Measles Cases In US Reach 1,046: Indiana Outbreak Ends
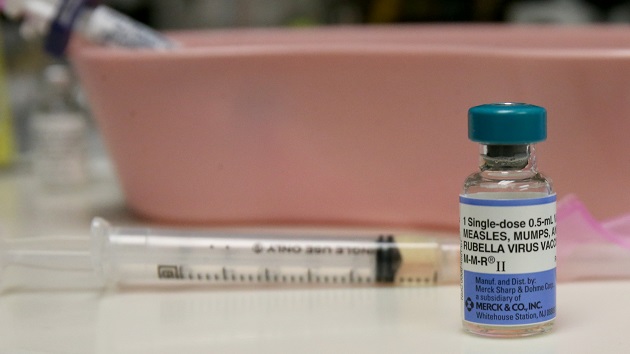
Table of Contents
The National Surge in Measles Cases
Statistics and Trends
The increase in measles cases across the US represents a serious public health challenge. Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) shows a dramatic rise compared to recent years, with [Insert specific numbers and percentage increase compared to previous years – cite CDC data]. This isn't uniformly distributed; some states have been more significantly impacted than others. For example, [mention specific states with high case numbers and cite sources]. This surge disproportionately affects vulnerable populations, including infants too young to be fully vaccinated and individuals with compromised immune systems.
- Significant Increase: [Insert specific data on the percentage increase and total number of cases].
- Regional Variations: Higher concentrations reported in [List states/regions].
- Vulnerable Populations: Infants under 6 months and immunocompromised individuals are at highest risk.
Causes of the Increase
Several factors contribute to this alarming rise in measles cases in the US. A critical factor is the decline in vaccination rates. [Cite data on declining vaccination rates]. This decrease is partly fueled by misinformation and vaccine hesitancy spread through social media and unreliable sources. Furthermore, international travel plays a significant role, with imported cases seeding outbreaks within the US. Measles is exceptionally contagious, easily spread through the air through coughing and sneezing, making containment challenging.
- Decreased Vaccination Rates: A direct correlation exists between lower vaccination rates and increased measles outbreaks.
- Misinformation and Vaccine Hesitancy: The spread of false information about vaccine safety significantly impacts public health.
- International Travel: Imported cases from countries with higher measles prevalence fuel outbreaks within the US.
- High Contagiousness: Measles spreads easily, requiring high vaccination rates for herd immunity.
The Indiana Outbreak: A Case Study
Timeline and Key Events
The Indiana measles outbreak, which began in [Start Date], was one of the largest in recent US history. It peaked in [Month, Year] with [Number] cases, before gradually declining thanks to intensive public health interventions. The outbreak was officially declared over on [End Date], after [Number] confirmed cases.
- Start Date: [Insert date]
- Peak: [Insert date and number of cases]
- End Date: [Insert date]
- Total Cases: 1046
Public Health Response
Indiana health officials implemented a robust response to contain the outbreak, including widespread vaccination campaigns targeting both susceptible individuals and their contacts. Extensive contact tracing helped identify and isolate infected individuals to prevent further spread. Quarantine measures were implemented in affected areas to limit community transmission.
- Vaccination Campaigns: Mass vaccination efforts in affected areas and surrounding communities.
- Contact Tracing: Identifying and monitoring individuals who had contact with infected persons.
- Quarantine Measures: Restricting movement in high-risk areas to limit transmission.
Lessons Learned from Indiana
The Indiana outbreak provided valuable lessons in managing measles outbreaks. The swift and comprehensive public health response proved effective in controlling the spread and ultimately ending the outbreak. However, it also highlighted the challenges posed by vaccine hesitancy and the need for improved communication strategies to address public concerns and misconceptions.
- Effectiveness of Rapid Response: Early intervention and comprehensive strategies proved crucial.
- Challenges of Vaccine Hesitancy: Addressing misinformation and building trust remains a critical challenge.
