New Algorithmic Standards And Migration Policies Accelerate Post-Quantum Cryptography's Growth To A Billion-Dollar Market
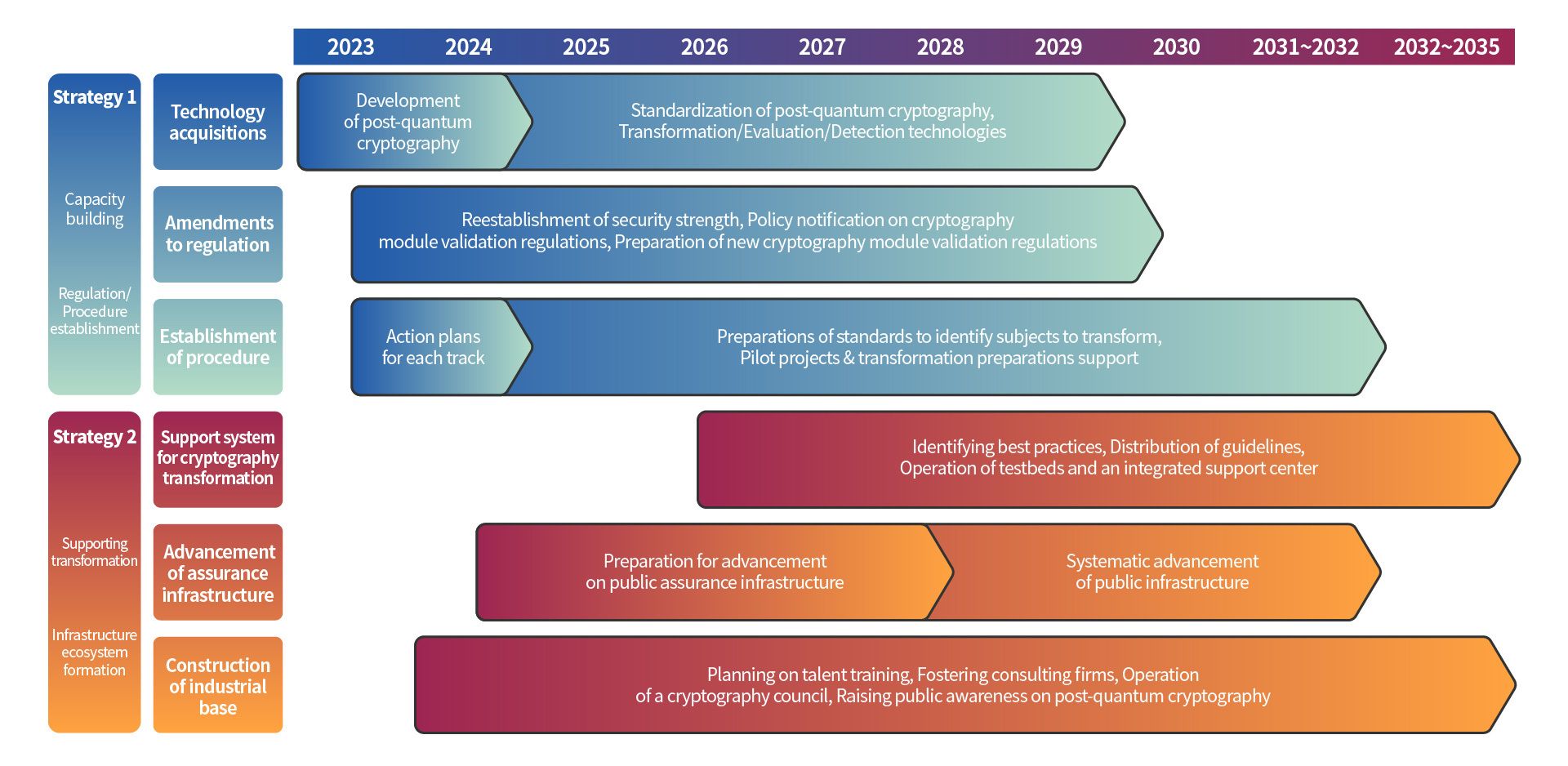
Table of Contents
The Rise of Standardized Post-Quantum Cryptographic Algorithms
Standardization is paramount for the widespread adoption and interoperability of any technology, and PQC is no exception. Without standardized algorithms, different systems would use incompatible methods, creating security vulnerabilities and hindering efficient data exchange. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has played a pivotal role in this process, leading a multi-year effort to evaluate and select promising PQC algorithms. This rigorous process ensures that the chosen algorithms are robust, efficient, and suitable for a variety of applications.
NIST has selected several algorithms for standardization, including:
- CRYSTALS-Kyber: A key encapsulation mechanism (KEM) known for its speed and efficiency, ideal for encrypting communication channels.
- CRYSTALS-Dilithium: A digital signature algorithm offering strong security and reasonable performance characteristics.
- FALCON: Another digital signature algorithm, providing a more compact signature size than Dilithium, suitable for resource-constrained environments.
- SPHINCS+: A digital signature algorithm offering the highest level of security guarantees, though with a larger signature size and lower performance compared to the others.
These standardized algorithms offer significant advantages:
- Increased security against quantum attacks: They are designed to resist attacks from both classical and quantum computers.
- Improved performance and efficiency: Compared to earlier PQC algorithms, these offer better performance and reduced computational overhead.
- Enhanced interoperability across different systems: Standardization ensures that different systems can communicate securely using the same cryptographic methods.
Government and Industry Migration Policies Fueling PQC Adoption
Governments worldwide recognize the urgency of transitioning to PQC and are actively implementing migration policies. Mandating the adoption of PQC is crucial for safeguarding national security and critical infrastructure. Countries like the United States and the United Kingdom have already initiated programs to evaluate and adopt PQC, and many others are following suit.
