Reduced Apple Harvest: Rosy Apple Aphid Impact And Predictions
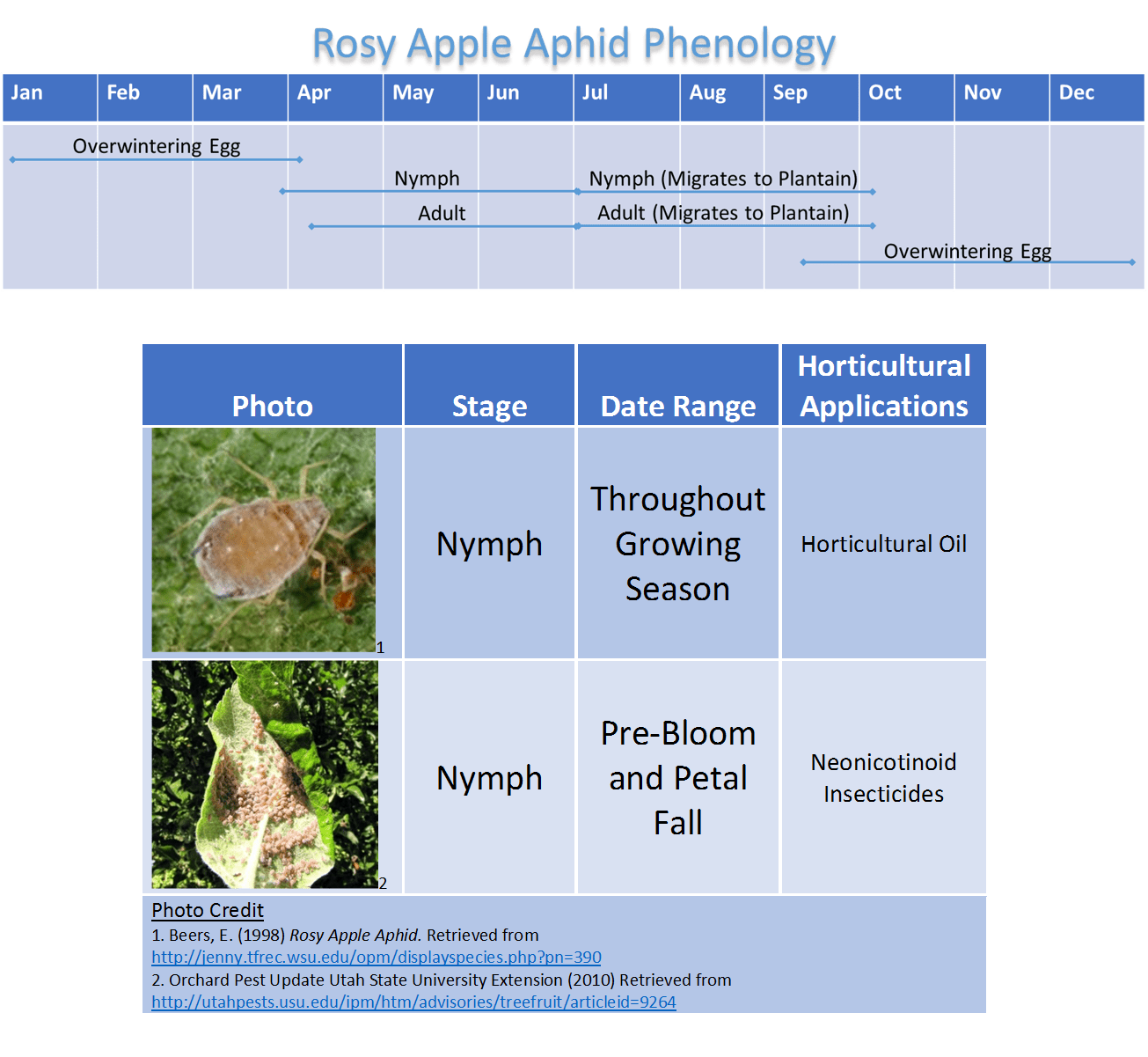
Table of Contents
Understanding the Rosy Apple Aphid and its Life Cycle
Identifying Rosy Apple Aphids
The rosy apple aphid ( Dysaphis plantaginea ) is a small, pear-shaped insect, typically ranging from 1.5 to 2.0 mm in length. They are easily identifiable by their characteristic pinkish-rosy color, often with darker markings on their bodies. Nymphs are smaller and lighter in color. Unlike some other apple pests, rosy apple aphids are typically found clustered along the veins on the underside of leaves, making identification easier with a close visual inspection. (Include images here if possible, showing different life stages of the aphid). Distinguishing them from other apple pests requires careful observation; knowing their preferred location on the plant is crucial for accurate identification.
Rosy Apple Aphid Life Cycle and Reproduction
Rosy apple aphids undergo a complex life cycle involving both sexual and asexual reproduction. Overwintering occurs as eggs laid on the buds of apple trees. As temperatures rise in spring, these eggs hatch into nymphs, which begin feeding on the young leaves and buds. These nymphs then develop into wingless adults, initiating the rapid reproduction phase. A single aphid can produce dozens of offspring, leading to massive infestations and the formation of dense colonies. This rapid reproduction rate, coupled with several generations per year, significantly contributes to the devastating impact on apple yields. Keywords: infestation, colonies, overwintering, rapid reproduction.
- Optimal conditions for aphid development: Warm temperatures (ideally between 65-75°F) and moderate humidity favor rapid aphid population growth.
- Predators and natural enemies: Ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps are natural predators that help control aphid populations.
- The role of host plants: Apple trees are the primary host plants for rosy apple aphids; their survival and reproduction heavily depend on the availability of apple trees.
