School Desegregation Order Terminated: A Turning Point In Education Equity
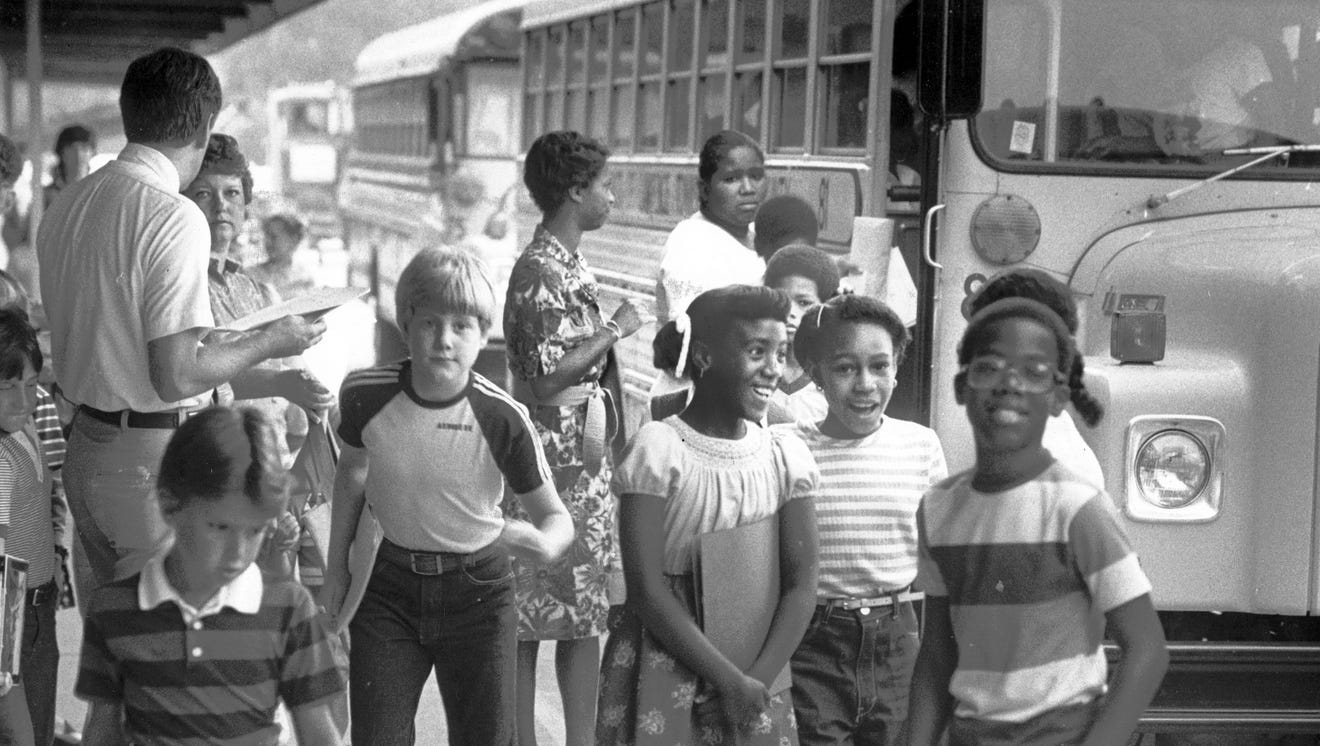
Table of Contents
The History of School Desegregation Orders and Their Impact
The history of school desegregation in the United States is a long and arduous journey, marked by landmark legal battles and persistent resistance. The landmark Supreme Court case Brown v. Board of Education (1954) declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students to be unconstitutional. However, the implementation of this decision faced significant resistance, leading to decades of legal battles and struggles to achieve meaningful integration. Following Brown, numerous federal court orders were issued mandating desegregation in various school districts across the nation. These orders often involved busing students, redrawing school district boundaries, and implementing affirmative action programs to achieve racial balance.
- Impact on student achievement: Studies have shown mixed results regarding the impact of school desegregation on student achievement. While some studies suggest positive effects, particularly for minority students, others found minimal impact or even negative consequences in certain contexts. The effectiveness often depended on the specific implementation of desegregation plans and the resources available to schools.
- Impact on racial integration in schools: School desegregation orders, while imperfect, undeniably led to increased racial integration in many schools. This increased exposure to diverse student populations offered potential benefits for social development and understanding.
- Socioeconomic effects of desegregation (or continued segregation): School desegregation efforts often intersected with socioeconomic disparities. Many desegregation plans struggled to address the underlying inequalities in school funding and resources that often disproportionately affected minority and low-income communities.
- Long-term effects on educational opportunities: The legacy of school segregation continues to manifest in persistent achievement gaps and disparities in educational opportunities. The long-term effects of the past are still felt today, highlighting the need for ongoing efforts to address systemic inequities.
