New Guidelines For Diagnosing, Preventing, And Treating Long COVID In Canada

Table of Contents
Long COVID, also known as Post-COVID-19 condition, presents significant challenges to Canadians. Affecting an estimated 10-30% of individuals following a COVID-19 infection, Long COVID's persistent symptoms dramatically impact the lives of those affected and place a strain on Canada's healthcare system. These new guidelines provide crucial information for both patients and healthcare providers, offering a clearer path towards diagnosis, prevention, and effective treatment of this complex condition. This article will explore the key areas covered in these vital new guidelines: diagnosis, prevention strategies, and available treatment options for Long COVID in Canada.
Diagnosing Long COVID in Canada: A Multifaceted Approach
Diagnosing Long COVID is challenging due to its wide range of symptoms and the lack of a single definitive test. The new guidelines emphasize a multifaceted approach, combining symptom assessment with the exclusion of other potential conditions.
Recognizing the Symptoms:
Long COVID symptoms vary significantly from person to person and often overlap. Recognizing the wide spectrum of potential symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- "Brain fog" (cognitive dysfunction)
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Chest pain
- Heart palpitations
- Loss of taste or smell (anosmia/ageusia)
- Gastrointestinal issues (e.g., diarrhea, nausea)
- Sleep disturbances (insomnia)
- Muscle pain (myalgia)
- Joint pain (arthralgia)
- Depression and anxiety
Diagnostic Challenges and Current Testing:
The absence of a specific diagnostic test for Long COVID necessitates a thorough evaluation. Diagnosis relies heavily on a comprehensive assessment of symptoms, duration, and severity, along with excluding other potential medical conditions. The guidelines suggest:
- Comprehensive symptom questionnaires to document the patient's experience.
- Blood tests to rule out other illnesses mimicking Long COVID symptoms.
- Imaging techniques (e.g., chest X-rays, CT scans) if clinically indicated.
- Referral to specialists such as pulmonologists, cardiologists, and neurologists, as needed.
The Role of Healthcare Providers:
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in diagnosing Long COVID. This involves:
- Taking a detailed patient history, focusing on the onset and evolution of symptoms.
- Performing a thorough physical examination to assess any physical signs.
- Implementing ongoing monitoring of the patient's condition to track symptom progression and treatment response.
Preventing Long COVID: Strategies for Mitigation and Post-Infection Care
While there's no guaranteed way to prevent Long COVID, several strategies can significantly reduce the risk. The new guidelines emphasize a multi-pronged approach:
Vaccination and Boosters:
Vaccination against COVID-19 remains the cornerstone of prevention. The guidelines strongly recommend completing the primary vaccination series and receiving booster shots as recommended by public health authorities.
- High vaccination rates are crucial to reducing overall COVID-19 cases, thus minimizing the incidence of Long COVID.
- Booster shots enhance immune protection against severe disease and potential long-term complications.
- Access to vaccines should be ensured for all eligible Canadians.
Early Treatment of COVID-19:
Early antiviral treatment of COVID-19 may lessen the severity of the initial infection and potentially reduce the risk of developing Long COVID.
- Antiviral medications, such as Paxlovid, may be beneficial when administered early in the course of infection.
- Access to these treatments is crucial and should be prioritized for high-risk individuals.
- Eligibility criteria for antiviral treatment vary; consult with a healthcare professional.
Lifestyle Factors and Risk Reduction:
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can potentially mitigate the risk of developing Long COVID or lessen its severity.
- A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall health and immune function.
- Regular physical activity, tailored to individual capabilities, can improve physical and mental well-being.
- Effective stress management techniques, such as mindfulness or yoga, can positively impact both physical and mental health. Resources and support programs are available through various community organizations.
Treating Long COVID in Canada: A Holistic Approach
Managing Long COVID requires a holistic approach, acknowledging the wide array of symptoms and their impact on various aspects of a person's life. The new guidelines advocate for a multidisciplinary approach.
