New COVID-19 Variants BA.1 And LF.7 In India: INSACOG Data & Risk Assessment
Table of Contents
INSACOG's Role in Variant Surveillance
INSACOG plays a vital role in India's fight against COVID-19 by providing crucial genomic surveillance of SARS-CoV-2. Its network of laboratories across the country is instrumental in detecting and characterizing new variants, including BA.1 and LF.7.
INSACOG's Surveillance Network
INSACOG's nationwide network employs a robust methodology for variant surveillance:
- Sample Collection: Samples are collected from individuals testing positive for COVID-19, particularly those with severe illness or unusual clinical presentations.
- Sequencing: Advanced genomic sequencing technologies are used to determine the genetic makeup of the virus.
- Data Analysis: Sophisticated bioinformatic tools analyze the sequence data to identify new variants and track their mutations.
- Reporting: INSACOG regularly shares its findings with public health authorities and the scientific community, enabling timely responses to emerging threats.
This timely detection is critical for implementing effective public health interventions and preventing widespread outbreaks.
Data Collection and Analysis of BA.1 and LF.7
While specific real-time data on BA.1 and LF.7 prevalence in India fluctuates and requires referencing up-to-date INSACOG reports, INSACOG's data collection efforts focus on:
- Prevalence: Determining the percentage of COVID-19 cases attributed to BA.1 and LF.7.
- Geographic Distribution: Mapping the spread of these variants across different regions of India.
- Characteristics: Identifying unique mutations and analyzing their potential impact on transmissibility, severity, and vaccine effectiveness.
Analyzing this data allows for a better understanding of the variants' behavior and potential threat level within the Indian context. (Note: Specific numbers on prevalence and geographic distribution are subject to change and should be sourced directly from official INSACOG reports at the time of reading.)
Characteristics and Potential Risks of BA.1 and LF.7
Understanding the characteristics of BA.1 and LF.7 is essential for assessing their potential risk.
Transmissibility and Severity
Compared to earlier variants, BA.1 and LF.7 may exhibit:
- Increased Transmissibility: Potentially higher R0 values (basic reproduction number) indicating greater ease of spread.
- Varying Severity: The severity of illness caused by these variants might differ, although more research is needed to draw definitive conclusions. Data may show varying hospitalization and mortality rates compared to previous variants.
- Immune Evasion: Some evidence may suggest potential for increased immune evasion capabilities, reducing the effectiveness of prior infection-acquired immunity.
Further research is crucial to fully characterize the transmissibility and severity of these variants in the Indian population.
Impact on Vaccine Efficacy
The effectiveness of existing COVID-19 vaccines against BA.1 and LF.7 is a key concern.
- Reduced Efficacy: Studies may show a reduction in the effectiveness of vaccines against severe illness caused by these variants, although existing vaccines generally still offer protection against severe outcomes.
- Booster Shots: Booster shots may be necessary to maintain high levels of protection against these variants.
- Updated Vaccines: Development and deployment of updated vaccines tailored to these variants are crucial for maintaining long-term protection.
Monitoring vaccine effectiveness against these specific variants is ongoing and necessitates continuous evaluation.
Public Health Response and Mitigation Strategies
Effective public health measures are vital in managing the spread of BA.1 and LF.7.
Testing and Tracing
Robust testing and contact tracing strategies are critical:
- Increased Testing Capacity: Ensuring sufficient testing capacity to detect cases early.
- Effective Contact Tracing: Promptly identifying and isolating individuals who have been in contact with infected persons.
Vaccination and Booster Doses
Vaccination remains a cornerstone of the public health response:
- High Vaccination Coverage: Achieving high vaccination coverage among the eligible population is crucial.
- Booster Doses: Encouraging individuals to receive booster doses to enhance protection against new variants.
Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions (NPIs)
Implementing and adhering to NPIs remains crucial, especially in high-risk settings:
- Mask Wearing: Wearing masks in crowded indoor spaces.
- Social Distancing: Maintaining physical distance in public areas.
- Hand Hygiene: Frequent handwashing with soap and water or using hand sanitizer.
- Ventilation: Improving ventilation in indoor spaces.
These simple yet effective measures can significantly reduce transmission rates.
Conclusion
INSACOG's surveillance efforts provide invaluable data on the emergence and spread of new COVID-19 variants like BA.1 and LF.7 in India. While these variants may present potential challenges due to increased transmissibility or immune evasion, existing vaccines still offer protection against severe outcomes. Ongoing monitoring, vaccination campaigns, booster doses, and adherence to NPIs remain critical in mitigating their impact. Staying informed through official sources like INSACOG and the Ministry of Health is essential. Get vaccinated, get boosted, and practice responsible behavior to protect yourself and your community from new COVID-19 variants like BA.1 and LF.7 in India. Let's continue to work together to combat this virus.