The Impact of Rosy Apple Aphid Infestations on Apple Trees
Direct Damage to Apples
Rosy apple aphids directly damage apples by sucking sap from leaves, buds, and developing fruit. This sap-sucking activity weakens the tree, leading to reduced fruit size, distorted fruit shapes, and impaired fruit quality. Severely infested trees produce smaller, less marketable apples, resulting in significant yield reduction and decreased market value. Keywords: fruit quality, yield reduction, market value.
Indirect Damage through Honeydew and Sooty Mold
Aphids secrete a sticky substance called honeydew, which coats the leaves, branches, and fruit. This honeydew provides a breeding ground for sooty mold, a black fungus that further reduces photosynthesis and negatively impacts plant health. The combination of direct sap-sucking damage and indirect damage from honeydew and sooty mold can severely compromise the health and productivity of apple trees, affecting not only the current yield but also the tree's long-term health and future production. Keywords: honeydew, sooty mold, plant health.
- Economic consequences of reduced apple yields: Reduced harvests translate to significant financial losses for apple growers, impacting their income and the overall apple industry.
- Impact on apple orchard aesthetics: Heavy infestations affect the orchard’s appearance, reducing its aesthetic appeal and potentially impacting tourism or farm visits.
- Increased susceptibility to other diseases and pests: Weakened trees are more vulnerable to other diseases and pests, leading to further complications and losses.
Predicting Future Apple Harvests Based on Rosy Apple Aphid Populations
Monitoring Aphid Populations
Accurate prediction of future apple harvests requires effective monitoring of rosy apple aphid populations. Methods include regular visual inspections of trees, the use of sticky traps to capture aphids, and pheromone traps to attract and count adult aphids. Early detection is crucial for implementing timely management strategies. Keywords: population monitoring, pest management, early detection.
Predictive Modeling and Forecasting
Predictive modeling uses data on aphid populations, weather patterns (temperature, rainfall), and other factors to forecast future harvest yields. These models incorporate historical data and current environmental conditions to estimate the potential impact of aphid infestations. However, these models have limitations and require continuous improvement. Keywords: predictive modeling, harvest forecast, risk assessment.
- Factors influencing aphid population dynamics: Climate change (e.g., warmer temperatures) may increase aphid survival and reproduction rates, while pesticide resistance poses a challenge to effective control.
- Limitations of current prediction models: Model accuracy can be affected by unpredictable weather events or the emergence of new aphid strains.
- The role of integrated pest management (IPM) in minimizing aphid impact: IPM strategies aim to reduce aphid populations while minimizing the use of harmful pesticides, impacting model predictions and future harvest estimations.
Strategies for Managing Rosy Apple Aphids and Mitigating Harvest Losses
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Strategies
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) emphasizes a holistic approach to pest control. This involves implementing a combination of strategies such as biological control (introducing natural enemies like ladybugs), cultural control (pruning to improve air circulation and sunlight penetration, sanitation practices), and targeted pesticide use only when necessary. This minimizes environmental impact while effectively managing aphid populations. Keywords: integrated pest management, biological control, sustainable pest management.
The Role of Technology in Aphid Management
Technology plays an increasingly important role in aphid management. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras are used for aerial surveys to assess the extent of infestations, enabling targeted pesticide applications, reducing environmental impact and improving efficiency. This precision agriculture approach enhances the effectiveness of IPM strategies. Keywords: precision agriculture, drone technology, smart farming.
- Advantages and disadvantages of different management strategies: Each strategy has its own benefits and drawbacks, requiring careful consideration based on specific orchard conditions and resource availability.
- The importance of early detection and intervention: Early detection of infestations allows for prompt implementation of management strategies, significantly reducing the damage.
- Long-term strategies for sustainable apple production: A sustainable approach to apple production requires integrating IPM principles into long-term orchard management plans to ensure healthy trees and consistent yields.
Conclusion
The rosy apple aphid presents a significant threat to apple production, leading to a reduced apple harvest and substantial economic losses. Predicting future harvests accurately requires continuous monitoring of aphid populations, sophisticated predictive modeling, and a thorough understanding of factors influencing aphid dynamics. Implementing integrated pest management strategies and leveraging technological advancements are crucial for mitigating the effects of this devastating pest. Understanding the impact of the rosy apple aphid is crucial for safeguarding future apple harvests. By implementing effective management strategies and staying informed about the latest research, we can work towards mitigating the effects of this devastating pest and ensuring a bountiful apple harvest for years to come.

Featured Posts
-
 Jyoti Malhotra Arrest Travel Vlogger Accused Of Spying For Pakistan
May 19, 2025
Jyoti Malhotra Arrest Travel Vlogger Accused Of Spying For Pakistan
May 19, 2025 -
 Trump In Gazze Paylasimi Netanyahu Elon Musk Ve Lueksuen Goelgesinde Skandal
May 19, 2025
Trump In Gazze Paylasimi Netanyahu Elon Musk Ve Lueksuen Goelgesinde Skandal
May 19, 2025 -
 Uks Eurovision 2025 Showing 19th Place Explained
May 19, 2025
Uks Eurovision 2025 Showing 19th Place Explained
May 19, 2025 -
 Royal Mail Challenges Excessive Ofcom Regulation
May 19, 2025
Royal Mail Challenges Excessive Ofcom Regulation
May 19, 2025 -
 Orlando Magic Vs Dallas Mavericks Live Stream Odds And Game Information For March 27th
May 19, 2025
Orlando Magic Vs Dallas Mavericks Live Stream Odds And Game Information For March 27th
May 19, 2025
