Santorini Earthquake Trends: Decreasing Quakes, But Future Seismic Risk Remains Uncertain
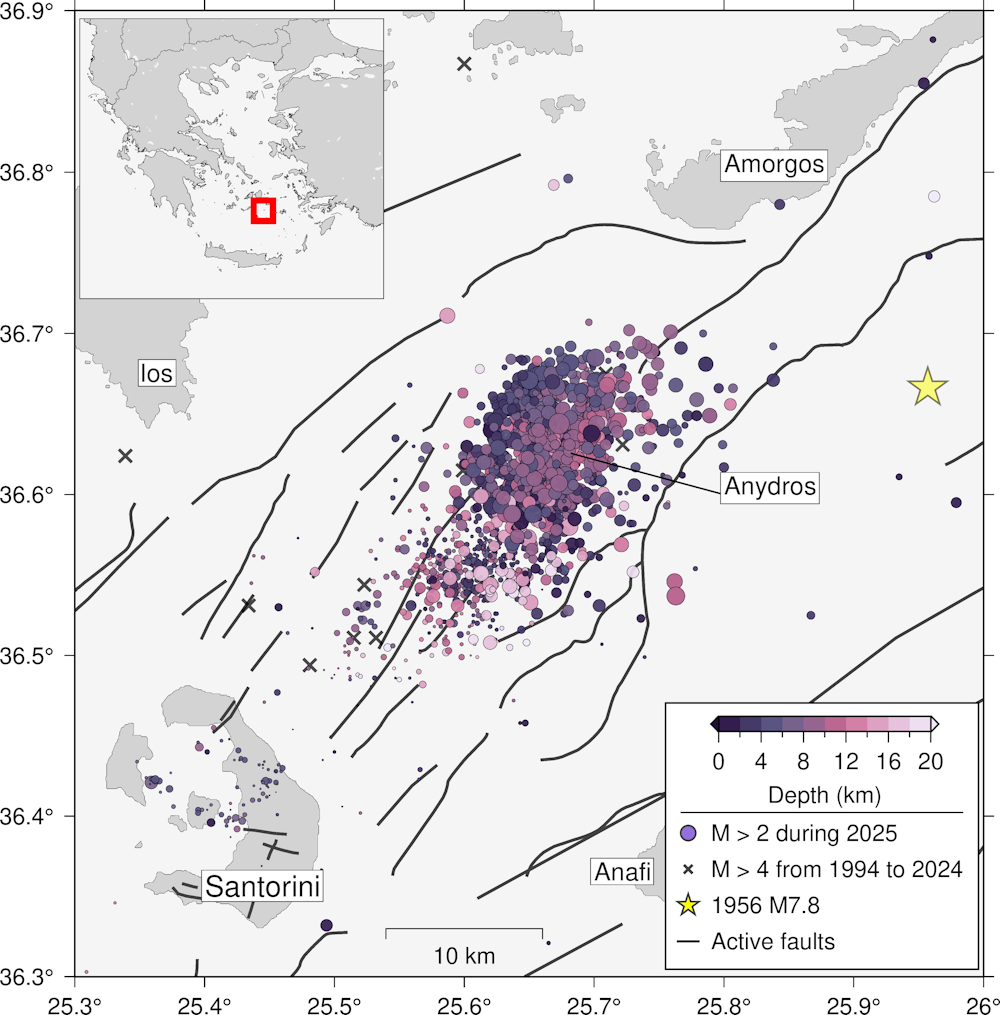
Table of Contents
Historical Seismic Activity in Santorini
Santorini's dramatic landscape is a direct result of its volcanic history, a history interwoven with powerful earthquakes. Throughout history, the island has experienced numerous significant seismic events, some causing devastating damage and shaping the island's very geography. These historical earthquakes provide crucial context for understanding current seismic activity and potential future risks.
- The Minoan Eruption (circa 1600 BC): This cataclysmic volcanic eruption is considered one of the largest in recorded history. It triggered massive tsunamis and widespread destruction, likely contributing to the demise of the Minoan civilization. The eruption itself was accompanied by intense seismic activity.
- 1956 Santorini Earthquake: This relatively recent earthquake caused significant damage to buildings and infrastructure, highlighting the island's vulnerability. The magnitude of this quake, while not as devastating as historical events, served as a stark reminder of the ongoing seismic risk.
- Archaeological Evidence: Excavations at Akrotiri, a Minoan city buried by the eruption, reveal evidence of significant earthquake damage predating the eruption, demonstrating a long history of seismic events impacting the island.
Numerous historical accounts and geological studies document these events, providing valuable insights into the long-term seismic behavior of Santorini. Further research into historical records and geological formations is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of Santorini's seismic history.
Recent Earthquake Trends and Data Analysis
Recent years have seen an apparent decrease in the frequency of noticeable earthquakes in Santorini compared to previous decades. This observation, however, does not indicate a lessening of the inherent seismic risk. Data from the National Observatory of Athens, the Hellenic Unified Seismological Network, and other international seismological institutions show a trend towards fewer high-magnitude events.
- Data from the last decade: Analysis reveals a reduced number of earthquakes exceeding magnitude 4.0 compared to previous decades, although smaller magnitude tremors still occur frequently.
