Pandemic Fiscal Support And Inflation: An ECB Perspective
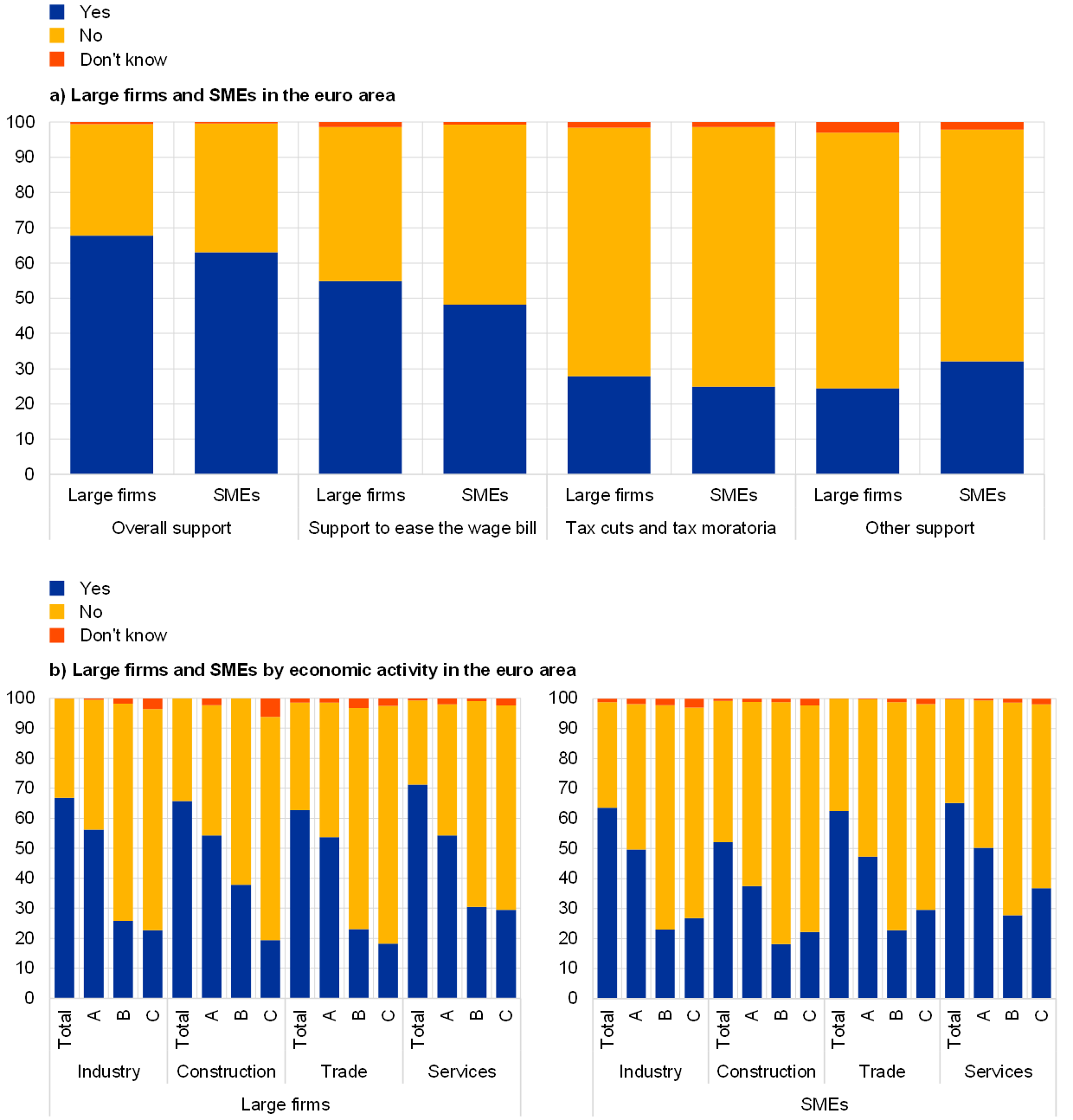
Table of Contents
The Scale and Nature of Pandemic Fiscal Support in the Eurozone
The Eurozone responded to the COVID-19 crisis with a massive wave of fiscal support, aiming to mitigate the economic fallout and protect jobs. This support took many forms, varying significantly across member states. Understanding the scale and nature of this intervention is crucial for analyzing its impact on inflation.
-
Quantifying the Stimulus: The overall fiscal stimulus amounted to several trillion euros, representing a significant percentage of the Eurozone's GDP. The exact figure varies depending on the methodology used and the timeframe considered, but it undeniably represents an unprecedented injection of funds into the economy.
-
Variations Across Member States: Fiscal responses differed considerably across Eurozone countries. Some nations opted for more generous furlough schemes, while others focused on direct cash transfers to individuals and businesses. This heterogeneity makes it challenging to draw universal conclusions about the relationship between fiscal support and inflation.
-
Composition of Fiscal Packages: The fiscal packages comprised a mix of direct transfers (such as unemployment benefits and direct cash payments) and indirect support (such as loan guarantees and tax deferrals). The relative proportion of these different types of support varied considerably, influencing their impact on aggregate demand and inflation.
