Ontario Faces $14.6 Billion Deficit: Analysis Of Tariff Effects
Table of Contents
The Direct Impact of Tariffs on Ontario Businesses
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, have a direct and significant impact on Ontario businesses, contributing substantially to the province's growing deficit. This impact manifests in several key ways:
Increased Costs of Goods and Services
Tariffs directly increase the price of imported goods and raw materials, impacting businesses across various sectors. This leads to a ripple effect throughout the economy:
- Increased production costs leading to higher prices for consumers: Businesses pass on increased input costs to consumers, leading to inflation and reduced purchasing power. This is particularly impactful on essential goods and services.
- Reduced competitiveness of Ontario businesses in global markets: Higher production costs make Ontario-made goods less competitive internationally, leading to reduced export volumes and market share. This is especially concerning for export-oriented sectors.
- Examples: The auto manufacturing sector, heavily reliant on imported parts, faces significant cost increases. Similarly, the agricultural sector, dependent on imported fertilizers and machinery, experiences reduced profitability. The technology industry, requiring specialized components from abroad, also suffers from escalating costs.
Reduced Export Opportunities
Retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries in response to Canadian tariffs significantly impact Ontario's export-oriented industries. This creates a challenging trade environment:
- Loss of market share to competitors: Higher prices for Ontario products make them less attractive to international buyers, leading to lost market share to competitors in countries with lower tariff barriers.
- Decreased revenue and potential job losses: Reduced export sales translate directly into lower revenue for businesses, potentially leading to layoffs and business closures. This contributes directly to the rise in unemployment and the widening Ontario deficit.
- Case studies: Analysis of specific industries, such as the lumber and agricultural sectors, reveals substantial revenue losses and job displacement due to retaliatory tariffs.
Indirect Effects of Tariffs on the Ontario Economy
The negative consequences of tariffs extend beyond their direct impact on businesses, affecting the broader Ontario economy in several indirect ways:
Supply Chain Disruptions
Tariffs introduce uncertainty and complexity into supply chains, leading to delays, increased costs, and inefficiencies:
- Increased logistics and transportation costs: Businesses must navigate complex tariff regulations and customs procedures, increasing logistical challenges and transportation expenses.
- Difficulty sourcing key inputs for production: Delays in receiving imported inputs can disrupt production schedules, leading to lost sales and production slowdowns.
- Analysis of the impact on specific supply chains: Examination of Ontario's key supply chains reveals widespread vulnerability to tariff-related disruptions, especially those relying heavily on imported components.
Impact on Consumer Spending
Higher prices due to tariffs reduce consumer purchasing power, dampening economic growth and exacerbating the Ontario deficit:
- Reduced consumer confidence and spending: Higher prices for goods and services erode consumer confidence, leading to decreased spending and reduced economic activity.
- Impact on retail sales and service industries: Reduced consumer spending directly impacts retail sales and the service industries that depend on consumer demand.
- Statistical data: Economic data reveals a clear correlation between tariff increases and declines in consumer spending and retail sales.
Job Losses and Unemployment
Increased costs and reduced competitiveness due to tariffs lead to business closures and job losses across various sectors:
- Analysis of job losses in specific industries impacted by tariffs: Detailed analysis reveals the substantial job losses in industries directly affected by tariffs, such as manufacturing and agriculture.
- Increased unemployment rate and its social consequences: Job losses contribute to a higher unemployment rate, leading to social and economic hardships for affected individuals and families.
- Potential solutions for mitigating job losses: Retraining programs, job creation initiatives, and government support can help mitigate the impact of job losses caused by tariffs.
Potential Solutions and Policy Recommendations
Addressing the Ontario deficit requires a comprehensive strategy that tackles the negative effects of tariffs:
Diversification of Trade Partners
Reducing reliance on specific trade partners can lessen the vulnerability of Ontario businesses to tariff shocks:
- Exploring new trade agreements and opportunities: Actively seeking new trade agreements with diverse partners can diversify export markets and reduce dependence on single trading partners.
- Investment in infrastructure to support trade with diverse partners: Investing in infrastructure, such as transportation and logistics networks, is crucial to support trade with diverse partners.