Multidisciplinary Care:
Effective Long COVID management often necessitates a team approach involving:
- Physicians to coordinate care and manage underlying medical conditions.
- Physiotherapists for rehabilitation and managing physical symptoms.
- Occupational therapists to help regain functional abilities and participate in daily activities.
- Mental health professionals to address the psychological impact of Long COVID.
- Referral pathways to facilitate access to these specialists are outlined in the guidelines.
Symptom Management Techniques:
Treatment strategies focus on alleviating specific symptoms, utilizing a range of approaches:
- Medication may be used to manage fatigue and other symptoms, as appropriate. Consult with your doctor to determine if medication is suitable for you.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation can help improve breathing and exercise tolerance in those with respiratory symptoms.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can aid in managing cognitive dysfunction ("brain fog") and emotional distress.
- Support groups and online resources provide emotional support and practical strategies for coping.
Research and Ongoing Developments:
Significant research efforts are underway in Canada to better understand and treat Long COVID. The guidelines highlight ongoing clinical trials investigating potential new therapies.
- The Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) is investing in several research projects focusing on the mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment of Long COVID.
- Clinical trials are evaluating novel therapies and approaches to improve symptom management.
- Continued funding for research is essential to advance our understanding and improve treatment options.
Conclusion: Taking Action on Long COVID in Canada
