Mental Health Care Reform: Challenges And Solutions

Table of Contents
The Current State of Mental Health Care: Identifying Key Challenges
The current mental healthcare system is plagued by numerous obstacles that prevent many from receiving the help they need. These challenges necessitate immediate and comprehensive reform.
Lack of Access to Care
Access to mental healthcare remains a significant hurdle for millions. This disparity is particularly pronounced in underserved communities.
- Limited availability of mental health professionals: A shortage of psychiatrists, psychologists, therapists, and counselors, especially in rural and underserved areas, means long wait times and limited access to specialized care. This creates significant mental health disparities.
- Long wait times for appointments and therapy sessions: Even when individuals find a provider, wait times can be excessively long, delaying crucial treatment and exacerbating existing conditions. This delay negatively impacts the affordability of mental healthcare as individuals may require more extensive treatment later on.
- High cost of treatment: The expense of mental healthcare, including therapy, medication, and hospitalization, often leads to underinsurance and treatment gaps. Many individuals are forced to forgo necessary care due to financial constraints, highlighting the urgent need for increased access to mental healthcare.
- Stigma associated with mental illness: The pervasive stigma surrounding mental illness prevents many from seeking help, fearing judgment, discrimination, or social isolation. This stigma further exacerbates the problem and hinders open conversations about mental health.
Inadequate Funding and Resource Allocation
Insufficient funding significantly hampers the ability of the mental healthcare system to effectively address the needs of the population.
- Insufficient government funding: Compared to physical health, mental health receives significantly less government funding, resulting in inadequate resources and understaffed facilities. This lack of mental health funding directly impacts the quality and availability of care.
- Understaffed mental health facilities and lack of resources: Many mental health facilities struggle with understaffing, limited resources, and outdated infrastructure, impacting the quality of care and patient outcomes. This lack of resources hinders effective treatment and prevention efforts.
- Limited investment in research and development: Insufficient investment in research and development of new treatments, technologies, and preventative strategies hinders progress in improving mental health outcomes. Increased mental health investment is crucial for advancing the field.
Systemic Barriers and Inefficiencies
The fragmented and inefficient nature of the current system further complicates access to care.
- Fragmented care delivery systems: A lack of coordination between different healthcare providers and services leads to fragmented care, making it difficult for individuals to navigate the system and receive comprehensive treatment. This contributes to healthcare system reform challenges.
- Lack of integration between physical and mental healthcare: The separation of physical and mental healthcare often results in missed opportunities for early intervention and integrated care, leading to poorer overall health outcomes. Integrated mental healthcare is essential for holistic well-being.
- Complex and confusing insurance processes: Navigating insurance processes for mental healthcare can be cumbersome and confusing, deterring individuals from seeking necessary care. Streamlining these processes is critical for improving mental health policy.
Proposed Solutions for Effective Mental Health Care Reform
Addressing the challenges requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on increased access, improved funding, and systemic improvements.
Increasing Access to Care
Expanding access to mental healthcare is paramount.
- Expanding the mental health workforce: Investing in training programs and recruitment initiatives is essential to increase the number of mental health professionals, particularly in underserved areas.
- Utilizing telehealth technology: Telehealth offers the potential to overcome geographical barriers and improve access to care in remote areas. Telehealth mental health services are becoming increasingly vital.
- Implementing policies to increase affordability: Expanding insurance coverage, implementing sliding-scale fees, and providing financial assistance programs are crucial to ensure affordability. This is directly related to the goal of affordable mental healthcare.
- Raising public awareness: Reducing stigma and encouraging help-seeking behavior through public awareness campaigns is essential to improve access to care.
Improving Funding and Resource Allocation
Increased and prioritized funding is essential.
- Increasing government funding for mental health services: Significant increases in government funding are needed to address the resource gaps and improve the quality of care. This is critical for mental health funding reform.
- Prioritizing mental health in national healthcare budgets: Mental health should be a priority alongside physical health. This prioritization is crucial for effective mental health budget allocation.
- Investing in research to develop innovative treatment approaches: Increased investment in research will lead to the development of more effective treatments and preventative strategies.
- Improving data collection and analysis: Better data collection and analysis are needed to inform policy decisions and track progress towards improving mental healthcare access.
Streamlining the System for Efficiency
Improving the efficiency and integration of the system is vital.
- Implementing integrated care models: Integrating physical and mental healthcare services can improve coordination, reduce duplication of efforts, and lead to better outcomes. Integrated care models are crucial for holistic treatment.
- Strengthening collaboration between providers: Enhanced collaboration between physical and mental healthcare providers is essential for seamless care transitions.
- Simplifying insurance processes: Simplifying insurance processes will make access to care easier for individuals.
- Developing user-friendly online resources: Providing easily accessible online resources and support systems can improve navigation of the system.
