Ozempic And Beyond: The Growing Applications Of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
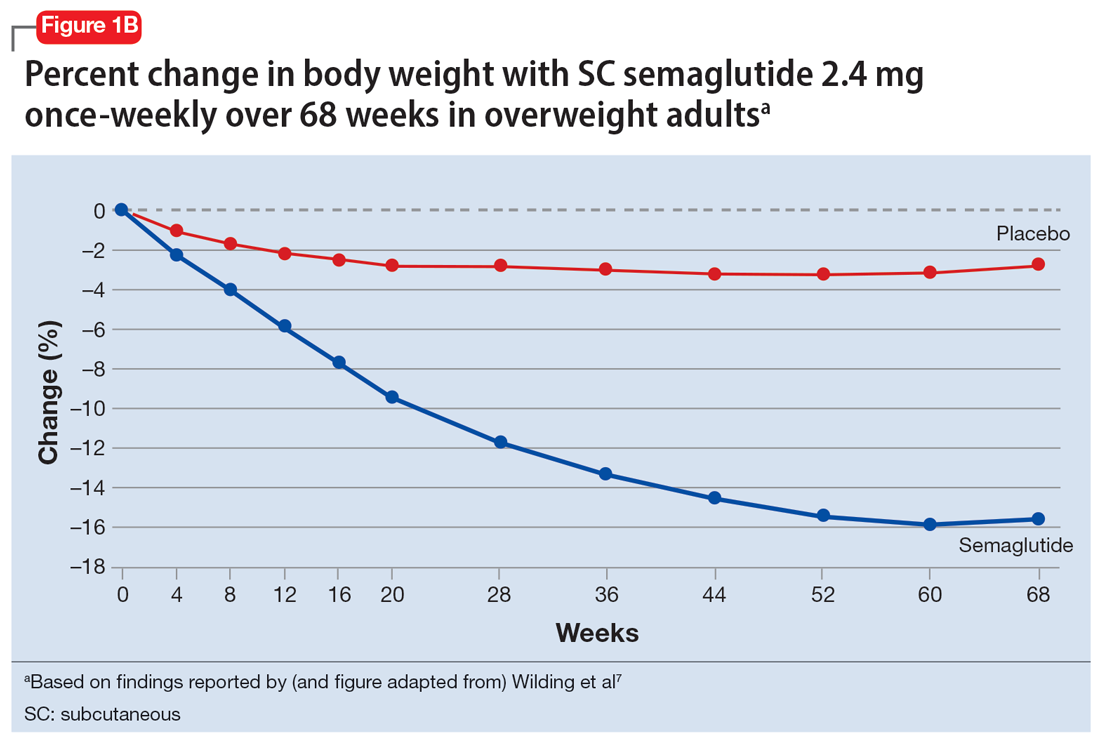
Table of Contents
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Management
Improved Glycemic Control
GLP-1 agonists are highly effective in improving glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). They achieve this through several mechanisms:
- Increased Insulin Secretion: GLP-1 RAs stimulate the release of insulin from the pancreas, particularly after meals, helping to lower blood sugar levels.
- Decreased Glucagon Secretion: They suppress the release of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar. This dual action effectively balances blood glucose levels.
- Slowed Gastric Emptying: GLP-1 agonists slow down the rate at which food leaves the stomach, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar after eating.
These combined effects result in significant reductions in HbA1c levels, a key indicator of long-term blood sugar control. Compared to other diabetes medications like sulfonylureas or metformin, GLP-1 agonists often offer superior glycemic control and additional benefits, such as weight loss. Examples of GLP-1 agonists commonly used in T2D treatment include Ozempic (semaglutide), Victoza (liraglutide), and Trulicity (dulaglutide).
Weight Management in Type 2 Diabetes
A significant advantage of GLP-1 receptor agonists is their ability to promote weight loss, a crucial aspect of managing type 2 diabetes. This weight reduction is achieved through:
- Appetite Suppression: GLP-1 agonists act on the brain to reduce appetite and increase feelings of fullness (satiety).
- Increased Satiety: Patients often report feeling fuller for longer after meals, leading to reduced caloric intake.
This weight loss not only improves insulin sensitivity but also has positive implications for cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of complications associated with obesity and T2D. Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated the significant weight loss achieved with GLP-1 agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Expanding Applications Beyond Type 2 Diabetes
Obesity Treatment
The efficacy of GLP-1 receptor agonists in promoting substantial weight loss has led to their increasing use as a standalone treatment for obesity, irrespective of diabetes status. These medications have shown:
- Efficacy in diverse patient populations: Studies demonstrate their effectiveness across a wide range of body mass indices (BMIs) and obesity-related comorbidities.