- Improved Communication Strategies: Clear and consistent messaging is essential to combat misinformation.
Prevention and Vaccination
Importance of MMR Vaccine
The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine is highly effective in preventing measles infection. A two-dose series provides over 97% protection. Vaccination remains the most crucial tool in preventing measles outbreaks and protecting individuals and communities.
- Effectiveness: The MMR vaccine is highly effective at preventing measles infection.
- Two-Dose Series: A two-dose series provides optimal protection.
- Herd Immunity: High vaccination rates are crucial for achieving herd immunity.
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy
Combating vaccine hesitancy requires a multi-pronged approach. Educating the public about the safety and efficacy of vaccines is crucial. This involves providing accurate information through trusted sources, such as healthcare professionals and reputable public health organizations, and countering misinformation with evidence-based facts.
- Education and Awareness Campaigns: Disseminating accurate information through various channels.
- Addressing Misconceptions: Tackling common myths and concerns surrounding vaccines.
- Building Trust: Promoting trust in healthcare professionals and public health authorities.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in promoting vaccination. They should actively engage in conversations with patients, addressing their concerns, and providing evidence-based information about the MMR vaccine's safety and efficacy. They should also advocate for vaccination within their communities.
- Patient Education: Providing accurate and accessible information to patients.
- Addressing Concerns: Addressing patient concerns and anxieties about vaccination.
- Community Advocacy: Promoting vaccination within their communities.
Conclusion
The significant increase in measles cases across the US, culminating in the now-concluded Indiana outbreak, underscores the persistent threat of this highly contagious disease. The critical importance of vaccination in preventing future outbreaks cannot be overstated. Increased vaccination rates and improved public health awareness are essential to combat the threat of measles. Protect yourself and your community from measles; learn more about measles prevention and get vaccinated against measles today. Stay updated on the latest measles cases in the US through reputable sources like the CDC. Consult your healthcare provider about the MMR vaccine and advocate for vaccination within your community.

Featured Posts
-
 Role Model Extends No Place Like Tour With Paris And London Dates
May 30, 2025
Role Model Extends No Place Like Tour With Paris And London Dates
May 30, 2025 -
 Bts Tiempo De Regreso Tras El Servicio Militar
May 30, 2025
Bts Tiempo De Regreso Tras El Servicio Militar
May 30, 2025 -
 311 Heat Related Deaths In England A Wake Up Call
May 30, 2025
311 Heat Related Deaths In England A Wake Up Call
May 30, 2025 -
 Deborra Lee Furness Speaks Out Navigating The End Of Her Marriage To Hugh Jackman
May 30, 2025
Deborra Lee Furness Speaks Out Navigating The End Of Her Marriage To Hugh Jackman
May 30, 2025 -
 Jet Ski Kawasaki Premium Tiga Model Terbaru Hadir Di Indonesia
May 30, 2025
Jet Ski Kawasaki Premium Tiga Model Terbaru Hadir Di Indonesia
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Alcaraz Cruises To Straight Sets Win At Barcelona Open
May 31, 2025
Alcaraz Cruises To Straight Sets Win At Barcelona Open
May 31, 2025 -
 Sage Hill Volleyball Cif Ss Finals Bound Following Victory Over Crean Lutheran
May 31, 2025
Sage Hill Volleyball Cif Ss Finals Bound Following Victory Over Crean Lutheran
May 31, 2025 -
 Beatles Biopic Cast Announced Whos Playing Who
May 31, 2025
Beatles Biopic Cast Announced Whos Playing Who
May 31, 2025 -
 The Beatles Cast Revealed A Look At The Actors
May 31, 2025
The Beatles Cast Revealed A Look At The Actors
May 31, 2025 -
 Star Trek Strange New Worlds Season 3 Teaser A Deeper Dive Into The New Season
May 31, 2025
Star Trek Strange New Worlds Season 3 Teaser A Deeper Dive Into The New Season
May 31, 2025