Conclusion
Effective mental health care reform requires a multifaceted approach addressing access, funding, and systemic issues. By implementing the solutions outlined above, we can create a more equitable and supportive system that ensures everyone has access to the mental healthcare they need. Let's work together to champion mental health care reform and build a healthier future for all. We urge policymakers and stakeholders to prioritize mental health care reform and invest in solutions that improve access, affordability, and the overall quality of care.

Featured Posts
-
 1 Mayis Kocaeli Kutlamada Meydana Gelen Arbede Detaylari
May 03, 2025
1 Mayis Kocaeli Kutlamada Meydana Gelen Arbede Detaylari
May 03, 2025 -
 Winter Weather Brings 800 Emergency Calls To Tulsa Fire Department
May 03, 2025
Winter Weather Brings 800 Emergency Calls To Tulsa Fire Department
May 03, 2025 -
 Mas Seguridad Y Eficiencia Sistema Penitenciario Incorpora 7 Vehiculos
May 03, 2025
Mas Seguridad Y Eficiencia Sistema Penitenciario Incorpora 7 Vehiculos
May 03, 2025 -
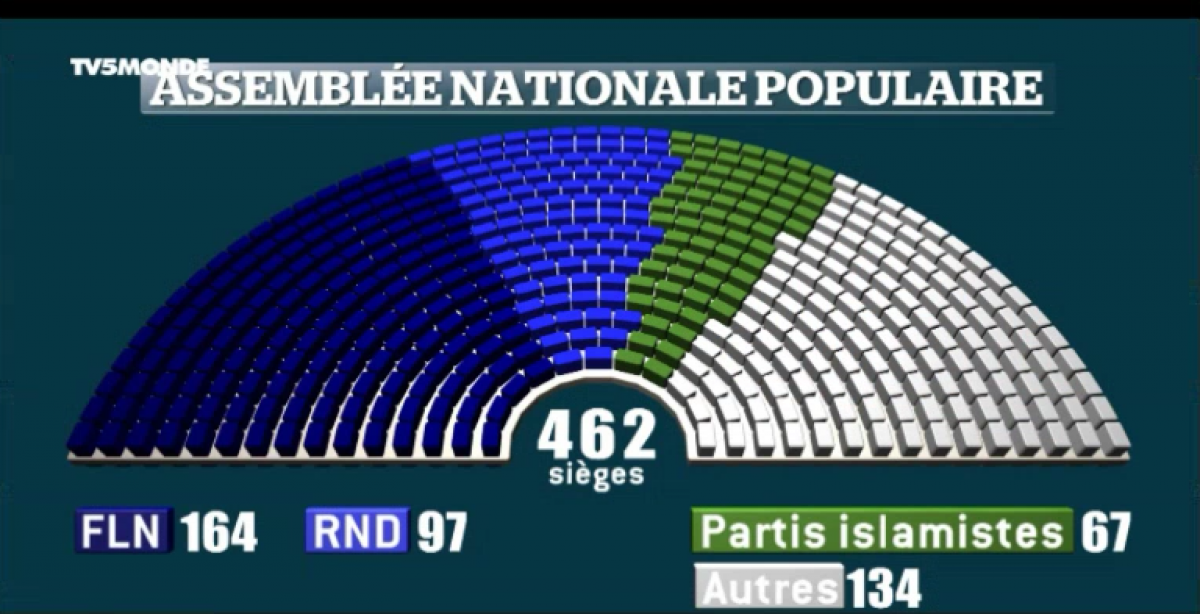 Reforme De La Loi Sur Les Partis Politiques En Algerie Reactions Du Pt Ffs Rcd Et Jil Jadid
May 03, 2025
Reforme De La Loi Sur Les Partis Politiques En Algerie Reactions Du Pt Ffs Rcd Et Jil Jadid
May 03, 2025 -
 Winter Storm Warning Four Or More Inches Of Snow Expected Tuesday Prepare For Bitter Cold
May 03, 2025
Winter Storm Warning Four Or More Inches Of Snow Expected Tuesday Prepare For Bitter Cold
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Nigel Farage Prefers Snp Victory In Next Scottish Election Reform Partys Stance Explained
May 03, 2025
Nigel Farage Prefers Snp Victory In Next Scottish Election Reform Partys Stance Explained
May 03, 2025 -
 Nigel Farage And The Savile Controversy Analyzing The Reform Partys New Slogan
May 03, 2025
Nigel Farage And The Savile Controversy Analyzing The Reform Partys New Slogan
May 03, 2025 -
 Reform Party Slogan Backlash Public Reaction To Farages Savile Remark
May 03, 2025
Reform Party Slogan Backlash Public Reaction To Farages Savile Remark
May 03, 2025 -
 Farages Controversial Savile Reference Reform Party Under Fire
May 03, 2025
Farages Controversial Savile Reference Reform Party Under Fire
May 03, 2025 -
 Nat West Reaches Settlement With Nigel Farage
May 03, 2025
Nat West Reaches Settlement With Nigel Farage
May 03, 2025
