Scottish Coastline Restoration: Seagrass Planting Bids And Their Impact
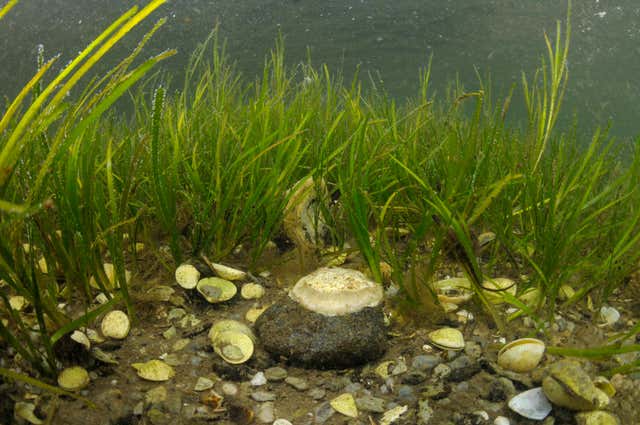

Table of Contents
The Importance of Seagrass Ecosystems in Scotland
Seagrass beds are often referred to as the "lungs of the sea," and for good reason. These underwater meadows play a crucial role in the health of Scotland's coastal waters. Their ecological importance is multifaceted, contributing significantly to carbon sequestration, providing vital habitat, and offering natural coastal protection.
- Carbon sequestration: Seagrass meadows are incredibly efficient carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide at a rate exceeding that of many terrestrial rainforests. This helps mitigate climate change and improve water quality.
- Habitat provision: They serve as nurseries for numerous commercially important fish species, such as cod and plaice, as well as providing refuge for invertebrates and other marine life. The complex structure of seagrass provides shelter and feeding grounds, supporting a rich and diverse food web.
- Coastal protection: The dense root systems of seagrass stabilize sediments, reducing coastal erosion and protecting shorelines from the impacts of storms and wave action. This natural defense mechanism is crucial in safeguarding vulnerable coastal communities and infrastructure.
- Biodiversity hotspots: Seagrass beds are biodiversity hotspots, supporting a vast array of marine life, from microscopic organisms to larger vertebrates. Their presence enhances the overall health and resilience of the entire coastal ecosystem.
Estimates suggest that Scotland has lost significant seagrass acreage over the past century. Restoring these vital habitats offers immense potential benefits, including increased fish stocks, improved water quality, enhanced coastal resilience, and a significant contribution to climate change mitigation. The potential for carbon sequestration alone makes investing in seagrass restoration a highly effective climate action strategy.
Seagrass Planting Bids: Funding and Project Implementation
Securing funding for ambitious seagrass restoration projects requires a competitive bidding process. Organizations across Scotland are vying for resources to undertake this crucial work.
- Bidders: A diverse range of organizations participate in these bids, including NGOs like the Marine Conservation Society, academic institutions like Scottish universities conducting marine research, and government agencies like NatureScot.
- Funding Sources: Funding sources are varied, encompassing government grants from bodies such as the Scottish Government and UK government departments, private investment from environmentally conscious companies, and even EU funding streams (where applicable post-Brexit).
- Successful Bid Criteria: Successful bids are judged on several key criteria, including the scientific feasibility of the proposed project, the level of community engagement planned, the long-term sustainability of the restoration efforts, and a clear demonstration of environmental benefit.
Several successful seagrass planting projects are underway in Scotland. These projects employ various methodologies, including the transplantation of seagrass shoots from existing healthy beds, the sowing of seeds, and the deployment of innovative techniques to enhance survival rates. The scale of these projects ranges from small-scale pilot schemes to larger, more ambitious undertakings aiming to restore extensive areas of seagrass habitat.
Assessing the Impact of Seagrass Restoration Projects
Monitoring the success of seagrass planting initiatives is paramount. A range of scientific methods are employed to track progress and evaluate impact.
- Monitoring techniques: These include regular underwater surveys to assess seagrass growth and survival rates, the use of remote sensing technologies like satellite imagery and drones to map seagrass extent, and biodiversity assessments to analyze changes in species abundance and distribution within restored areas.
