Taiwan's Nuclear Phase-Out: The Rise Of LNG Imports
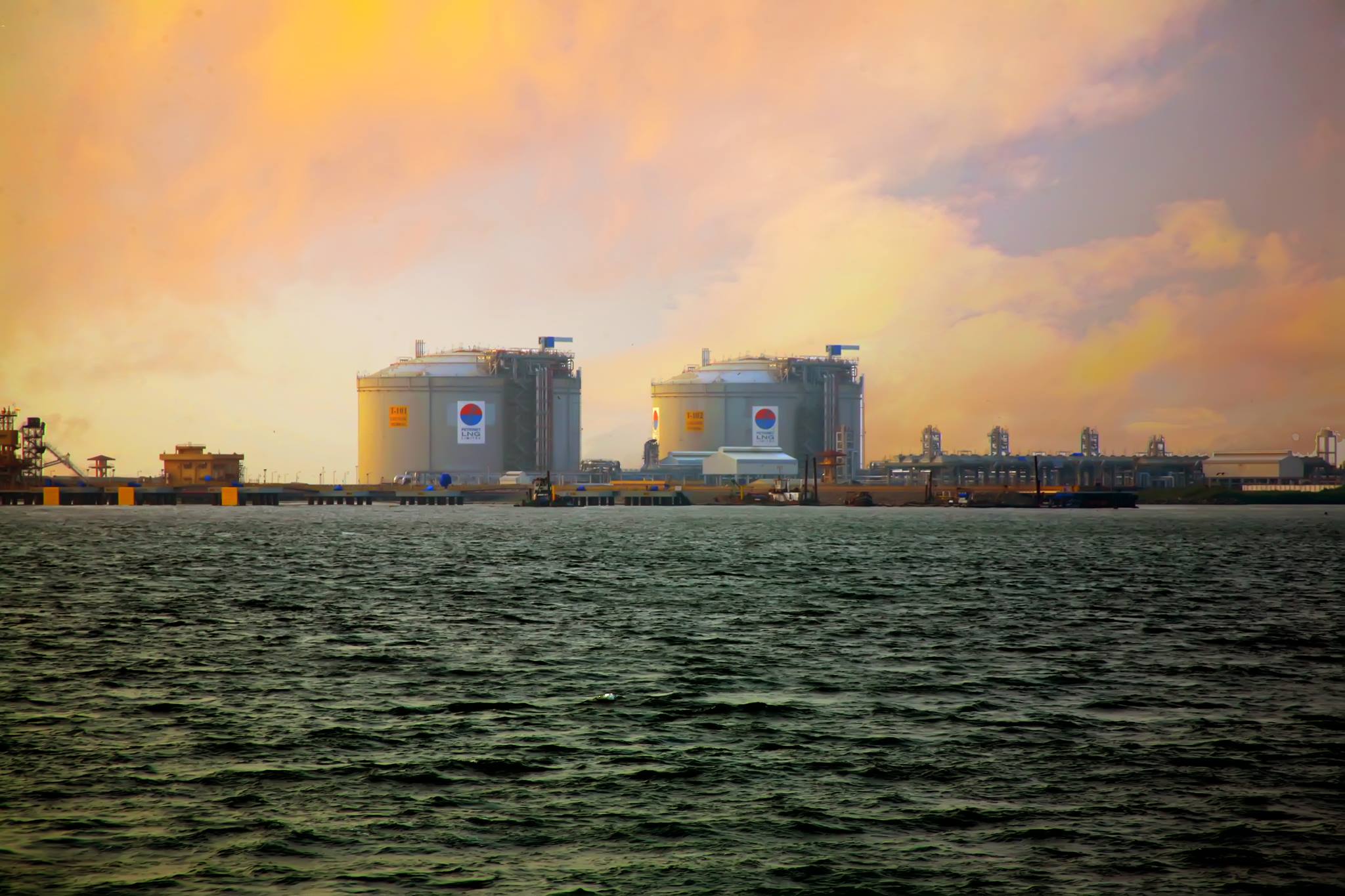

Table of Contents
The Nuclear Phase-Out Policy and its Rationale
Taiwan's decision to phase out nuclear power stems from a confluence of factors, including significant public opposition, heightened safety concerns amplified by the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in 2011, and evolving political priorities. The public's anxieties surrounding nuclear energy, fueled by fears of accidents and radioactive waste disposal, played a crucial role in shaping government policy.
- Timeline of nuclear plant closures: The closure timeline has been gradual, with specific plants slated for decommissioning over a period of years, impacting the overall energy mix.
- Government statements and policy documents supporting the phase-out: Official government communications and policy documents clearly articulate the commitment to a nuclear-free Taiwan, outlining the transition plan and supporting rationales. These documents are key to understanding the official stance and strategic goals.
- Public perception and activism surrounding nuclear energy in Taiwan: Anti-nuclear activism has been a powerful force in shaping public opinion and influencing government decisions. Citizen groups and environmental organizations have played a significant role in advocating for renewable energy alternatives.
The Surge in LNG Imports to Fill the Energy Gap
The reduction in nuclear power generation has created a substantial energy gap, necessitating a significant increase in Taiwan LNG imports. This has spurred substantial investment in infrastructure development to handle the increased volume of LNG, including the expansion and construction of import terminals and pipeline networks.
- Statistics on LNG import volume growth: Data showcasing the exponential rise in LNG imports since the commencement of the nuclear phase-out vividly illustrates the scale of the energy transition. This growth presents both economic opportunities and logistical challenges.