-
The Role of the EU's Recovery and Resilience Facility: The EU's Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF) played a significant role, providing substantial funding to member states for investments and reforms aimed at boosting economic recovery and resilience. This program further contributed to the overall fiscal stimulus.
ECB's Monetary Policy Response to Pandemic-Induced Inflation
The ECB responded to the pandemic with an extraordinarily accommodative monetary policy. This aimed to prevent a severe economic contraction and to support lending to businesses and households.
-
Quantitative Easing (QE) and Negative Interest Rates: The ECB implemented large-scale QE programs, purchasing government bonds and other assets to inject liquidity into the financial system and lower long-term interest rates. Negative interest rates were also introduced to encourage lending and investment.
-
Rationale for Accommodative Policy: The rationale behind this accommodative policy was to prevent a credit crunch, to keep borrowing costs low, and to support aggregate demand during a period of unprecedented uncertainty. The ECB aimed to prevent a deflationary spiral.
-
Communication Strategy and Inflation Expectations: The ECB's communication strategy played a crucial role in shaping inflation expectations. Initially, the ECB emphasized the temporary nature of the inflationary pressures stemming from supply chain disruptions.
-
Shift in ECB's Approach: As inflation rose persistently above the ECB's target, the central bank gradually shifted its approach. This involved slowing down the pace of asset purchases and eventually raising interest rates. This demonstrated a response to the increasing inflationary pressures and a move away from the highly accommodative stance.
The Relationship Between Fiscal Support and Inflation: An ECB Perspective
The ECB's assessment of the link between fiscal stimulus and inflation is nuanced and complex. While acknowledging the role of fiscal support in boosting demand, the ECB also highlighted other contributing factors.
-
Supply-Side Bottlenecks: The ECB emphasized the significant role of supply-side bottlenecks, such as disruptions to global supply chains and shortages of raw materials, in driving up prices. These bottlenecks constrained supply, leading to upward pressure on prices irrespective of demand-side factors.
-
Demand-Side Pressures: Nevertheless, the ECB also recognized that the fiscal stimulus contributed to demand-side pressures. The increased disposable income resulting from government support programs fuelled demand, further exacerbating inflationary pressures.
-
Temporary Nature of Inflation (Initial Assessment): Initially, the ECB argued that the inflationary pressures were largely temporary, driven by transitory factors like supply chain disruptions. This perspective has evolved as inflation proved more persistent.
-
Disentangling Fiscal and Monetary Effects: Disentangling the specific effects of fiscal and monetary policies on inflation is a challenging task. The two policies acted in concert, making it difficult to isolate the individual contribution of each.
Addressing Concerns About Inflationary Pressures
To address the rising inflationary pressures, the ECB has taken several measures:
-
Tapering QE and Raising Interest Rates: The ECB has gradually reduced its asset purchases (tapering QE) and has started to increase interest rates. These actions aim to curb excessive demand and cool down inflation.
-
Rationale for Policy Shift: The shift in policy reflects a recognition that persistent inflation requires a more restrictive monetary policy stance. The goal is to anchor inflation expectations around the ECB's target and maintain price stability.
-
Potential Risks and Trade-offs: Raising interest rates carries risks, such as slowing economic growth and potentially increasing borrowing costs for businesses and households. The ECB carefully weighs these risks against the need to control inflation.
-
Effectiveness and Impact: The effectiveness of the ECB's measures in controlling inflation is subject to ongoing evaluation. The impact on financial markets and the real economy remains a key focus of analysis and debate.
Conclusion
The ECB's perspective on the relationship between pandemic fiscal support and inflation is complex and evolving. While the substantial fiscal stimulus undoubtedly contributed to demand-side pressures, supply-side bottlenecks also played a crucial role. The ECB's initial response involved highly accommodative monetary policies, but as inflation became more persistent, a shift to a more restrictive stance was implemented, including tapering QE and raising interest rates. The ongoing debate focuses on the long-term consequences of both the fiscal stimulus and the ECB's policy response, including the potential trade-offs between controlling inflation and maintaining economic growth. For a deeper understanding of the intricate relationship between pandemic fiscal support and inflation, continue your research by exploring the ECB's publications and policy statements on this crucial economic issue. Further examination of the ECB's pandemic fiscal support and inflation policies is vital for informed economic discussion.

Featured Posts
-
 Nine Killed In Vancouver Filipino Festival Car Crash
Apr 29, 2025
Nine Killed In Vancouver Filipino Festival Car Crash
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Jancker Klagenfurt Und Der Bundesliga Abstiegskampf Ein Trainerwechsel Steht Bevor
Apr 29, 2025
Jancker Klagenfurt Und Der Bundesliga Abstiegskampf Ein Trainerwechsel Steht Bevor
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Luxury Car Sales In China Bmw Porsche And The Road Ahead
Apr 29, 2025
Luxury Car Sales In China Bmw Porsche And The Road Ahead
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Yukon Government Considers Contempt Action Against Mine Manager
Apr 29, 2025
Yukon Government Considers Contempt Action Against Mine Manager
Apr 29, 2025 -
 British Paralympian Sam Ruddock Missing In Las Vegas Urgent Search Underway
Apr 29, 2025
British Paralympian Sam Ruddock Missing In Las Vegas Urgent Search Underway
Apr 29, 2025
