Taiwan Turns To LNG: Replacing Nuclear Power With Natural Gas
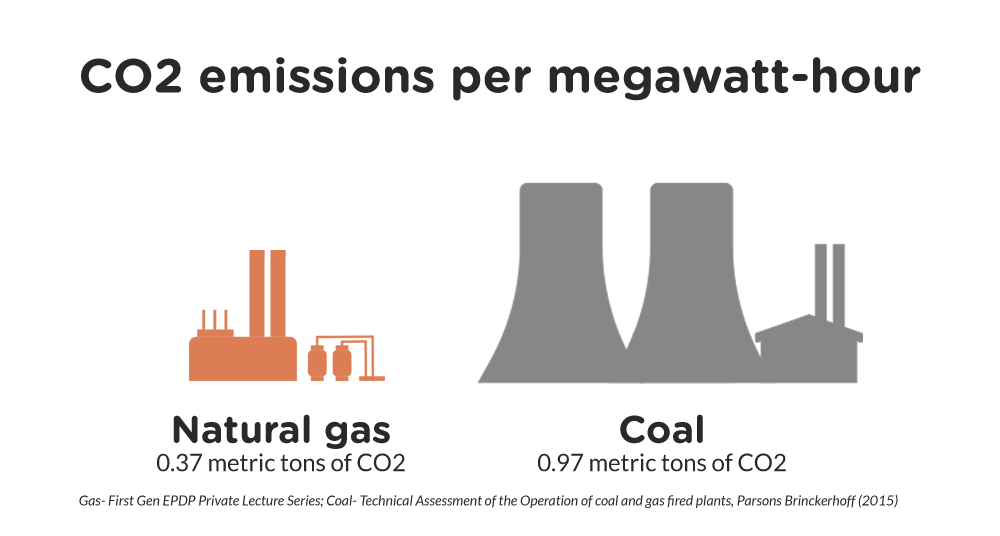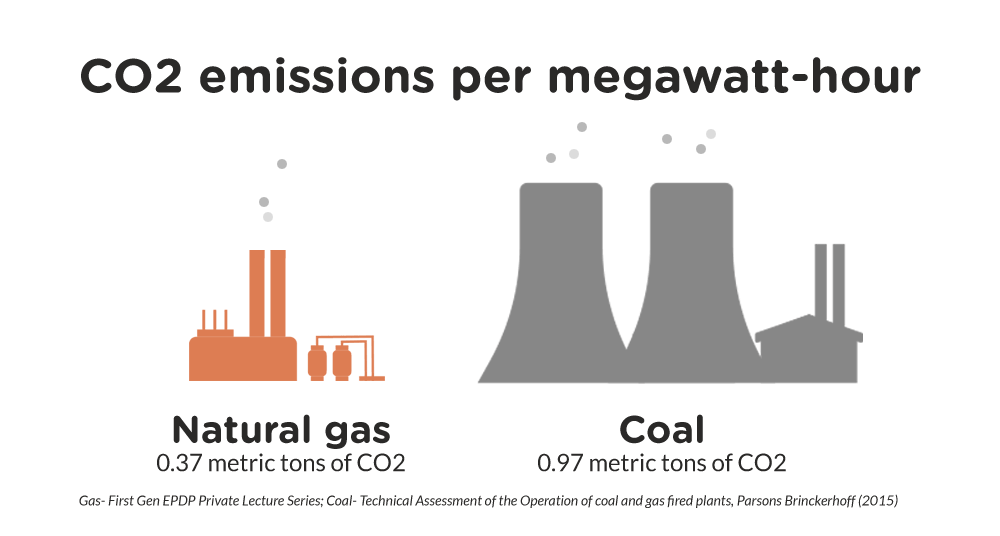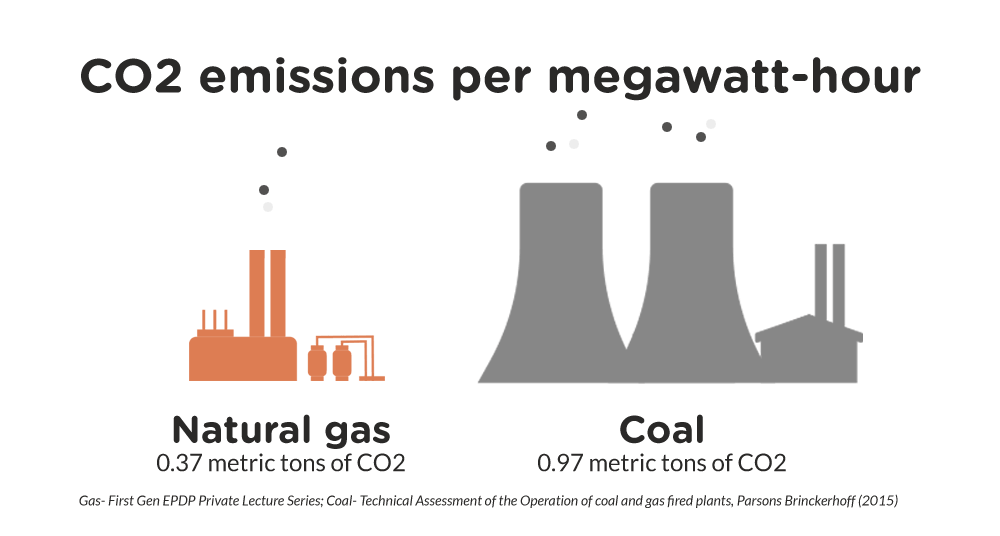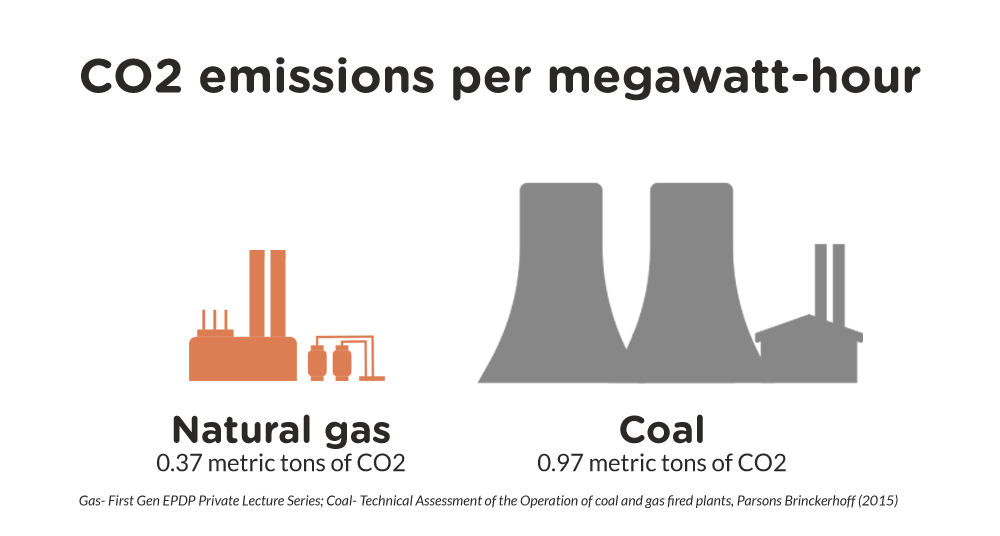
Table of Contents
The Decline of Nuclear Power in Taiwan
The decreasing reliance on nuclear power in Taiwan is a result of a confluence of factors, primarily public opposition and the aging infrastructure of existing plants.
Public Opposition and Safety Concerns
- History of Anti-Nuclear Protests: Decades of anti-nuclear protests, fueled by concerns about safety and waste disposal, have significantly shaped public opinion.
- Specific Incidents: Incidents, both real and perceived, have eroded public trust in nuclear energy. These include minor accidents at existing plants and the global impact of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in Japan.
- Impact of Fukushima: The 2011 Fukushima disaster dramatically amplified existing anxieties, leading to widespread calls for phasing out nuclear power. The public perception shifted significantly towards viewing nuclear energy as inherently risky, influencing government policy.
Aging Nuclear Plants and Decommissioning Plans
- Operational Plants and Decommissioning: Taiwan currently operates three nuclear power plants, but their lifespans are nearing an end. The government has announced plans to decommission these plants, necessitating a substantial shift towards alternative energy sources.
- Decommissioning Costs: The process of decommissioning nuclear power plants is incredibly complex and expensive, placing a significant financial burden on the government.
- Need for Alternatives: The looming closure of nuclear plants underscores the urgent need for reliable and sufficient alternative power generation capacity, making the Taiwan LNG transition a pivotal undertaking. The technical challenges of decommissioning and the long-term implications for grid stability are immense. Managing the transition without impacting electricity supply remains a key challenge.
The Rise of LNG as a Primary Energy Source
With the planned phase-out of nuclear power, Taiwan has increasingly turned to LNG to fill the energy gap. This has led to significant infrastructural development and a complex geopolitical landscape.
Increased LNG Imports and Infrastructure Development
- Growth in LNG Imports: Over the past decade, Taiwan has witnessed a substantial increase in LNG imports to meet its growing energy needs.
- New LNG Terminals and Pipelines: Significant investments have been made in constructing new LNG receiving terminals, expanding storage capacity, and building extensive pipeline networks to distribute the gas across the island.
- Economic Implications: The increased reliance on LNG imports has significant economic implications, including potential price volatility tied to global LNG markets and a dependence on foreign suppliers.