- Impact indicators: Key indicators of success include increased seagrass cover, higher survival rates of planted shoots, enhanced biodiversity within the restored areas, and demonstrable improvements in coastal protection.
- Challenges: Challenges faced include appropriate site selection considering factors like water quality, sediment type, and wave exposure, as well as the ongoing need for long-term maintenance and monitoring to ensure the persistence of the restored seagrass meadows.
Challenges and Future Directions for Seagrass Restoration in Scotland
Scaling up seagrass planting efforts to achieve significant and lasting impact requires addressing several challenges:
- Sustainable funding: Securing long-term funding for maintenance, monitoring, and adaptive management is critical for the ongoing success of these projects.
- Climate change impacts: Addressing the potential impacts of climate change, such as rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification, on seagrass survival and resilience is essential. Research into climate-resilient seagrass species and planting techniques is needed.
- Public awareness: Raising public awareness and fostering community involvement in seagrass restoration efforts is crucial for building support and ensuring the long-term sustainability of these initiatives.
Future research should focus on improving planting techniques, developing innovative monitoring strategies, and better understanding the long-term effects of climate change on seagrass ecosystems. Collaboration among researchers, policymakers, and stakeholders is essential to develop effective and sustainable seagrass restoration strategies.
Conclusion
Seagrass planting bids are playing a pivotal role in the revitalization of Scotland's coastline. These projects offer a powerful combination of ecological benefits, contributing significantly to biodiversity, coastal protection, and climate change mitigation through robust carbon sequestration. While challenges remain, particularly in securing sustained funding and addressing the impacts of climate change, the positive impact of successful seagrass restoration is undeniable. Continued investment in research, innovative approaches to planting and monitoring, and strong community engagement are vital to ensure the long-term success of these vital conservation efforts. The future of Scotland's coastline depends on our collective commitment to protecting and restoring this precious natural resource.
Call to Action: Support and participate in initiatives promoting Scottish coastline restoration through seagrass planting. Learn more about upcoming seagrass planting bids and how you can contribute to this crucial work. Volunteer your time, donate to relevant organizations, or simply spread awareness about the importance of seagrass meadows. Together, we can safeguard Scotland's precious coastline for future generations.

Featured Posts
-
 How To Pay For Spotify On I Phone New Payment Options Explained
May 04, 2025
How To Pay For Spotify On I Phone New Payment Options Explained
May 04, 2025 -
 Canelo Alvarez Vs Ggg Nyc Press Conference Heralds Undisputed Championship Bout
May 04, 2025
Canelo Alvarez Vs Ggg Nyc Press Conference Heralds Undisputed Championship Bout
May 04, 2025 -
 Pula Gibonni Najavio Veliki Koncert
May 04, 2025
Pula Gibonni Najavio Veliki Koncert
May 04, 2025 -
 The Kanye West Bianca Censori Relationship A Look At Power Imbalances
May 04, 2025
The Kanye West Bianca Censori Relationship A Look At Power Imbalances
May 04, 2025 -
 Sheins Stalled London Ipo Us Tariffs Cast A Long Shadow
May 04, 2025
Sheins Stalled London Ipo Us Tariffs Cast A Long Shadow
May 04, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Verstappens New Arrival Childs Birth Announced Before Miami Race
May 04, 2025
Verstappens New Arrival Childs Birth Announced Before Miami Race
May 04, 2025 -
 Max Verstappen Welcomes Baby Ahead Of Miami Grand Prix Name Unveiled
May 04, 2025
Max Verstappen Welcomes Baby Ahead Of Miami Grand Prix Name Unveiled
May 04, 2025 -
 Max Verstappens First Child Name Announced Before Miami Grand Prix
May 04, 2025
Max Verstappens First Child Name Announced Before Miami Grand Prix
May 04, 2025 -
 Maks Ferstappen Obyavlenie O Rozhdenii Docheri
May 04, 2025
Maks Ferstappen Obyavlenie O Rozhdenii Docheri
May 04, 2025 -
 Lili Ferstappen Rozhdenie Docheri Gonschika Formuly 1
May 04, 2025
Lili Ferstappen Rozhdenie Docheri Gonschika Formuly 1
May 04, 2025
