Rosy Apple Aphid Infestation: Significant Reduction In Apple Production Expected
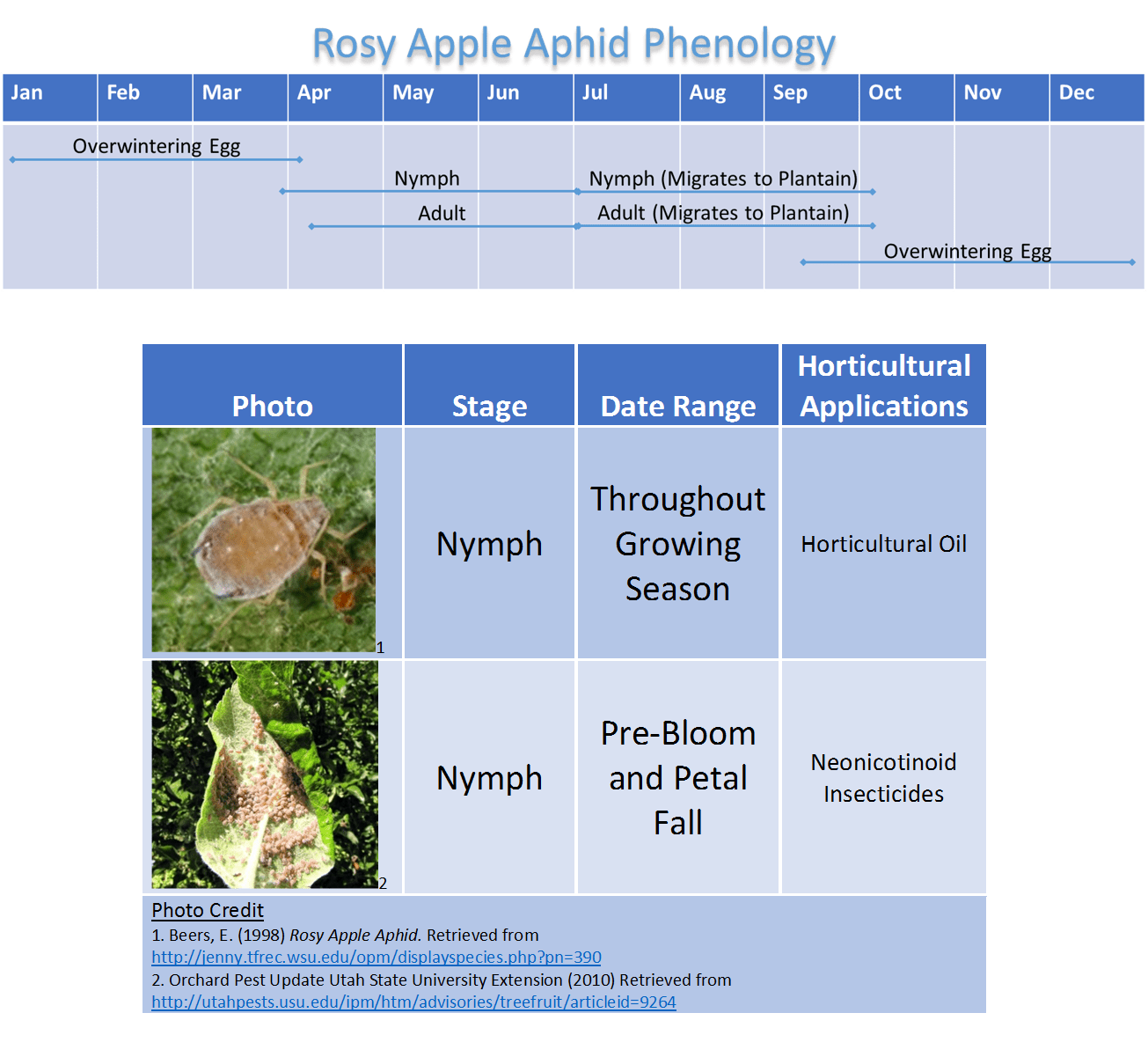
Table of Contents
Understanding Rosy Apple Aphid Behavior and Life Cycle
The rosy apple aphid's life cycle is complex and contributes to its rapid spread and ability to inflict significant damage. Its prolific reproduction and adaptability make it a formidable apple pest. Understanding this life cycle is key to effective apple aphid infestation management.
-
Life Cycle: The rosy apple aphid overwinters as eggs laid on the buds of apple trees. In spring, these eggs hatch into nymphs, which undergo several molts before developing into adult aphids. Adult aphids reproduce asexually throughout the growing season, resulting in rapid population growth and multiple generations. This high infestation rate makes quick action essential. The seasonal impact is greatest during spring and early summer.
-
Stages of Development:
- Egg: Tiny, oval, and reddish-brown, laid on apple buds.
- Nymph: Small, wingless aphids that actively feed.