Featured Posts
-
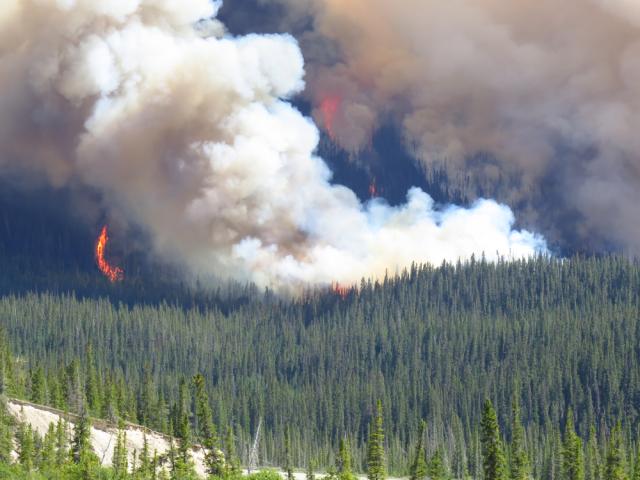 Impact Of Alberta Wildfires On Oil Production And Energy Security
May 31, 2025
Impact Of Alberta Wildfires On Oil Production And Energy Security
May 31, 2025 -
 Navigating Office Lunches 6 Etiquette Rules To Follow
May 31, 2025
Navigating Office Lunches 6 Etiquette Rules To Follow
May 31, 2025 -
 Wildfires In Canada Unprecedented Evacuations And Transborder Smoke Impact
May 31, 2025
Wildfires In Canada Unprecedented Evacuations And Transborder Smoke Impact
May 31, 2025 -
 Nypd Detective Allegedly Assisted In Crypto Kidnapping
May 31, 2025
Nypd Detective Allegedly Assisted In Crypto Kidnapping
May 31, 2025 -
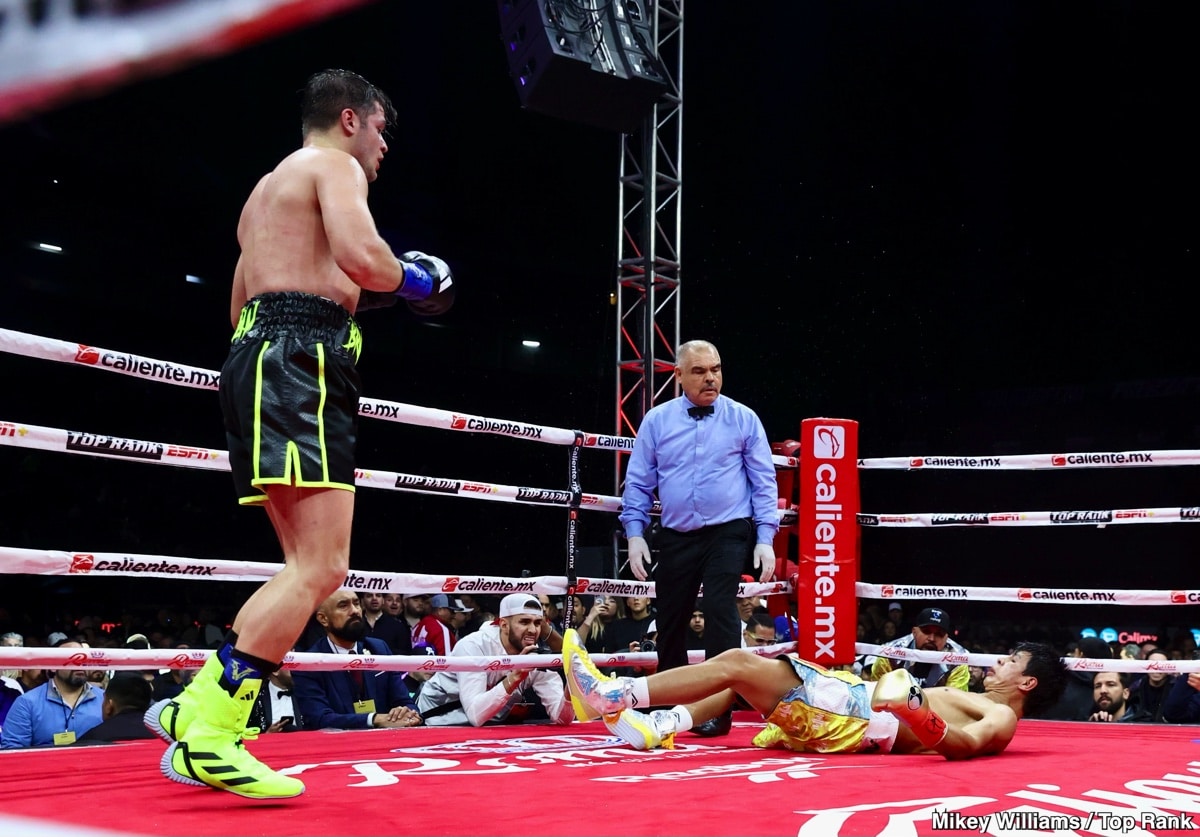 Jaime Munguia Wins Points Decision Over Bruno Surace In Riyadh Rematch
May 31, 2025
Jaime Munguia Wins Points Decision Over Bruno Surace In Riyadh Rematch
May 31, 2025
