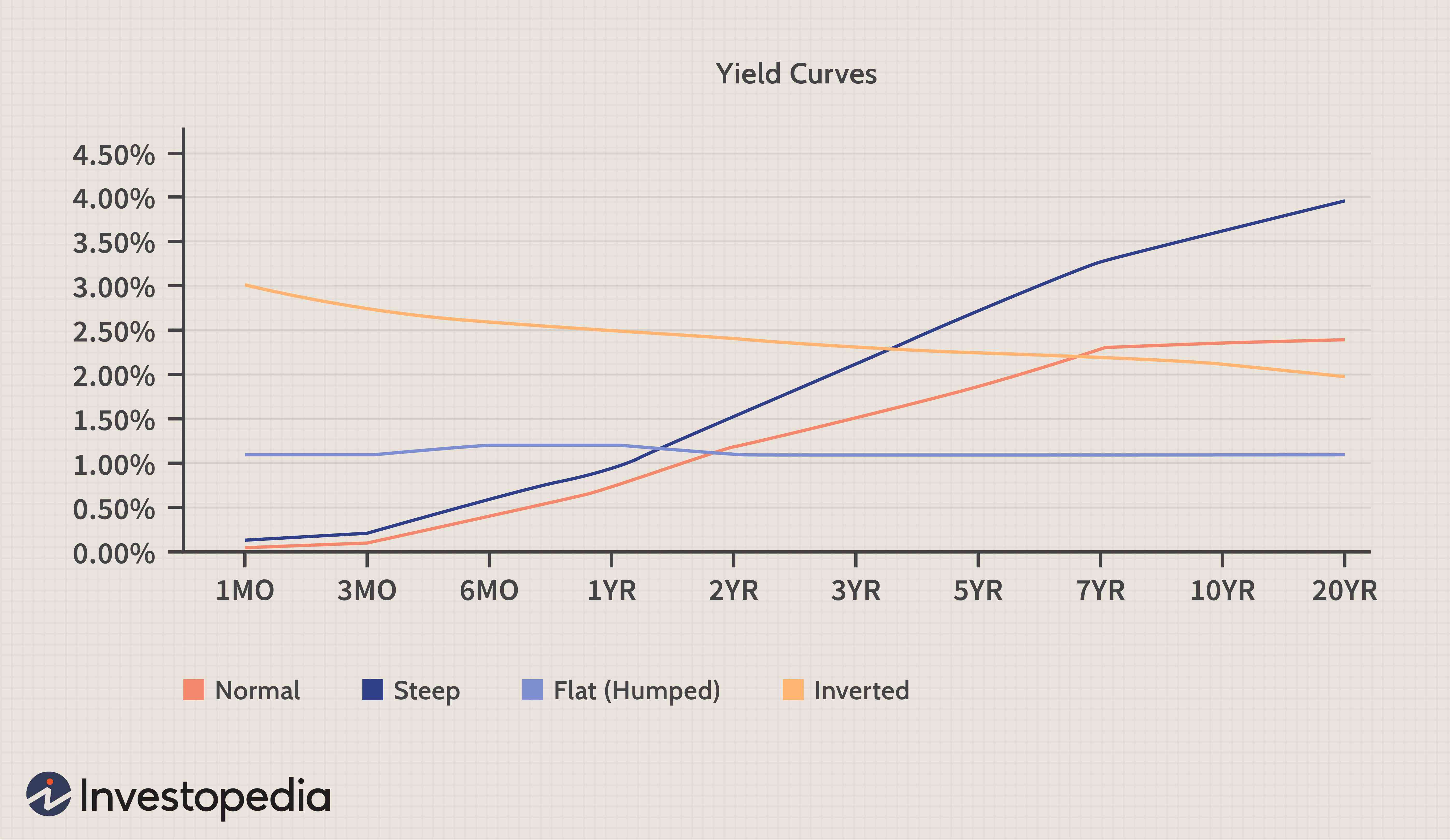
Table of Contents
The Mechanics of a Steepening Bond Yield Curve in Japan
A yield curve graphically represents the relationship between the interest rates (yields) and the time to maturity of debt securities with the same credit quality. It's measured by plotting the yields of government bonds with varying maturities. In Japan, this means analyzing the yields of Japanese Government Bonds (JGBs).
- Short-term JGBs: These bonds typically mature within one to five years. Their yields reflect current monetary policy and short-term market expectations.
- Long-term JGBs: These bonds have maturities of 10 years or more. Their yields reflect long-term economic expectations, inflation forecasts, and risk assessments.
The slope of the yield curve reflects market expectations of future interest rates. A steepening yield curve, as we're seeing in Japan, indicates that investors expect higher interest rates in the future. This contrasts with a flattening yield curve (where the difference between short-term and long-term yields shrinks) or an inverted yield curve (where short-term yields exceed long-term yields), which often precede economic slowdowns or recessions.