- Monitoring Technologies: Advanced seismic monitoring stations across the Aegean Sea, including those located on Santorini itself, provide real-time data on seismic activity, enabling more accurate assessments of earthquake frequency and magnitude.
- Peer-Reviewed Studies: Several peer-reviewed studies analyzing seismic data from the Santorini area support this observed decrease in high-magnitude earthquakes, but underscore the need for continued vigilance.
While the decrease in frequency of larger earthquakes is encouraging, it's crucial to avoid complacency. The data highlights the importance of ongoing monitoring and analysis of seismic activity to accurately assess future risks. Visual representations of this data, such as graphs illustrating earthquake magnitude and frequency over time, would further clarify the observed trend.
Geological Factors Contributing to Santorini's Seismic Activity
Santorini's unique geological setting is the primary driver of its seismic activity. The island sits atop a complex volcanic system within the Aegean arc, a highly active tectonic region. The interplay of volcanic processes and tectonic plate movement creates a dynamic and unstable environment.
- The Volcanic Caldera: Santorini's iconic caldera, a massive volcanic crater formed by past eruptions, is a significant contributor to seismic activity. Magma movement beneath the caldera generates pressure, causing tremors and occasional larger earthquakes.
- Tectonic Plate Boundaries: The convergence of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates in the Aegean Sea region generates significant stress and strain, leading to frequent earthquakes throughout the area, including Santorini.
- Magma Chambers: The presence of magma chambers beneath the island further increases the potential for seismic events. Pressure fluctuations within these chambers can trigger earthquakes of varying magnitudes.
Understanding these geological factors is essential for accurately assessing the long-term seismic risk and developing effective mitigation strategies.
Assessing Future Seismic Risk: Uncertainties and Predictions
Predicting earthquakes with precision remains a significant challenge in seismology. While scientists can identify regions of high seismic risk based on geological factors and historical data, predicting the exact timing and magnitude of future earthquakes is currently impossible. Santorini, due to its complex geological setting, poses particular challenges for accurate earthquake forecasting.
- Limitations of Prediction Models: Current earthquake prediction models rely on statistical analysis of past seismic activity and geological data. These models provide probabilities of future events, but not precise predictions.
- Ongoing Research: Scientists are continuously refining earthquake prediction models and developing new monitoring techniques to improve accuracy. Research focuses on improving our understanding of the processes leading to earthquakes, such as magma movement and tectonic stress accumulation.
- Importance of Preparedness: Given the inherent uncertainties in earthquake prediction, focusing on preparedness and mitigation strategies is paramount. This includes strengthening building codes, developing early warning systems, and educating the public about earthquake safety.
The Importance of Seismic Monitoring and Early Warning Systems
Sophisticated seismic monitoring networks are crucial for detecting and measuring earthquakes, providing essential data for risk assessment and early warning systems. These networks utilize a variety of seismic sensors to detect even the smallest tremors.
- Seismic Sensors: A range of sensors, including broadband seismometers and accelerometers, are strategically placed to capture seismic waves generated by earthquakes, enabling precise location and magnitude determination.
- Early Warning Systems: Early warning systems can provide precious seconds or minutes of warning before the arrival of strong shaking, allowing for actions to minimize damage and potential casualties. These systems require sophisticated real-time data processing and rapid communication infrastructure.
- Existing Systems: The Hellenic Unified Seismological Network plays a vital role in monitoring seismic activity in the Aegean region, including Santorini. While an island-specific early warning system might not yet exist, the broader regional network provides valuable data for assessing the risk.
Conclusion
Santorini earthquake trends reveal a recent decrease in the frequency of high-magnitude earthquakes, but the island remains seismically active, and future seismic risk persists. The complex interplay of volcanic and tectonic factors contributes to this ongoing risk. While predicting the precise timing and magnitude of future events is not possible, ongoing monitoring, research, and robust preparedness strategies are crucial. Understanding the geological factors and continued monitoring efforts are paramount. Stay informed about Santorini earthquake trends by following reputable sources like the National Observatory of Athens and the Hellenic Unified Seismological Network, and take steps to prepare yourself and your property for potential seismic activity. Learn about earthquake preparedness and safety measures to minimize potential risks.

Featured Posts
-
 Mtv Vs Cbs Did The Vma Simulcast Signal Mtvs Decline
May 11, 2025
Mtv Vs Cbs Did The Vma Simulcast Signal Mtvs Decline
May 11, 2025 -
 James O Keefes Undercover Footage More Trouble For Prince Andrew
May 11, 2025
James O Keefes Undercover Footage More Trouble For Prince Andrew
May 11, 2025 -
 Chem Zanimalis Boris Dzhonson I Ego Zhena V Tekhase Foto
May 11, 2025
Chem Zanimalis Boris Dzhonson I Ego Zhena V Tekhase Foto
May 11, 2025 -
 Anunoby Anota 27 Puntos Knicks Vencen A Sixers En Emocionante Partido
May 11, 2025
Anunoby Anota 27 Puntos Knicks Vencen A Sixers En Emocionante Partido
May 11, 2025 -
 Who Played Most With Thomas Mueller At Bayern Munich A Statistical Analysis
May 11, 2025
Who Played Most With Thomas Mueller At Bayern Munich A Statistical Analysis
May 11, 2025
