Long COVID Prevention: The Role Of COVID-19 Vaccines
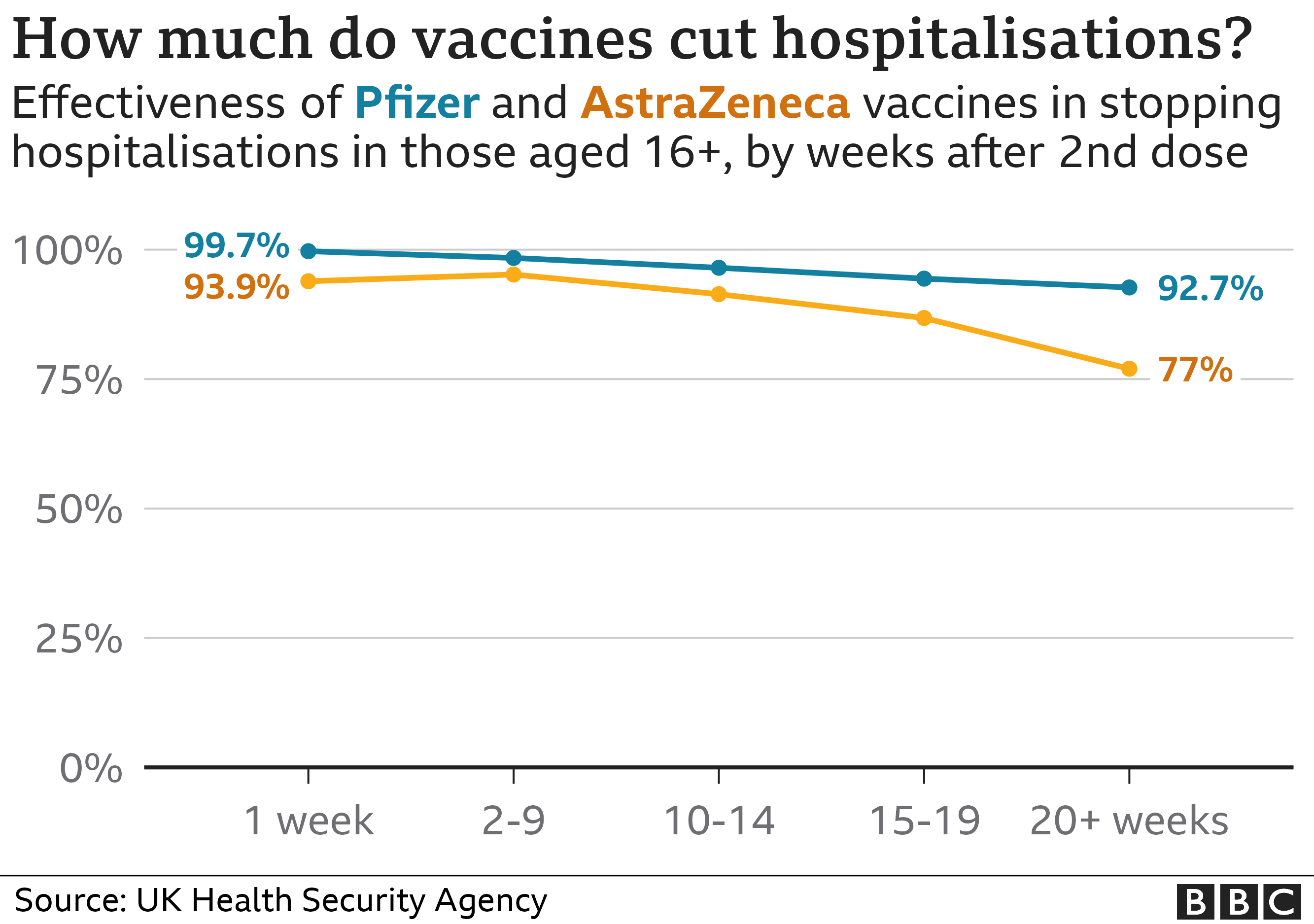
Table of Contents
COVID-19 Vaccines Reduce the Risk of Initial COVID-19 Infection
Vaccination significantly lowers your chances of contracting COVID-19 in the first place, thereby reducing your risk of developing Long COVID. By preventing the initial infection, you drastically minimize the potential for long-term complications.
- Data shows a significant reduction in infection rates among vaccinated individuals. Numerous studies have demonstrated that fully vaccinated individuals have a considerably lower risk of contracting COVID-19 compared to unvaccinated individuals. These studies consistently show a substantial decrease in infection rates, offering strong evidence for the vaccine's effectiveness in preventing initial infection.
- Specific vaccine efficacy studies confirm this protective effect. Clinical trials for various COVID-19 vaccines, including mRNA vaccines and viral vector vaccines, have shown high efficacy rates in preventing COVID-19 infection. These results underscore the importance of vaccination as a primary strategy for Long COVID prevention.
- The importance of different vaccine types and booster shots cannot be overstated. While initial vaccination series offer strong protection, booster shots are vital for maintaining high immunity levels, especially against emerging variants. The type of vaccine and the timing of booster shots play a key role in maximizing protection against both initial infection and the development of Long COVID.
Vaccines Mitigate the Severity of COVID-19 Illness
Even if a vaccinated individual contracts COVID-19, the vaccine significantly lessens the severity of the illness. A less severe initial infection is strongly correlated with a lower risk of developing Long COVID. This means fewer severe symptoms and a shorter recovery period.