- Key suppliers of LNG to Taiwan: Identifying Taiwan's major LNG suppliers helps analyze its energy security vulnerabilities and potential risks associated with geopolitical instability in key supplier regions. Diversification of suppliers is crucial for minimizing such risks.
- Investment in LNG infrastructure projects: The substantial investments in LNG import terminals and related infrastructure highlight the economic implications of the energy transition and demonstrate the scale of the undertaking.
Economic Impacts of Increased LNG Reliance
The increased reliance on imported LNG carries significant economic consequences. Price volatility in the global LNG market poses a major challenge, impacting electricity prices for consumers and businesses. The potential for trade imbalances due to the high cost of LNG imports also raises concerns.
- Impact on electricity prices for consumers and businesses: Fluctuations in global LNG prices directly translate into changes in electricity costs, potentially affecting the competitiveness of Taiwanese businesses and the affordability of energy for households.
- Potential for trade imbalances due to LNG imports: The substantial expenditure on LNG imports can lead to trade deficits and increased dependence on foreign energy markets, impacting Taiwan's overall economic stability.
- Government subsidies and support mechanisms for the energy sector: Government intervention, through subsidies and support mechanisms, plays a crucial role in mitigating some of the economic risks associated with the shift to LNG-based energy.
Environmental Considerations of the LNG Transition
While LNG is often presented as a cleaner alternative to coal, the transition still presents environmental challenges. The combustion of LNG releases greenhouse gases, albeit at lower levels than coal, raising concerns about carbon emissions and climate change.
- Comparison of CO2 emissions from nuclear vs. LNG: A comparison of the carbon footprint of nuclear power and LNG highlights the trade-offs involved in the energy transition and the need for complementary strategies to mitigate emissions.
- Government initiatives to reduce emissions from LNG use: Exploring government policies aimed at reducing emissions from LNG-based power generation is crucial to understanding the broader environmental strategy. This includes exploring carbon capture and storage technologies.
- Exploration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power in Taiwan: The integration of renewable energy sources into Taiwan's energy mix is essential to reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating the environmental impact of the transition.
Geopolitical Implications of Taiwan's LNG Dependence
Taiwan's increased dependence on international LNG suppliers introduces geopolitical complexities. Disruptions in the global LNG market due to geopolitical tensions or supplier-related issues could severely impact Taiwan's energy security.
- Diversification of LNG import sources to reduce reliance on single suppliers: Strategies to diversify LNG import sources are crucial in mitigating risks and enhancing energy security, ensuring a robust supply chain.
- Potential for geopolitical tensions to impact LNG supply: Analyzing how geopolitical instability in key LNG-producing regions could affect Taiwan's energy supply is critical for understanding potential vulnerabilities.
- Taiwan's energy security strategy in the context of regional dynamics: Taiwan's energy security strategy must consider its geopolitical context, including its relationship with neighboring countries and its position in the global energy market.
Conclusion
Taiwan's nuclear phase-out has undeniably driven a substantial increase in Taiwan LNG imports, creating a complex interplay of economic, environmental, and geopolitical considerations. The transition necessitates careful management to mitigate risks associated with price volatility, greenhouse gas emissions, and reliance on international energy markets. The success of this transition hinges on a balanced approach that integrates strategies for diversifying energy sources, promoting energy efficiency, and investing in renewable energy technologies.
Understanding the complexities of Taiwan LNG imports is crucial for navigating the future of its energy sector. Further research and analysis are needed to ensure a secure, sustainable, and affordable energy future for Taiwan. Learn more about the implications of Taiwan LNG imports and explore the future of energy in Taiwan.

Featured Posts
-
 Restrictions De Circulation Sur Le Boulevard Fhb Ex Vge Deux Roues Et Trois Roues Concernes A Partir Du 15 Avril
May 20, 2025
Restrictions De Circulation Sur Le Boulevard Fhb Ex Vge Deux Roues Et Trois Roues Concernes A Partir Du 15 Avril
May 20, 2025 -
 The Us Typhon Missile System A Comprehensive Overview Of Its Presence In The Philippines
May 20, 2025
The Us Typhon Missile System A Comprehensive Overview Of Its Presence In The Philippines
May 20, 2025 -
 Lou Gala Exploring The Breakout Star Of The Decameron
May 20, 2025
Lou Gala Exploring The Breakout Star Of The Decameron
May 20, 2025 -
 Le Marche Africain Des Solutions Spatiales Mass Innovation Et Developpement En Afrique
May 20, 2025
Le Marche Africain Des Solutions Spatiales Mass Innovation Et Developpement En Afrique
May 20, 2025 -
 Hmrc Child Benefit Notifications What To Look Out For
May 20, 2025
Hmrc Child Benefit Notifications What To Look Out For
May 20, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Impact Of Layoffs On Abc News Shows Programming
May 20, 2025
Impact Of Layoffs On Abc News Shows Programming
May 20, 2025 -
 Layoffs At Abc News What Does This Mean For Show Name
May 20, 2025
Layoffs At Abc News What Does This Mean For Show Name
May 20, 2025 -
 Analysis Abc News Layoffs And Their Effect On Programming
May 20, 2025
Analysis Abc News Layoffs And Their Effect On Programming
May 20, 2025 -
 Analysis Abc News Shows Survival After Significant Layoffs
May 20, 2025
Analysis Abc News Shows Survival After Significant Layoffs
May 20, 2025 -
 Future Of Popular Abc News Show Questioned Post Layoffs
May 20, 2025
Future Of Popular Abc News Show Questioned Post Layoffs
May 20, 2025
