Rising Federal Debt: Its Impact On Mortgage Rates And Borrowers
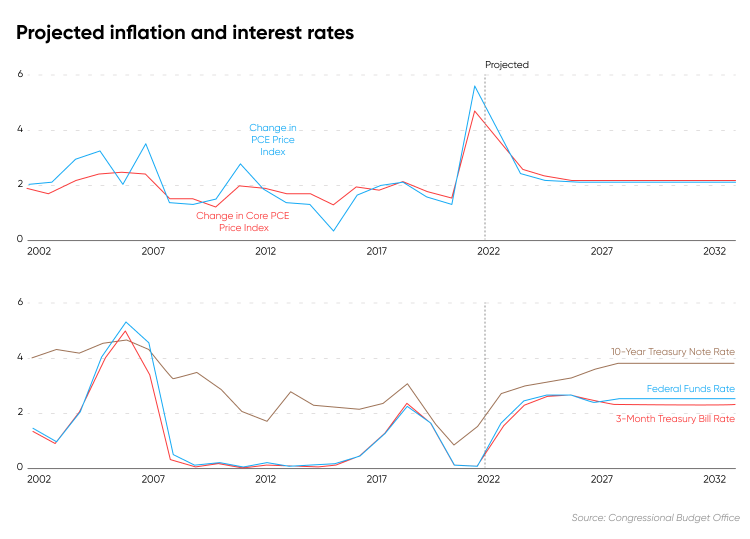
Table of Contents
H2: The Relationship Between Federal Debt and Interest Rates
Increased government borrowing to finance the national debt fundamentally increases the demand for loanable funds. This increased demand pushes interest rates higher across the board, impacting various sectors, including the housing market. Think of it like this: the government is competing with you and other private borrowers for a limited pool of money.
- Increased government borrowing competes with private sector borrowing (including mortgages). When the government needs to borrow heavily, it absorbs a significant portion of available capital, leaving less for private sector lending.
- Higher demand for funds leads to higher interest rates across the board. Basic supply and demand economics dictates that increased demand with a relatively fixed supply leads to higher prices – in this case, higher interest rates.
- The Federal Reserve's response to inflation, often fueled by government spending, can also impact rates. Government spending can contribute to inflation. To combat this, the Federal Reserve often raises interest rates, further increasing borrowing costs for consumers.
- The crowding-out effect: This describes the phenomenon where increased government borrowing "crowds out" private investment. As government borrowing soaks up available funds, businesses and individuals find it harder and more expensive to secure loans, impacting economic growth.
H3: The Role of Inflation
Government spending, particularly deficit spending financed by borrowing, can contribute significantly to inflation. When the government borrows and spends large sums of money, it increases the money supply without a corresponding increase in the production of goods and services. This leads to an increase in demand relative to supply, driving up prices. This inflation then erodes the purchasing power of consumers and makes mortgages less affordable. Higher inflation often prompts the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates aggressively, further impacting mortgage rates.
H2: How Rising Federal Debt Directly Impacts Mortgage Rates
Increased federal debt influences investor sentiment and market dynamics, directly affecting mortgage rates. Investors, assessing the increased risk associated with higher national debt, demand higher yields on mortgage-backed securities (MBS).
- Increased risk perception associated with higher national debt. Higher national debt increases the perceived risk of default or future inflation, making investors wary.
- Impact on Treasury yields and their correlation with mortgage rates. Treasury yields, which reflect the return on government bonds, serve as a benchmark for other interest rates, including mortgages. Higher Treasury yields typically translate into higher mortgage rates.
- Explanation of how mortgage rates are influenced by the yield curve. The yield curve illustrates the relationship between interest rates and the maturity of debt. A steepening yield curve, often associated with rising long-term interest rates (influenced by government borrowing), can signal higher future mortgage rates.
- Impact of government bond auctions on the overall interest rate environment. Large government bond auctions can absorb significant amounts of capital, impacting the overall interest rate environment and pushing mortgage rates upward.
H3: The Impact on Mortgage Affordability
Higher mortgage rates directly impact affordability. As interest rates increase, monthly mortgage payments rise, making homeownership less accessible for many potential buyers. This can lead to decreased demand in the housing market, potentially impacting property values and overall market stability. For example, a small increase in interest rates can significantly increase the total cost of a mortgage over its lifetime.
H2: Strategies for Borrowers in a High-Debt Environment
Navigating a high-debt environment with rising mortgage rates requires strategic planning and proactive measures.
- Shop around for the best mortgage rates. Comparing offers from multiple lenders is crucial to securing the most favorable terms.
- Consider a shorter-term mortgage to reduce overall interest paid. While monthly payments will be higher, you’ll pay less interest overall.
- Improve your credit score to qualify for better rates. A higher credit score demonstrates creditworthiness, making you a less risky borrower and potentially securing lower interest rates.
- Save a larger down payment to reduce the loan amount. A larger down payment reduces the loan amount, thereby lowering the monthly payments and overall interest paid.
- Explore government-backed loan programs (if applicable). Programs like FHA loans can offer more accessible options for borrowers with lower credit scores or smaller down payments.
H3: Long-Term Financial Planning in a High-Debt Economy
Thorough financial planning is crucial in a high-debt economy characterized by potentially fluctuating interest rates. Creating a realistic budget, tracking expenses, and planning for unexpected events are essential to maintaining financial stability. Consulting with a qualified financial advisor can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
Conclusion:
The rising federal debt poses a significant challenge to the economy, and its impact on mortgage rates is undeniable. As government borrowing increases, competition for loanable funds rises, resulting in higher interest rates for mortgages. This, in turn, affects mortgage affordability and potentially the overall housing market. Borrowers need to be aware of these dynamics and take proactive steps to navigate this environment, such as securing the best possible interest rates and improving their credit scores. Staying informed about the relationship between rising federal debt and mortgage rates is crucial for making sound financial decisions. Understanding the implications of rising federal debt on your mortgage is key to responsible homeownership.

Featured Posts
-
 First Class Stamp Price Hike 1 70 Blow To Consumers
May 19, 2025
First Class Stamp Price Hike 1 70 Blow To Consumers
May 19, 2025 -
 Are Off Field Issues Distracting Clemson Fans From Spring Practice
May 19, 2025
Are Off Field Issues Distracting Clemson Fans From Spring Practice
May 19, 2025 -
 Toekomst Maastricht Airport Minder Passagiers In 2025
May 19, 2025
Toekomst Maastricht Airport Minder Passagiers In 2025
May 19, 2025 -
 Stolen Dreams A Restaurant Owners Fight For Justice
May 19, 2025
Stolen Dreams A Restaurant Owners Fight For Justice
May 19, 2025 -
 Uk Voters Express Concerns Over Governments Spring Budget Proposals
May 19, 2025
Uk Voters Express Concerns Over Governments Spring Budget Proposals
May 19, 2025