The new guidelines provide a crucial framework for diagnosing, preventing, and treating Long COVID in Canada. They emphasize the importance of early intervention, a multifaceted approach to diagnosis, and access to comprehensive multidisciplinary care. The key takeaways are the importance of vaccination, lifestyle modifications, early COVID-19 treatment, and a holistic approach to managing symptoms. If you suspect you have Long COVID, consult with your healthcare provider to receive a thorough evaluation and appropriate management. Learn more about the new Long COVID guidelines in Canada and find resources for diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Take control of your health and seek support today.

Featured Posts
-
 De Mening Van Van Der Gijp Over De Opvolging Van Farioli
May 29, 2025
De Mening Van Van Der Gijp Over De Opvolging Van Farioli
May 29, 2025 -
 Harry Potter Remake Snape And Mc Gonagalls Plan A Look At The Films Core Principles
May 29, 2025
Harry Potter Remake Snape And Mc Gonagalls Plan A Look At The Films Core Principles
May 29, 2025 -
 O Megalos Proypologismos Toy Tramp Kai I Antidrasi Toy Elon Mask Stis Ipa
May 29, 2025
O Megalos Proypologismos Toy Tramp Kai I Antidrasi Toy Elon Mask Stis Ipa
May 29, 2025 -
 Live Musics Future Examining Live Nations Influence According To The Wall Street Journal
May 29, 2025
Live Musics Future Examining Live Nations Influence According To The Wall Street Journal
May 29, 2025 -
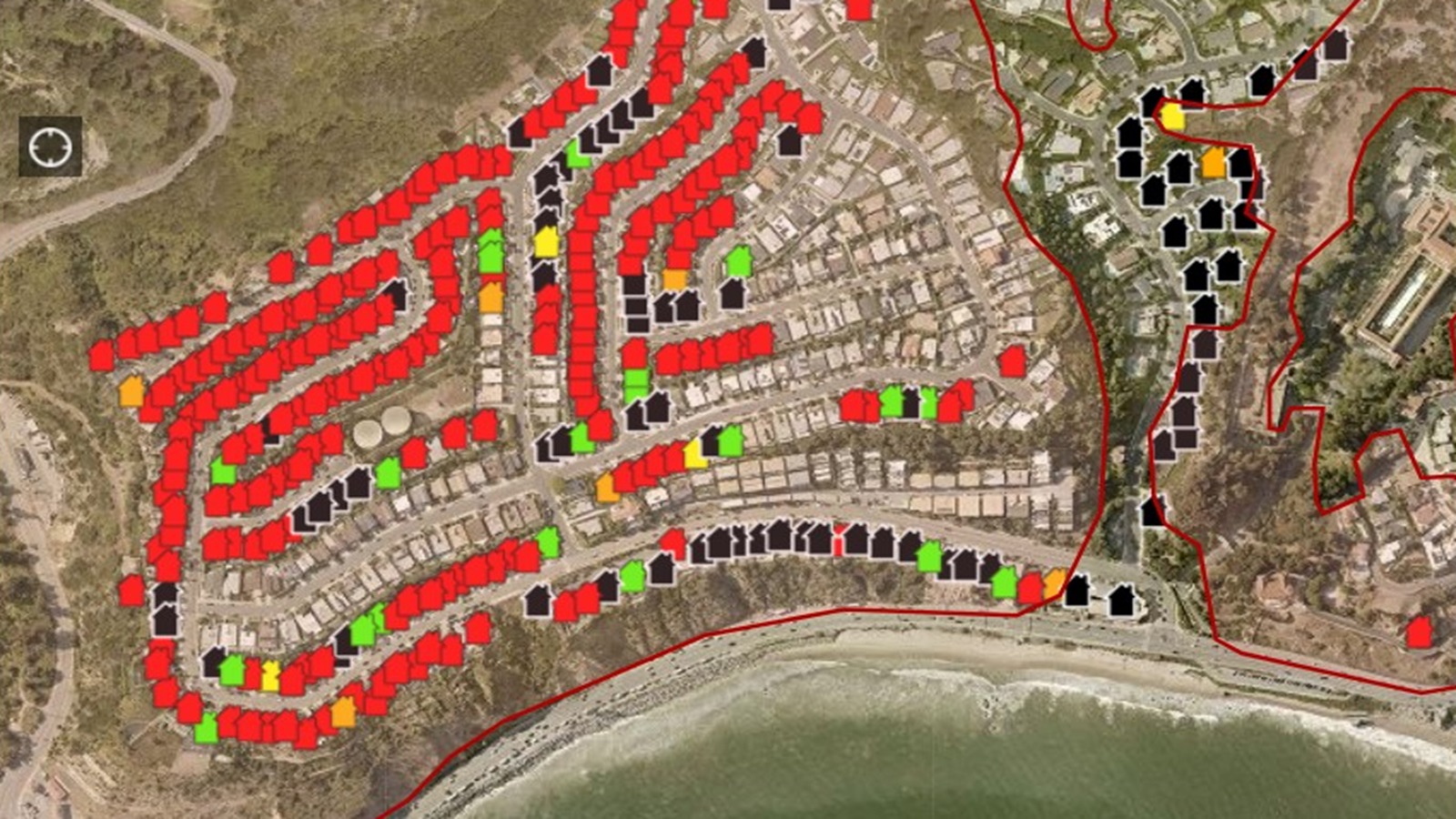 Homes Destroyed Celebrity Losses In The La Palisades Fire
May 29, 2025
Homes Destroyed Celebrity Losses In The La Palisades Fire
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 2025 Love Moto Stop Cancer Online Auction Items Up For Auction
May 31, 2025
2025 Love Moto Stop Cancer Online Auction Items Up For Auction
May 31, 2025 -
 Donate And Bid 2025 Love Moto Stop Cancer Online Auction
May 31, 2025
Donate And Bid 2025 Love Moto Stop Cancer Online Auction
May 31, 2025 -
 Cycle News Magazine In Depth Look At Issue 17 2025
May 31, 2025
Cycle News Magazine In Depth Look At Issue 17 2025
May 31, 2025 -
 Cycle News Magazine Issue 12 2025 New Bikes Gear And Racing Highlights
May 31, 2025
Cycle News Magazine Issue 12 2025 New Bikes Gear And Racing Highlights
May 31, 2025 -
 Love Moto Stop Cancer 2025 Online Auction Live
May 31, 2025
Love Moto Stop Cancer 2025 Online Auction Live
May 31, 2025