The Rationale Behind the Termination of the Desegregation Order
The decision to terminate the school desegregation order was likely based on a combination of factors. Proponents argued that the order had served its purpose and that sufficient integration had been achieved. This claim often ignored the persistent racial and socioeconomic segregation still evident in many school systems.
- Claims of successful integration: Arguments for termination often centered on the claim that schools had achieved a sufficient level of racial integration, rendering the order obsolete. However, this often overlooked the subtle, yet pervasive, forms of segregation that persist even in seemingly integrated schools.
- Arguments for local control of schools: Advocates for termination frequently emphasized the importance of local control over education, suggesting that school districts should be free to manage their own affairs without external oversight. This argument, however, often disregarded the historical context of local control being used to perpetuate segregation.
- Concerns about the financial burden of maintaining desegregation efforts: The cost of implementing and maintaining desegregation plans, including busing and other initiatives, was often cited as a reason for termination. This argument, while acknowledging a real financial burden, failed to address the larger issue of equitable funding for all schools.
- Potential for legal challenges to the termination: The termination of the desegregation order itself might face legal challenges, based on arguments that it violates the constitutional rights of students to equal educational opportunities.
Analysis of the Legal Arguments Surrounding the Termination
The legal arguments used to justify the termination of the desegregation order will require careful scrutiny. Examining the legal precedents and constitutional principles involved is crucial. Any dissenting opinions or counterarguments will need thorough analysis to fully grasp the legal complexities of this decision and its potential long-term consequences. The legal battle over school desegregation is far from over.
Implications of the Termination for Educational Equity
The termination of the desegregation order poses significant risks to educational equity. The potential for increased racial segregation, exacerbated achievement gaps, and re-segregation of school districts is a serious concern.
- Increased racial segregation in schools: The most immediate concern is the potential for a return to more racially segregated schools. This would likely exacerbate existing inequalities and limit opportunities for minority students.
- Exacerbation of achievement gaps: The already significant achievement gaps between different racial and socioeconomic groups are likely to widen without the active intervention and monitoring provided by the desegregation order.
- Potential for re-segregation of school districts: The termination of the order could lead to the re-segregation of school districts, as schools are left to their own devices, potentially reverting to patterns of segregation.
- Impact on funding disparities between schools: Funding disparities between schools often correlate with racial and socioeconomic segregation. The termination of the order could worsen these funding disparities.
Potential Solutions and Future Strategies for Ensuring Educational Equity
Maintaining or restoring educational equity requires proactive and comprehensive strategies. These may include increased funding for under-resourced schools, the implementation of affirmative action programs, and a renewed commitment to diversity and inclusion initiatives.
- Increased funding for under-resourced schools: Addressing the persistent funding disparities between schools is crucial. This requires significant investment in under-resourced schools, particularly those serving minority and low-income communities.
- Implementation of affirmative action programs in education: Affirmative action programs can play a role in promoting diversity and ensuring equitable access to education. These programs need to be carefully designed and implemented to address potential concerns about fairness and equity.
- Promotion of diversity and inclusion initiatives: Schools need to actively promote diversity and inclusion through curriculum development, staff training, and student support programs.
- Strengthening of civil rights enforcement mechanisms: Stronger enforcement of civil rights laws is essential to ensure that schools comply with existing regulations and to prevent a return to segregated education.
Conclusion
The termination of this school desegregation order represents a significant turning point in the fight for educational equity. While the legal arguments and rationale behind the termination require careful examination, the potential consequences for racial segregation and educational disparities are alarming. The legacy of school segregation continues to cast a long shadow on educational opportunities for many students. The key takeaways are that the fight for educational equity is far from over and that proactive measures are needed to prevent a rollback of progress and ensure that all students have equal access to a quality education. Let's work together to ensure that the termination of this school desegregation order doesn't lead to a rollback of progress, but instead spurs renewed efforts to achieve true educational equity for all children. Learn more about how you can fight for school desegregation and support initiatives promoting equal access to education. The future of school desegregation and educational equity depends on our collective commitment to creating a just and equitable education system for all.