Support for Ontario Businesses
Government aid and subsidies can help businesses absorb the increased costs of tariffs and remain competitive:
- Financial assistance programs for affected industries: Targeted financial assistance programs can help businesses offset the increased costs of tariffs and maintain operations.
- Tax incentives to stimulate investment and job creation: Tax incentives can encourage businesses to invest in new technologies, increase production, and create jobs.
Negotiation and Trade Diplomacy
Active participation in international trade negotiations is crucial in reducing tariff barriers:
- Strategic engagement with trading partners to resolve trade disputes: Proactive diplomacy and strategic engagement with trading partners are necessary to resolve trade disputes and reduce tariff barriers.
- Advocating for fair trade practices and reduced protectionism: Ontario must advocate for fair trade practices and reduced protectionism at both the national and international levels.
Conclusion
Ontario's $14.6 billion deficit is a complex issue, but the negative effects of tariffs are undeniably a major contributing factor. Understanding the direct and indirect impacts of tariffs – from increased costs for businesses to reduced consumer spending and job losses – is critical to developing effective solutions. Addressing the Ontario deficit requires a multi-pronged approach, including diversification of trade, support for businesses, and proactive engagement in international trade negotiations. Ignoring the devastating effects of tariff effects on the Ontario economy will only worsen the situation. We need decisive action now to mitigate the damage and pave the way for a stronger and more resilient economy. Let's work together to find solutions to address the Ontario deficit caused by the harmful impact of tariffs and build a more robust and sustainable economic future for Ontario.

Featured Posts
-
 Reddit Service Restored Following Recent Outage Users Can Access Platform Again
May 17, 2025
Reddit Service Restored Following Recent Outage Users Can Access Platform Again
May 17, 2025 -
 Network18 Media And Investments Stock Price Today April 21 2025 Nse And Bse Data Technical Analysis
May 17, 2025
Network18 Media And Investments Stock Price Today April 21 2025 Nse And Bse Data Technical Analysis
May 17, 2025 -
 Ontario Online Casinos Ranked Mirax Casinos Position As A Top Payout Casino In 2025
May 17, 2025
Ontario Online Casinos Ranked Mirax Casinos Position As A Top Payout Casino In 2025
May 17, 2025 -
 Rising Phone Repair Costs The Legacy Of Trumps Tariffs
May 17, 2025
Rising Phone Repair Costs The Legacy Of Trumps Tariffs
May 17, 2025 -
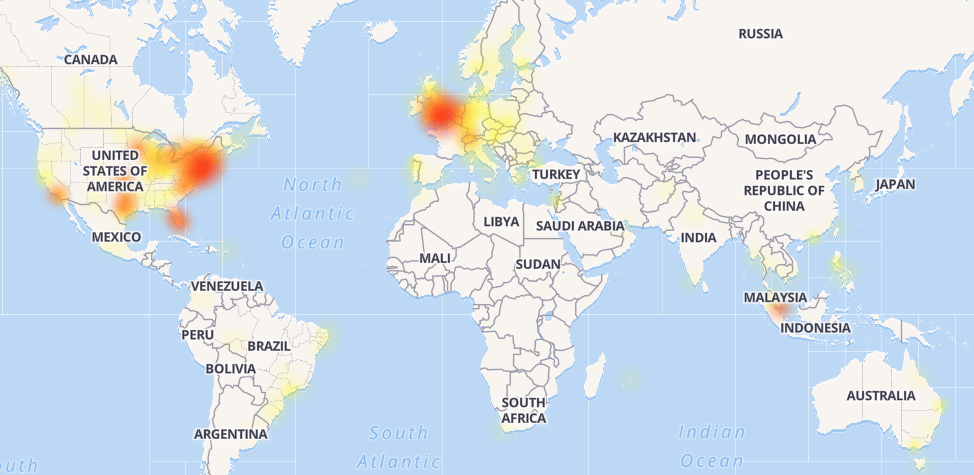 Global Reddit Outage Leaves Users Offline
May 17, 2025
Global Reddit Outage Leaves Users Offline
May 17, 2025