- Studies demonstrate reduced hospitalization and death rates in vaccinated individuals. Data consistently shows that vaccinated individuals, even if infected, are far less likely to require hospitalization or experience severe complications leading to death. This reduced severity is directly linked to a lower risk of progressing to Long COVID.
- Less severe symptoms translate to a reduced likelihood of long-term complications. Milder symptoms such as a mild cough or fatigue, rather than severe pneumonia or organ damage, lessen the chances of developing long-term issues associated with Long COVID. The intensity of the initial infection plays a significant role in the risk of long-term consequences.
- The impact on various patient demographics is crucial. While vaccines are highly effective across age groups, individuals with pre-existing conditions may benefit from additional layers of protection. Understanding how vaccines affect different demographics allows for targeted public health interventions to maximize Long COVID prevention efforts.
Potential Mechanisms of Vaccine-Mediated Long COVID Protection
While the exact mechanisms by which vaccines prevent Long COVID are still under investigation, ongoing research points to several potential pathways:
- Immune response and its role in preventing persistent inflammation: Vaccines stimulate a robust immune response, potentially preventing the persistent inflammation believed to contribute to Long COVID. The body's ability to quickly and effectively clear the virus minimizes the duration of inflammation, thus reducing the risk of long-term damage.
- Ongoing research into the virus's impact on various organ systems: Scientists are actively studying how SARS-CoV-2 affects different organs and systems, and how vaccines might intervene in these processes. This research will further elucidate the protective mechanisms of vaccines against Long COVID.
- The potential role of vaccines in preventing immune dysregulation: Some researchers believe that Long COVID may be linked to immune dysregulation. Vaccines may help to prevent or mitigate this dysregulation, thus reducing the risk of long-term complications.
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy and Misinformation
Addressing vaccine hesitancy and misinformation is crucial for maximizing the population-level impact of COVID-19 vaccination in Long COVID prevention.
- Debunking myths about vaccine side effects: Common concerns about vaccine side effects need to be addressed with factual information, emphasizing that while side effects can occur, they are usually mild and temporary. The benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks.
- Emphasizing the safety and efficacy of approved vaccines: Rigorous testing and monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines ensure their safety and efficacy. Clear communication about these processes is vital to building public trust.
- Providing links to reputable sources of information: Reliable sources like the CDC and WHO provide accurate, up-to-date information on COVID-19 vaccines, addressing concerns and combating misinformation.
The Importance of Staying Up-to-Date with Vaccinations
Staying current with vaccination recommendations, including booster shots, is vital for maintaining optimal protection against COVID-19 and Long COVID.
- Data on waning immunity and the importance of boosters: Immunity from initial vaccination series can wane over time, making booster shots necessary to maintain high levels of protection against infection and severe illness, including Long COVID.
- Information on emerging variants and their impact on vaccine effectiveness: The emergence of new variants necessitates updated vaccines or booster shots to ensure continued protection against these variants. Staying updated with the latest recommendations is essential.
- Guidance on accessing vaccinations: Easy access to COVID-19 vaccines, including boosters, is crucial for ensuring high vaccination rates and maximizing population-level protection against Long COVID.
Conclusion
COVID-19 vaccines are a crucial tool in preventing Long COVID by reducing the risk of initial infection and mitigating illness severity. The evidence overwhelmingly supports vaccination as a highly effective preventative measure against this debilitating condition. Protect yourself from the debilitating effects of Long COVID. Get vaccinated today and stay up-to-date on your booster shots. Learn more about Long COVID prevention and vaccination strategies at [link to relevant resource].

Featured Posts
-
 Mena Lw Ansf Alqwmu Fy Dhkra Astqlalna
May 29, 2025
Mena Lw Ansf Alqwmu Fy Dhkra Astqlalna
May 29, 2025 -
 Hujan Di Bandung Pukul 1 Siang Ramalan Cuaca 22 April
May 29, 2025
Hujan Di Bandung Pukul 1 Siang Ramalan Cuaca 22 April
May 29, 2025 -
 Queensland Music Awards Antisemitism Controversy Erupts
May 29, 2025
Queensland Music Awards Antisemitism Controversy Erupts
May 29, 2025 -
 Rick Derringer Dead At 77 Remembering The Legendary Guitarist
May 29, 2025
Rick Derringer Dead At 77 Remembering The Legendary Guitarist
May 29, 2025 -
 Living Fence Construction Plants Planning And Installation
May 29, 2025
Living Fence Construction Plants Planning And Installation
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Nyt Mini Crossword Answers For Monday March 31 2025
May 31, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Answers For Monday March 31 2025
May 31, 2025 -
 Solve The Nyt Mini Crossword Hints For March 31 2025
May 31, 2025
Solve The Nyt Mini Crossword Hints For March 31 2025
May 31, 2025 -
 Nyt Mini Crossword Today March 31 2025 Complete Answers
May 31, 2025
Nyt Mini Crossword Today March 31 2025 Complete Answers
May 31, 2025 -
 Solve The Nyt Mini Crossword Hints And Answers For April 19th Saturday
May 31, 2025
Solve The Nyt Mini Crossword Hints And Answers For April 19th Saturday
May 31, 2025 -
 Todays Nyt Mini Crossword May 7 Answers And Explanations
May 31, 2025
Todays Nyt Mini Crossword May 7 Answers And Explanations
May 31, 2025