- Long-term weight management benefits: While further long-term studies are ongoing, initial data suggests sustained weight loss with continued treatment.
- Comparison with other weight-loss strategies: GLP-1 receptor agonists often outperform other weight-loss approaches in terms of both the amount of weight lost and the maintenance of that weight loss.
Cardiovascular Disease Prevention
Emerging research suggests that GLP-1 receptor agonists may offer significant cardiovascular benefits, reducing the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in high-risk individuals, with or without diabetes. This protection may be attributed to:
- Improved blood pressure control: Studies have shown a reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
- Reduced inflammation: GLP-1 RAs have anti-inflammatory properties that may contribute to cardiovascular protection.
- Improved lipid profile: Some studies indicate improvements in cholesterol levels.
Clinical trial data has supported these findings, demonstrating a reduction in cardiovascular events, hospitalization, and even mortality in certain patient populations.
Other Potential Applications
Research is exploring the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in other areas:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Early studies suggest a potential role in improving liver function and reducing liver fat content.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Some preliminary evidence indicates that GLP-1 RAs may improve metabolic parameters and even reduce symptoms of PCOS.
These are early findings, and more research is needed to confirm the efficacy and safety of GLP-1 agonists in these conditions.
Side Effects and Considerations
Common Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, GLP-1 receptor agonists can cause side effects, most commonly gastrointestinal issues such as:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
These side effects usually lessen over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
Contraindications and Precautions
GLP-1 receptor agonists are not suitable for everyone. Contraindications include:
- A history of pancreatitis
- Certain types of tumors (e.g., medullary thyroid cancer)
- Severe kidney disease
It's crucial for patients to discuss their medical history with their healthcare provider to determine if GLP-1 receptor agonists are appropriate. Individual patient assessment and physician consultation are vital before starting any treatment with GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Conclusion
GLP-1 receptor agonists, exemplified by Ozempic, are proving to be a transformative class of medications with broad applications beyond their initial use in type 2 diabetes. Their ability to improve glycemic control, promote significant weight loss, and potentially reduce cardiovascular risk makes them a valuable tool in managing diabetes and obesity. Ongoing research continues to explore their potential in other areas, such as NAFLD and PCOS. However, it is crucial to remember that these medications, like all pharmaceuticals, can have side effects. Learn more about GLP-1 receptor agonists and discuss your options with your doctor today! Personalized medicine is key, and professional guidance is essential in determining the suitability of GLP-1 receptor agonists for your individual health needs.

Featured Posts
-
 Bianca Censoris Bold Bra And Thong Look While Roller Skating
May 28, 2025
Bianca Censoris Bold Bra And Thong Look While Roller Skating
May 28, 2025 -
 Ohio Train Derailment Aftermath The Lingering Threat Of Toxic Chemicals
May 28, 2025
Ohio Train Derailment Aftermath The Lingering Threat Of Toxic Chemicals
May 28, 2025 -
 Glp 1 Drugs Are They Right For You Understanding Ozempic And Similar Medications
May 28, 2025
Glp 1 Drugs Are They Right For You Understanding Ozempic And Similar Medications
May 28, 2025 -
 Ryujinx Switch Emulator Development Officially Ends After Nintendo Contact
May 28, 2025
Ryujinx Switch Emulator Development Officially Ends After Nintendo Contact
May 28, 2025 -
 Galaxy S25 Ultra 256 Go A 953 75 E Avis Caracteristiques Et Prix
May 28, 2025
Galaxy S25 Ultra 256 Go A 953 75 E Avis Caracteristiques Et Prix
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 New Music Jacob Alon Shares August Moon
May 30, 2025
New Music Jacob Alon Shares August Moon
May 30, 2025 -
 Industry Spotlight Jacob Alon
May 30, 2025
Industry Spotlight Jacob Alon
May 30, 2025 -
 Listen Now Jacob Alons August Moon
May 30, 2025
Listen Now Jacob Alons August Moon
May 30, 2025 -
 Rising Star Jacob Alon S Journey In Industry
May 30, 2025
Rising Star Jacob Alon S Journey In Industry
May 30, 2025 -
 Is Jacob Alons Fairy In A Bottle The Next Big Hit
May 30, 2025
Is Jacob Alons Fairy In A Bottle The Next Big Hit
May 30, 2025