- Adult: Winged or wingless aphids; the winged forms disperse to new locations.
-
Feeding Locations: Rosy apple aphids primarily feed on the underside of young leaves, causing leaf curling and distortion. They also feed on shoots and buds.
-
Environmental Factors: Warmer temperatures and moderate humidity favor rapid population growth. Extreme weather conditions can, however, limit their development.
Identifying Rosy Apple Aphid Infestations: Early Detection is Key
Early detection of a rosy apple aphid infestation is paramount for minimizing damage. Recognizing the visual symptoms early allows for prompt intervention and prevents the apple aphid infestation from reaching devastating levels.
- Visual Signs of Infestation:
- Leaf Curling: Leaves become severely curled and distorted, often reddish in color.
- Honeydew Production: Aphids excrete a sticky substance called honeydew, which provides a breeding ground for sooty mold, a black fungus that further reduces photosynthesis.
- Aphid Presence: Clusters of pinkish-gray aphids can be seen on the undersides of leaves and young shoots. Close visual identification is crucial.
[Insert images/illustrations here showing infected apple leaves and aphids]
-
Importance of Early Detection: Early detection significantly reduces the extent of damage and allows for less intensive control measures. Delaying intervention can lead to substantial yield losses and compromised fruit quality.
-
Inspection Methods: Regular monitoring, including visual checks of leaves and shoots, especially during the spring and early summer months, is essential for early detection.
The Impact of Rosy Apple Aphid Infestations on Apple Production
Rosy apple aphid infestations have severe consequences for apple production, leading to both direct and indirect losses. The economic impact on growers can be substantial.
-
Direct Effects:
- Yield Reduction: Heavy infestations cause significant reductions in apple yield.
- Fruit Quality: Apples may be smaller, misshapen (deformed apples), and develop blemishes, impacting their marketability.
- Premature Fruit Drop: Infested trees may experience premature fruit drop, further reducing the harvest.
-
Indirect Effects: Honeydew production fosters sooty mold growth, reducing photosynthesis and making the tree more susceptible to other diseases.
-
Economic Impact: The financial losses incurred due to reduced yields, poor fruit quality, and increased management costs can be substantial, making apple pest control a top priority for growers. [Insert statistics on economic impact if available].
Management and Control Strategies for Rosy Apple Aphids
Effective rosy apple aphid management requires a multi-pronged approach using integrated pest management (IPM) principles. This involves combining several control methods for optimal results while minimizing environmental impact.
-
Biological Control:
- Natural Predators: Encouraging natural predators such as ladybugs, lacewings, and hoverflies can help control aphid populations.
-
Cultural Control:
- Pruning: Proper pruning improves air circulation and reduces aphid infestation.
- Sanitation: Removing fallen leaves and other debris can help eliminate overwintering eggs.
-
Chemical Control:
- Pesticides: Specific insecticides can be used to control aphid populations, but their use should be carefully considered and integrated into an IPM strategy.
-
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Combining these methods to achieve the best results while minimizing environmental impact is crucial. An IPM strategy balances the use of biological, cultural, and chemical controls to effectively manage apple pest populations sustainably.
Protecting Apple Crops from Rosy Apple Aphid Infestation
Rosy apple aphid infestations pose a serious threat to apple production, leading to significant yield reductions and decreased fruit quality. Early detection through regular monitoring is crucial, and proactive implementation of integrated pest management (IPM) strategies is essential to prevent or mitigate the devastating impact of these apple pests. By combining biological controls, cultural practices, and carefully considered use of chemical controls, growers can effectively protect their apple crops from rosy apple aphids. For more information on managing rosy apple aphids and other apple pests, consult your local agricultural extension office or reputable online resources. [Insert link to relevant website here]

Featured Posts
-
 Ofcom Regulation Royal Mails Plea For Change
May 19, 2025
Ofcom Regulation Royal Mails Plea For Change
May 19, 2025 -
 Rescate Y Transformacion En Cortes Quienes Son Los Aspirantes A La Diputacion
May 19, 2025
Rescate Y Transformacion En Cortes Quienes Son Los Aspirantes A La Diputacion
May 19, 2025 -
 Inscripcion De Candidatos Cne Plazo Final Para Quienes No Fueron A Primarias
May 19, 2025
Inscripcion De Candidatos Cne Plazo Final Para Quienes No Fueron A Primarias
May 19, 2025 -
 Unlock Postmans Full Potential Expert Level Techniques
May 19, 2025
Unlock Postmans Full Potential Expert Level Techniques
May 19, 2025 -
 Syzitiseis Ypoyrgon Eksoterikon Kyproy Kai Oyggarias Kypriako Kai Proedria Ee Sto Epikentro
May 19, 2025
Syzitiseis Ypoyrgon Eksoterikon Kyproy Kai Oyggarias Kypriako Kai Proedria Ee Sto Epikentro
May 19, 2025
