Ozempic For Everyone? Exploring GLP-1 Drugs And Expanding Use Cases
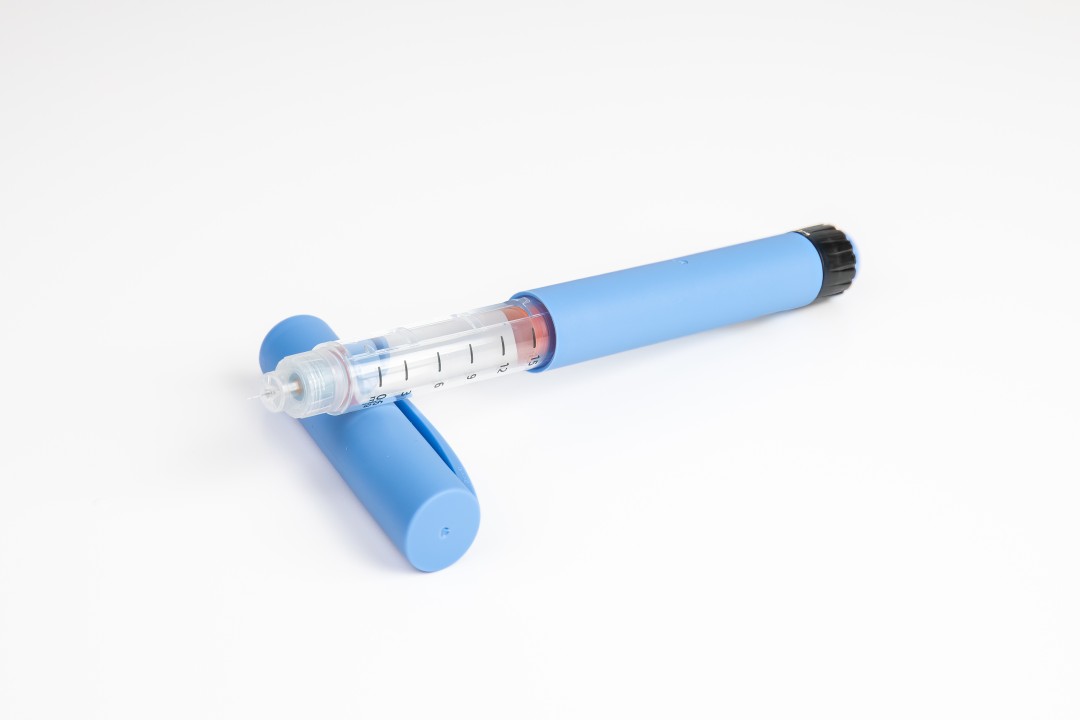
Table of Contents
Understanding GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Their Mechanism of Action
GLP-1 receptor agonists, like Ozempic (semaglutide), Wegovy (semaglutide), and Saxenda (liraglutide), are a class of medications that mimic the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a naturally occurring hormone in the body. Their primary mechanism of action revolves around regulating blood sugar and appetite. This dual action makes them effective in managing both type 2 diabetes and obesity.
How do they work? GLP-1 receptor agonists work in several ways:
- Increase insulin release when blood sugar is high: This helps to lower blood glucose levels effectively, particularly after meals.
- Decrease glucagon secretion: Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar. By suppressing glucagon, GLP-1 agonists further contribute to better blood sugar control.
- Slow gastric emptying: This leads to a feeling of fullness and satiety, helping individuals eat less and manage their caloric intake.
- May directly impact brain regions regulating appetite: Research suggests that GLP-1 agonists may influence appetite centers in the brain, leading to reduced food cravings and increased feelings of fullness.
Approved Uses of GLP-1 Drugs: Beyond Type 2 Diabetes
While initially developed for type 2 diabetes management, the FDA has approved GLP-1 receptor agonists for additional indications. The primary approved uses include:
- Type 2 diabetes management: GLP-1 drugs effectively improve glycemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes, helping to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Ozempic, for example, is specifically designed for this purpose.
- Chronic weight management in adults with obesity or overweight with at least one weight-related condition: Wegovy, a higher dose of semaglutide than Ozempic, is specifically approved for chronic weight management in obese or overweight adults. The dosage differences between Ozempic and Wegovy reflect this distinction in intended use.