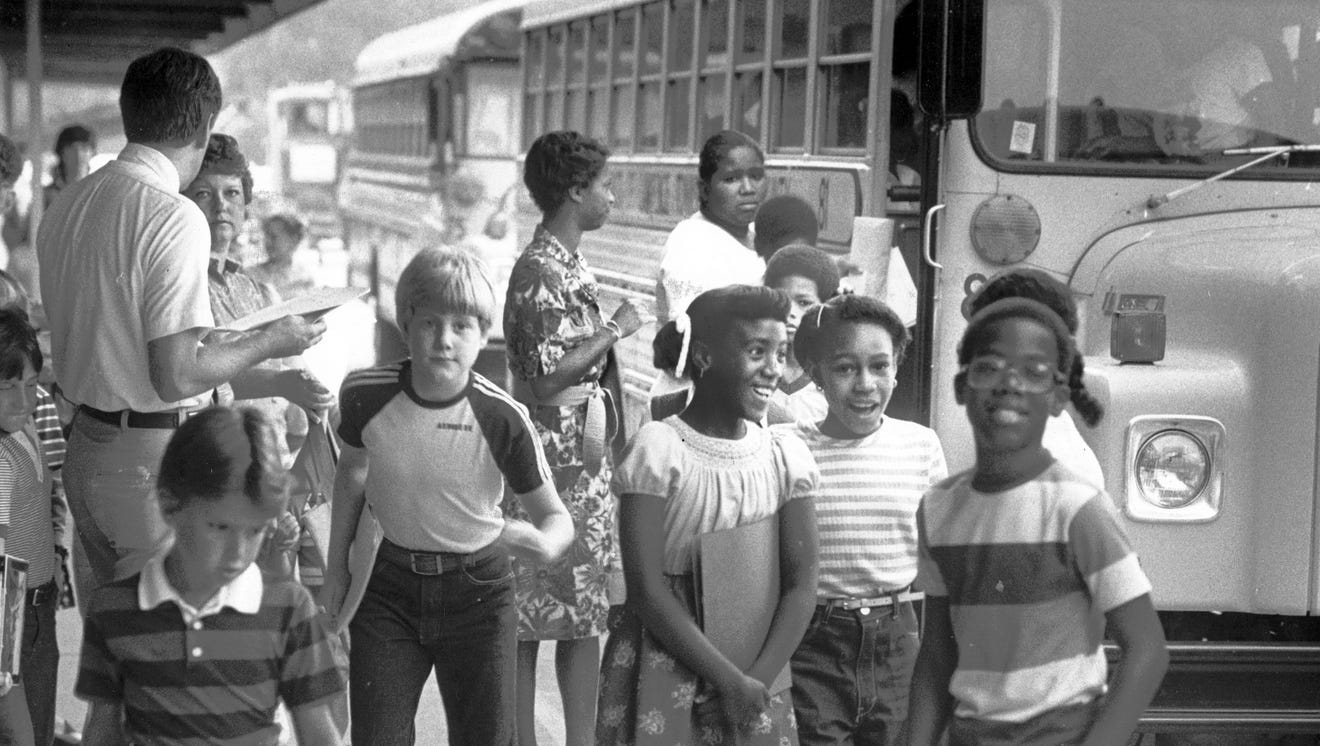
Featured Posts
-
 Wzyr Altjart Alsewdy Ybhth Frs Alastthmar Almshtrk Me Adhrbyjan
May 02, 2025
Wzyr Altjart Alsewdy Ybhth Frs Alastthmar Almshtrk Me Adhrbyjan
May 02, 2025 -
 Tesla Rejects Report Of Musks Potential Removal
May 02, 2025
Tesla Rejects Report Of Musks Potential Removal
May 02, 2025 -
 Nuclear Litigation Examining Current Cases And Future Implications
May 02, 2025
Nuclear Litigation Examining Current Cases And Future Implications
May 02, 2025 -
 Justice Department Dismisses Longstanding School Desegregation Order Implications For The Future
May 02, 2025
Justice Department Dismisses Longstanding School Desegregation Order Implications For The Future
May 02, 2025 -
 Trumps Tariffs A Court Challenge And Judicial Review
May 02, 2025
Trumps Tariffs A Court Challenge And Judicial Review
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Pm Modi To Co Chair Ai Summit Address Business Leaders In France
May 03, 2025
Pm Modi To Co Chair Ai Summit Address Business Leaders In France
May 03, 2025 -
 Image Rare La Profonde Emotion D Emmanuel Macron Face A La Douleur Des Victimes Israeliennes
May 03, 2025
Image Rare La Profonde Emotion D Emmanuel Macron Face A La Douleur Des Victimes Israeliennes
May 03, 2025 -
 Netanyahu Desapprouve Le Soutien De Macron A Un Etat Palestinien
May 03, 2025
Netanyahu Desapprouve Le Soutien De Macron A Un Etat Palestinien
May 03, 2025 -
 Pm Modis France Visit Ai Summit Co Chairmanship And Ceo Forum Address
May 03, 2025
Pm Modis France Visit Ai Summit Co Chairmanship And Ceo Forum Address
May 03, 2025 -
 Reaction Emotionnelle D Emmanuel Macron Apres Avoir Rencontre Des Victimes Israeliennes
May 03, 2025
Reaction Emotionnelle D Emmanuel Macron Apres Avoir Rencontre Des Victimes Israeliennes
May 03, 2025