Diversification of LNG Suppliers and Geopolitical Considerations
- Key Suppliers and Geopolitical Risks: Taiwan's primary LNG suppliers include countries with varying geopolitical relationships, creating potential risks to energy security.
- Diversification Efforts: To mitigate these risks, Taiwan is actively pursuing efforts to diversify its LNG import sources, seeking to reduce its dependence on any single supplier. This includes forging new partnerships and agreements with alternative suppliers.
- Strategic Importance of Diversification: Diversification is of paramount strategic importance, reducing vulnerability to geopolitical instability or potential supply disruptions. The economic and political ramifications of relying heavily on a few suppliers are considerable.
Environmental Impacts and Mitigation Strategies
While LNG offers a less carbon-intensive alternative to nuclear power, its environmental impact is still significant, demanding mitigation strategies.
Reducing Carbon Emissions from LNG
- Environmental Impact Compared to Nuclear: LNG combustion releases greenhouse gases, although significantly less than coal. However, it remains a fossil fuel, contributing to climate change.
- Transition to Cleaner Energy: The government is promoting the transition towards cleaner energy sources alongside LNG, aiming for a balanced approach. This strategy includes significant investments in renewable energy technologies.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): The exploration and implementation of CCS technologies are crucial to lessen the environmental footprint of LNG use in Taiwan’s energy mix.
Addressing Air Pollution from LNG Combustion
- Air Quality Concerns: The combustion of LNG, while cleaner than coal, still produces emissions that can impact air quality, affecting public health.
- Regulations and Emission Control Technologies: Stricter regulations and the adoption of advanced emission control technologies are crucial to minimize these impacts.
- Role of Renewable Energy: The expansion of renewable energy sources can further reduce reliance on LNG and, consequently, diminish air pollution. This integrated approach is critical.
Conclusion
Taiwan's Taiwan LNG transition from nuclear power to LNG is a complex undertaking with significant implications for its energy security, economy, and environment. While LNG offers a relatively cleaner alternative to nuclear power in the short term, long-term strategies must focus on diversifying energy sources and aggressively developing renewable energy to reduce carbon emissions and ensure sustainable energy independence. The successful integration of renewable energies alongside LNG is vital for a sustainable energy future. To understand the full impact of this energy transition, further research into the long-term sustainability of Taiwan’s reliance on LNG and the successful integration of renewable energies is crucial. Learn more about the future of the Taiwan LNG transition and its implications for the island’s energy future.

Featured Posts
-
 Prica S Reddita Postaje Film Sa Sydney Sweeney
May 21, 2025
Prica S Reddita Postaje Film Sa Sydney Sweeney
May 21, 2025 -
 Pivdenniy Mist Detalniy Analiz Remontu Pidryadnikiv Ta Finansuvannya
May 21, 2025
Pivdenniy Mist Detalniy Analiz Remontu Pidryadnikiv Ta Finansuvannya
May 21, 2025 -
 Wayne Gretzky Trump Tariffs And Canadian Patriotism A Complex Relationship
May 21, 2025
Wayne Gretzky Trump Tariffs And Canadian Patriotism A Complex Relationship
May 21, 2025 -
 Freepoint Eco Systems Announces Ing Project Finance Facility
May 21, 2025
Freepoint Eco Systems Announces Ing Project Finance Facility
May 21, 2025 -
 Court Challenge To Racial Hatred Tweet Sentence By Ex Tory Councillors Wife
May 21, 2025
Court Challenge To Racial Hatred Tweet Sentence By Ex Tory Councillors Wife
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Prokrisi Gia Tin Kroyz Azoyl Xari Ston Giakoymaki Telikos Champions League
May 21, 2025
Prokrisi Gia Tin Kroyz Azoyl Xari Ston Giakoymaki Telikos Champions League
May 21, 2025 -
 Los Antzeles Giakoymakis Analyontas Tis Pithanotites Mias Metagrafis
May 21, 2025
Los Antzeles Giakoymakis Analyontas Tis Pithanotites Mias Metagrafis
May 21, 2025 -
 Giakoymakis To Endiaferon Tis Los Antzeles Kai Oi Epomenes Ekselikseis
May 21, 2025
Giakoymakis To Endiaferon Tis Los Antzeles Kai Oi Epomenes Ekselikseis
May 21, 2025 -
 Fa Cup Rashfords Brace Leads Aston Villa To Win Against Preston
May 21, 2025
Fa Cup Rashfords Brace Leads Aston Villa To Win Against Preston
May 21, 2025 -
 I Metagrafi Giakoymaki Stin Los Antzeles Pragmatikotita I Fimes
May 21, 2025
I Metagrafi Giakoymaki Stin Los Antzeles Pragmatikotita I Fimes
May 21, 2025