The key differences lie in dosage and FDA approval: Ozempic is approved for type 2 diabetes, while Wegovy, using a higher dose of the same active ingredient, targets weight loss in obese or overweight adults. Both medications have shown significant improvements in:
- Improved glycemic control in Type 2 diabetes.
- Significant weight loss in obese and overweight individuals.
- Cardiovascular benefits in some high-risk patients. This is an important area of ongoing research.
Exploring Expanding Use Cases and Ongoing Research
The therapeutic potential of GLP-1 agonists extends beyond their currently approved uses. Research is ongoing to explore their efficacy in various conditions, including:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) treatment: Studies suggest that GLP-1 agonists may improve symptoms associated with PCOS, such as weight management and irregular menstrual cycles.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) management: Early research indicates a potential role in reducing inflammation and improving liver function in individuals with NAFLD.
- Heart failure management: Some research points to potential benefits in reducing cardiovascular events in patients with heart failure.
- Potential role in Alzheimer's disease prevention: While still in early stages of research, some studies suggest a potential link between GLP-1 agonists and a reduced risk of Alzheimer's disease. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings and understand the mechanisms involved. The results to date are promising but far from conclusive.
Risks and Side Effects Associated with GLP-1 Drugs
Like all medications, GLP-1 receptor agonists carry potential risks and side effects. The most common side effects are gastrointestinal, including:
- Gastrointestinal side effects (most common): Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation are frequently reported. These side effects often lessen over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
- Increased risk of pancreatitis (rare but serious): Although rare, pancreatitis is a serious side effect that requires immediate medical attention.
- Potential for gallbladder problems: Gallstones may develop in some individuals.
- Impact on kidney function (especially in patients with pre-existing conditions): Patients with pre-existing kidney issues should be carefully monitored.
It’s crucial to discuss potential risks and side effects with your healthcare provider before starting treatment. Open communication with your doctor is key to managing any potential adverse effects.
Who Should Consider GLP-1 Drugs? A Detailed Look at Patient Suitability
Determining the suitability of GLP-1 drugs requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Individual risk assessment is crucial: Your doctor will assess your overall health, medical history, and current medications to determine if GLP-1 agonists are a safe and appropriate option.
- Not suitable for everyone with obesity: These medications are not a magic bullet for weight loss and aren't appropriate for everyone.
- Consider existing medical conditions: Certain pre-existing conditions may influence the decision to prescribe these medications.
- Medication interactions: GLP-1 agonists can interact with other medications.
Before starting any GLP-1 medication, a thorough consultation with a doctor or endocrinologist is essential. They can perform a complete evaluation, assess your individual risk factors, and discuss potential benefits and risks, ensuring you make an informed decision.
Conclusion
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy offer significant benefits for managing type 2 diabetes and promoting weight loss. Their mechanism of action, targeting both blood sugar regulation and appetite control, makes them effective for many individuals. However, these medications are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Understanding their mechanism, approved uses, expanding research, potential risks, and individual patient suitability is vital. Before considering GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic or Wegovy for weight loss or diabetes management, consult your doctor or endocrinologist to determine if they are the right choice for you. They can assess your individual needs and help you make an informed decision regarding GLP-1 medications. Learn more about the potential benefits and risks of GLP-1 drugs by scheduling a consultation today.

Featured Posts
-
 Abd Tueketici Kredileri Mart Ayinda Artti Detayli Analiz
May 28, 2025
Abd Tueketici Kredileri Mart Ayinda Artti Detayli Analiz
May 28, 2025 -
 Smartphone Samsung Galaxy S25 128 Go Avis Prix Et Bon Plan
May 28, 2025
Smartphone Samsung Galaxy S25 128 Go Avis Prix Et Bon Plan
May 28, 2025 -
 Watch Pacers Vs Bulls Game Time And Streaming Details For March 10th
May 28, 2025
Watch Pacers Vs Bulls Game Time And Streaming Details For March 10th
May 28, 2025 -
 A List Legal Battle Intensifies New Developments In The Lively Baldoni Case
May 28, 2025
A List Legal Battle Intensifies New Developments In The Lively Baldoni Case
May 28, 2025 -
 Review Wes Andersons The Phoenician Scheme Cannes Film Festival 2023
May 28, 2025
Review Wes Andersons The Phoenician Scheme Cannes Film Festival 2023
May 28, 2025
