Saskatchewan Wildfire Season: Hotter Summer Fuels Concerns
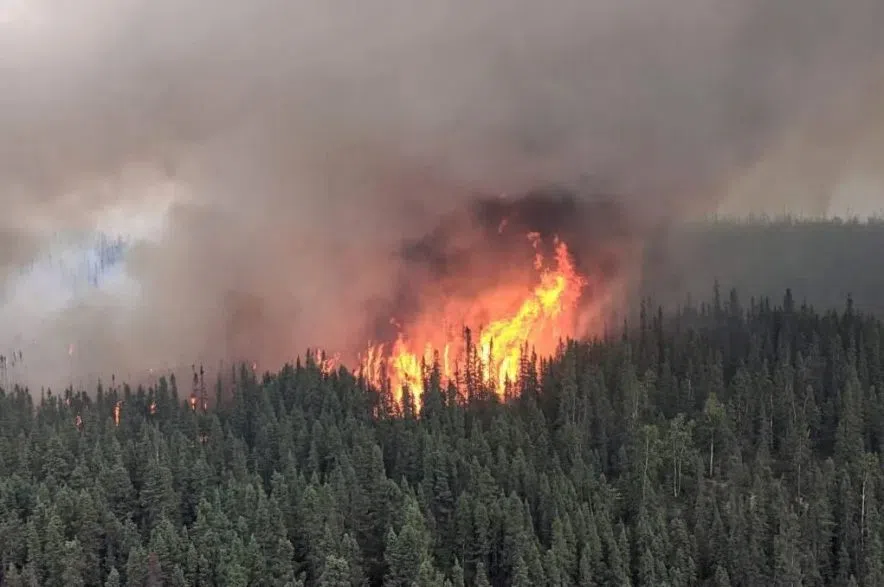

Table of Contents
Rising Temperatures and Drought Conditions in Saskatchewan
Climate Change's Impact
Climate change is undeniably fueling the intensity of Saskatchewan's wildfire seasons. Environment Canada data shows a clear upward trend in average temperatures, with the last decade experiencing some of the warmest years on record. This warming trend leads to several factors that exacerbate wildfire risks:
- Increased average temperatures: Higher temperatures dry out vegetation, making it highly flammable.
- Reduced snowfall: Less snowfall means less moisture in the soil, leaving the landscape parched and vulnerable.
- Earlier snowmelt: An earlier snowmelt accelerates the drying process, creating a longer fire season.
- Prolonged dry periods: Extended periods without significant rainfall intensify drought conditions, creating a tinderbox ready to ignite.
Impact on Vegetation
Drought conditions significantly impact vegetation, transforming the Saskatchewan landscape into a wildfire hazard. The lack of moisture increases the flammability of various plant types:
- Dried-out grasses: Dry grasses are extremely susceptible to ignition and rapid fire spread.
- Increased density of underbrush: Dense underbrush acts as fuel, allowing fires to move quickly through the landscape.
- Dead trees: Dead trees, weakened by drought, are easily ignited and contribute to intense, crown fires.
Specifically, the grasslands and boreal forests prevalent in Saskatchewan are particularly vulnerable during prolonged dry spells. The combination of dry vegetation and strong winds creates ideal conditions for rapid fire spread and large-scale wildfires.
Increased Wildfire Activity and its Consequences
Frequency and Severity
Recent years have witnessed a disturbing increase in both the frequency and severity of wildfires in Saskatchewan. While historical data shows periodic wildfire activity, the current trend surpasses historical averages significantly. This is evident in:
- Number of wildfires: A marked increase in the number of wildfires reported annually.
- Hectares burned: A substantial rise in the total area of land affected by wildfires.
- Duration of fire seasons: Longer fire seasons extending well into the autumn months.
(Ideally, a chart or graph visualizing this data would be included here.)
Economic and Social Impacts
The consequences of increased wildfire activity extend far beyond the immediate damage to the environment. Saskatchewan's economy and its communities suffer significant impacts:
- Economic losses: Damage to infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and power lines, leads to substantial economic losses. The timber industry also suffers significant losses. Tourism is severely disrupted, affecting local businesses. The costs associated with wildfire suppression efforts are also considerable.
- Health issues: Smoke from wildfires poses serious health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations. Respiratory illnesses, such as asthma and bronchitis, are common.
- Disruption to communities: Wildfires can lead to evacuations, displacement of communities, and the loss of homes and livelihoods.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Role of Fire Management Agencies
Provincial and federal agencies play a crucial role in wildfire prevention and suppression. These agencies employ various strategies:
- Fire suppression techniques: Utilizing highly trained crews and advanced firefighting equipment.
- Controlled burns: Conducting prescribed burns to reduce fuel loads and prevent larger, uncontrolled wildfires.
- Public awareness campaigns: Educating the public about wildfire prevention and safety measures.
- Early warning systems: Implementing systems to monitor fire danger and provide timely warnings.
Community Preparedness and Responsibilities
Community preparedness is essential in mitigating wildfire risks. Individuals and communities must take proactive steps:
- Creating defensible space around homes: Clearing vegetation and creating a buffer zone to protect homes from approaching wildfires.
- Fire safety precautions: Practicing safe campfire habits and following fire bans.
- Evacuation plans: Developing and practicing evacuation plans in case of a wildfire emergency.
- Awareness of fire bans: Staying informed about fire bans and restrictions imposed by authorities.
Conclusion
The increased risk of Saskatchewan wildfires this season is a result of a confluence of factors: hotter summers, prolonged drought conditions, and increased wildfire activity, all exacerbated by climate change. The long-term impacts of climate change on wildfire risk in Saskatchewan remain a significant concern. It is crucial to stay informed about fire bans, evacuation orders, and to take proactive measures to protect our communities and environment. Learn more about Saskatchewan wildfire safety and preparedness by visiting the official government websites. Together, we can mitigate the risks and safeguard Saskatchewan from devastating wildfires. Take action today for a safer Saskatchewan wildfire season.

Featured Posts
-
 The Impact Of A Narcissistic Father Miley Cyrus Perspective
May 31, 2025
The Impact Of A Narcissistic Father Miley Cyrus Perspective
May 31, 2025 -
 Vatican City To Feature As Grand Finale Location For Giro D Italia 2025
May 31, 2025
Vatican City To Feature As Grand Finale Location For Giro D Italia 2025
May 31, 2025 -
 Navigating Office Lunches 6 Etiquette Rules To Follow
May 31, 2025
Navigating Office Lunches 6 Etiquette Rules To Follow
May 31, 2025 -
 Banksy Auction Iconic Broken Heart Artwork
May 31, 2025
Banksy Auction Iconic Broken Heart Artwork
May 31, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Dangerous Climate Whiplash On Cities A Comprehensive Report
May 31, 2025
The Impact Of Dangerous Climate Whiplash On Cities A Comprehensive Report
May 31, 2025