The benefits of proactive migration strategies are considerable:
- Minimizing future disruption: A gradual transition allows organizations to adapt to new technologies without significant service interruptions.
- Safeguarding sensitive data: Implementing PQC early safeguards against future quantum computer attacks and potential data breaches.
Examples of driving forces include:
- Government initiatives driving PQC implementation in critical infrastructure: This includes sectors like finance, energy, and healthcare.
- Industry partnerships fostering collaboration on PQC migration strategies: Shared knowledge and resources accelerate the adoption process.
- Increased investment in research and development of PQC technologies: Funding research helps to improve the performance and security of PQC algorithms.
Market Drivers and Investment Opportunities in Post-Quantum Cryptography
The projected billion-dollar market for PQC is fueled by several key factors:
- Increased cybersecurity threats and the looming quantum computing threat: The need for strong, quantum-resistant cryptography is becoming increasingly urgent.
- Growing awareness of PQC among businesses and organizations: More companies understand the risks associated with current encryption and are actively seeking PQC solutions.
- Significant investment from venture capitalists and other investors: The potential returns have attracted considerable investment in the PQC sector.
The demand for PQC solutions spans multiple sectors:
- Finance: Protecting financial transactions and sensitive customer data.
- Healthcare: Securing medical records and patient information.
- Government: Protecting national security and critical infrastructure.
Investment opportunities exist in various areas:
- PQC technology development: Creating new, more efficient algorithms.
- PQC implementation: Helping organizations migrate to PQC-based systems.
- PQC consulting services: Providing expert advice on PQC adoption and management.
Challenges and Considerations for Post-Quantum Cryptography Migration
Migrating to PQC is not without its challenges:
- Complexity of integrating PQC into existing systems: Existing systems need to be updated to support new algorithms.
- Need for skilled professionals to implement and manage PQC solutions: Specialized expertise is required for successful implementation.
- Cost of migration and ongoing maintenance: Upgrading systems and training personnel comes at a cost.
Careful planning is essential:
- Phased migration strategies: A gradual approach minimizes disruption and allows for thorough testing.
- Thorough risk assessment: Identifying vulnerabilities and prioritizing areas for migration.
- Collaboration and knowledge sharing: Working with experts and industry partners.
Continuous improvement is needed:
- Ongoing research and development: This ensures the continued improvement of PQC algorithms and their efficiency.
- Adaptability to evolving threats: PQC must evolve to address emerging security challenges.
Securing the Future with Post-Quantum Cryptography
The rapid growth of the post-quantum cryptography market is driven by the convergence of standardized algorithms, proactive government policies, and the growing awareness of the quantum threat. The importance of standardized algorithms like CRYSTALS-Kyber and CRYSTALS-Dilithium, alongside proactive migration strategies, cannot be overstated in securing data against future quantum computing threats. The significant investment opportunities and the need for continued innovation in the PQC space underscore its vital role in the future of cybersecurity.
Begin the transition to post-quantum cryptography now and protect your organization's valuable data. Learn more about Post-Quantum Cryptography and explore how to integrate PQC solutions into your systems to safeguard against the quantum threat. Don't wait until it's too late; secure your future with post-quantum cryptography today.

Featured Posts
-
 Rozpodil Romskoyi Populyatsiyi V Ukrayini Analiz Ta Faktori
May 13, 2025
Rozpodil Romskoyi Populyatsiyi V Ukrayini Analiz Ta Faktori
May 13, 2025 -
 Philippine Capital Schools Closed Due To Intense Heat Wave
May 13, 2025
Philippine Capital Schools Closed Due To Intense Heat Wave
May 13, 2025 -
 Nba Draft Lottery 2024 The Chicago Bulls Pursuit Of Cooper Flagg
May 13, 2025
Nba Draft Lottery 2024 The Chicago Bulls Pursuit Of Cooper Flagg
May 13, 2025 -
 Niedersachsen And Bremen Entwarnung Nach Bombendrohung An Braunschweiger Grundschule
May 13, 2025
Niedersachsen And Bremen Entwarnung Nach Bombendrohung An Braunschweiger Grundschule
May 13, 2025 -
 Catch Up On All The Key Efl Highlights Weekly Roundups And More
May 13, 2025
Catch Up On All The Key Efl Highlights Weekly Roundups And More
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Di Capriojeva Transformacija Reakcije Obozavatelja Nakon Novih Fotografija Slobodna Dalmacija
May 13, 2025
Di Capriojeva Transformacija Reakcije Obozavatelja Nakon Novih Fotografija Slobodna Dalmacija
May 13, 2025 -
 Slobodna Dalmacija Promijenjeni Di Caprio Fotografije Koje Ce Vas Iznenaditi
May 13, 2025
Slobodna Dalmacija Promijenjeni Di Caprio Fotografije Koje Ce Vas Iznenaditi
May 13, 2025 -
 Leonardo Di Caprio Nevjerojatna Transformacija Slobodna Dalmacija
May 13, 2025
Leonardo Di Caprio Nevjerojatna Transformacija Slobodna Dalmacija
May 13, 2025 -
 Romeo Juliet How Leonardo Di Caprio Averted A Catastrophe
May 13, 2025
Romeo Juliet How Leonardo Di Caprio Averted A Catastrophe
May 13, 2025 -
 Leonardo Di Caprios Untold Story Preventing A Romeo Juliet Rollerblading Accident
May 13, 2025
Leonardo Di Caprios Untold Story Preventing A Romeo Juliet Rollerblading Accident
May 13, 2025