[Insert simple chart here illustrating a steepening yield curve, clearly labeling short-term and long-term yields and the widening gap.]
Factors Contributing to the Steepening Yield Curve in Japan
Several factors are driving the steepening bond yield curve in Japan.
The Bank of Japan's (BOJ) Policy Shift
The BOJ's recent adjustments to its yield curve control (YCC) policy are a primary driver.
- Previous YCC Policy: The BOJ aimed to keep long-term interest rates low to stimulate economic growth and combat deflation. This involved actively purchasing JGBs to suppress yields.
- Reasons for the Policy Shift: The BOJ's recent shift reflects growing concerns about persistent inflation, driven partly by rising global energy and commodity prices. Global monetary policy tightening, particularly by the Federal Reserve, also put pressure on the BOJ to adjust its stance.
- Market Reaction: The market reacted to the BOJ's adjustments with a surge in long-term JGB yields, widening the gap between short-term and long-term rates, leading to the steepening yield curve.
Inflationary Pressures
Rising inflation is another key contributor to the steepening curve.
- Current Inflation Rate: Japan is experiencing a higher-than-expected inflation rate, fueled by rising import costs and increased domestic demand.
- Inflation Expectations: Market participants anticipate that inflation will remain elevated for some time, pushing up expectations for future interest rate hikes and consequently, long-term bond yields.
- Global Inflation Impact: Global inflationary pressures are exacerbating the situation, making it more difficult for the BOJ to maintain its previous ultra-loose monetary policy.
Global Economic Uncertainty
Global economic headwinds are also contributing to the steepening yield curve in Japan.
- US Interest Rate Hikes: The Federal Reserve's aggressive interest rate hikes are strengthening the US dollar, impacting the Japanese yen and influencing Japanese bond yields.
- Geopolitical Instability: Geopolitical risks, including the war in Ukraine and tensions in East Asia, increase uncertainty and often lead investors to favor safer assets, potentially impacting JGB yields.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Persistent global supply chain disruptions contribute to inflationary pressures and increase economic uncertainty, affecting investor sentiment and bond yields.
Implications of the Steepening Bond Yield Curve for the Japanese Economy
The steepening yield curve carries significant implications for the Japanese economy.
Impact on Government Borrowing Costs
Rising long-term yields directly increase the cost of government borrowing.
- National Debt: Japan carries a substantial national debt, and higher borrowing costs will increase the burden of servicing this debt.
- Government Spending: Increased borrowing costs could constrain government spending on crucial social programs and infrastructure projects.
Effects on Corporate Investment
Higher borrowing costs translate to more expensive loans for businesses.
- Business Expansion: Companies may postpone or cancel expansion plans due to the increased cost of capital.
- Job Creation: Reduced corporate investment can negatively impact job creation and overall economic growth.
Consequences for the Japanese Yen
The steepening yield curve can also influence the exchange rate of the Japanese yen.
- Interest Rates and Currency Values: Higher interest rates generally attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency. However, the impact on the yen is complex and depends on various other factors, including global economic conditions.
- Exports and Imports: Changes in the yen's value affect the competitiveness of Japanese exports and the cost of imports.
Conclusion
The steepening bond yield curve in Japan presents a complex challenge with significant implications for the nation's economic future. The Bank of Japan's policy shift, coupled with inflationary pressures and global economic uncertainty, has created a volatile environment. Understanding the mechanics and implications of this steepening curve is crucial for navigating the potential headwinds facing the Japanese economy. Staying informed about the evolving situation and the Bank of Japan's responses is vital. Continue to monitor the developments surrounding the steepening bond yield curve in Japan and its impact on JGBs to make informed decisions about your investments and economic outlook. Analyzing the interplay between the BOJ's actions, inflation, and global economic factors is key to understanding the future trajectory of the Japanese economy and the Japanese bond yield curve.

Featured Posts
-
 Coquimbo Unido 0 0 Everton Vina Resumen Y Estadisticas
May 17, 2025
Coquimbo Unido 0 0 Everton Vina Resumen Y Estadisticas
May 17, 2025 -
 Reviewing The Week Identifying And Addressing Past Setbacks
May 17, 2025
Reviewing The Week Identifying And Addressing Past Setbacks
May 17, 2025 -
 Kak Dubay Stal Vtoroy Moskvoy Trudnosti I Vozmozhnosti Dlya Rossiyan
May 17, 2025
Kak Dubay Stal Vtoroy Moskvoy Trudnosti I Vozmozhnosti Dlya Rossiyan
May 17, 2025 -
 Jalen Brunsons Injury A Detailed Look At The Knicks Point Guard Situation
May 17, 2025
Jalen Brunsons Injury A Detailed Look At The Knicks Point Guard Situation
May 17, 2025 -
 Private Equity Buys Boston Celtics For 6 1 Billion Fan Concerns And Analysis
May 17, 2025
Private Equity Buys Boston Celtics For 6 1 Billion Fan Concerns And Analysis
May 17, 2025
