The Campus Farm: A Living Laboratory For Life Cycle Studies
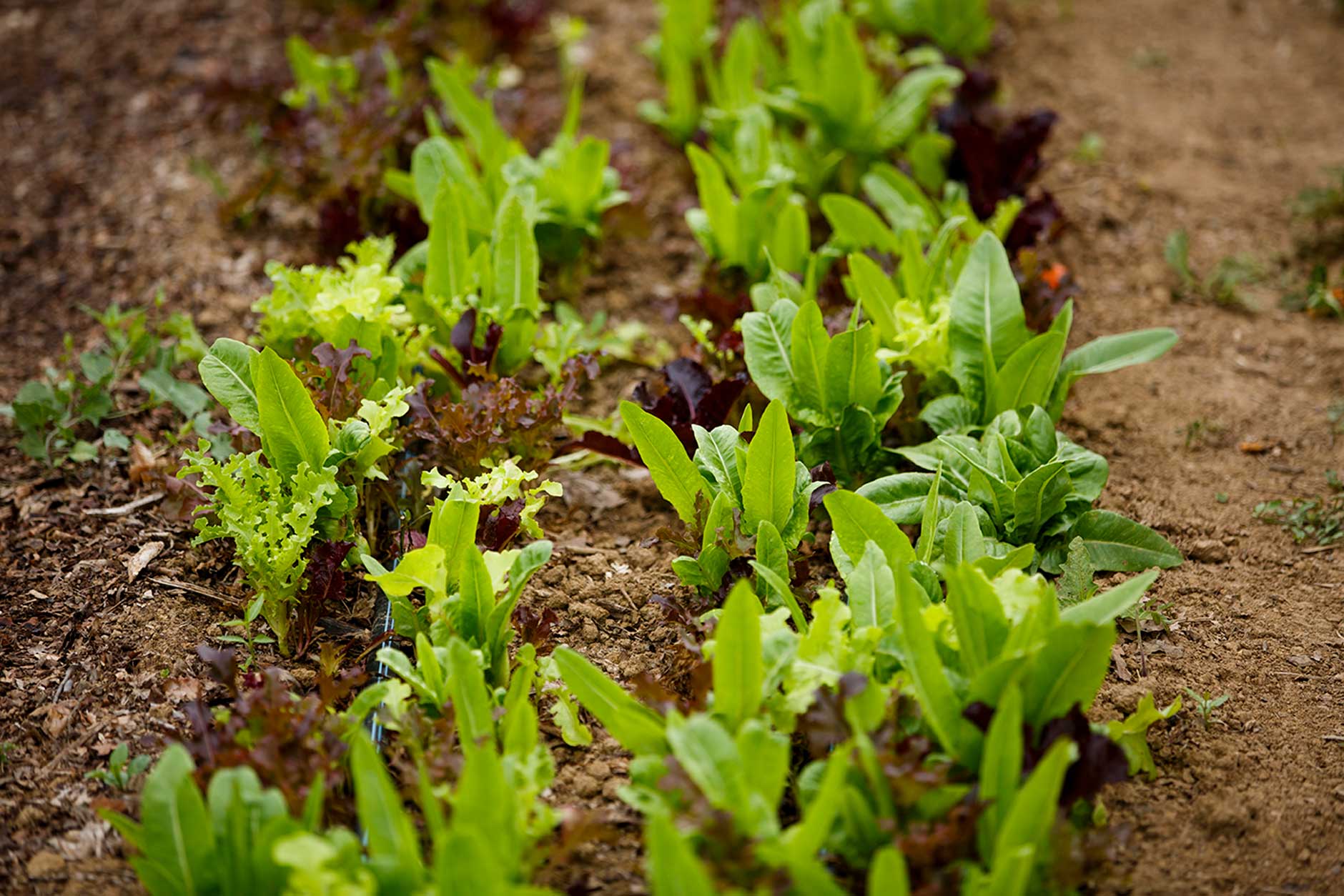

Table of Contents
Experiential Learning and Environmental Awareness
Hands-on experience on a campus farm cultivates environmental awareness in several crucial ways. Students directly engage with the natural world, gaining a practical understanding of ecological principles often missing in traditional classroom settings. This experiential learning translates to a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of environmental systems.
- Direct observation of plant growth and development: Students witness firsthand the stages of plant growth, from seed germination to maturity, understanding the influence of factors like sunlight, water, and nutrients.
- Understanding the impact of environmental factors: They learn how weather patterns, soil health, and pest infestations affect crop yields, developing a keen awareness of environmental challenges and the importance of sustainable agricultural practices.
- Practical application of sustainable agricultural techniques: Campus farms often employ sustainable methods like crop rotation, composting, and integrated pest management, providing students with practical experience in environmentally friendly agriculture.
- Increased awareness of food systems and their environmental footprint: By participating in the entire food production process, students gain a clearer understanding of the resources required to produce food and the environmental impact of different food choices. This fosters a deeper understanding of sustainable agriculture and its crucial role in environmental stewardship.
This hands-on learning significantly impacts student attitudes towards sustainability. Exposure to sustainable agriculture practices fosters a sense of environmental responsibility and ecological literacy, motivating students to adopt more sustainable lifestyles and advocate for environmental protection.
Life Cycle Studies in Action: From Seed to Table
A campus farm offers a unique opportunity to study the complete life cycle of crops, providing practical experience across all stages.
- Seed selection and planting techniques: Students learn about selecting appropriate seeds, understanding seed germination rates, and implementing proper planting techniques for optimal growth.
- Soil preparation and nutrient management: They gain experience in preparing soil for planting, understanding soil composition, and implementing nutrient management strategies to ensure healthy plant growth, learning the importance of soil health in organic farming.
- Pest and disease management (organic methods): Students learn about integrated pest management (IPM) and other organic methods for controlling pests and diseases, minimizing the environmental impact of pest control.
- Harvesting and post-harvest handling: They participate in harvesting crops at their peak ripeness, learning proper harvesting techniques and post-harvest handling to minimize food waste.
- Food preservation and processing techniques: Students explore various methods of food preservation, such as canning, freezing, and drying, extending the shelf life of harvested produce and reducing food waste reduction.
These hands-on experiences reinforce theoretical knowledge with practical application, promoting a deeper understanding of sustainable agricultural practices and their role in food security. The entire process, from seed germination to harvesting techniques and beyond, is a testament to the practical learning environment offered by the campus farm.
Research Opportunities and Data Collection on the Campus Farm
The campus farm provides a fertile ground for diverse research projects, offering students valuable experience in scientific methodology and data analysis.
- Investigating the effects of different farming methods: Students can compare the yields and environmental impact of organic vs. conventional farming methods, gathering empirical data to support sustainable agriculture practices.
- Studying the impact of climate change on crop yields: Research can focus on how changing weather patterns affect crop growth and develop strategies for adapting to climate change impacts on agriculture.
- Analyzing soil health and nutrient cycling: Students can investigate the impact of different farming practices on soil health and nutrient cycling, contributing to our understanding of sustainable soil management.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of pest and disease management strategies: Research projects can evaluate the effectiveness of organic pest control methods, contributing to the development of more sustainable pest management strategies.
This research experience equips students with practical skills in agricultural research, data analysis, experimental design, and scientific reporting, enhancing their employability and future research potential.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration and Community Engagement
Campus farms naturally foster interdisciplinary collaboration, bringing together students and faculty from various academic departments. Biology, agriculture, sociology, and even business students can contribute to research projects and community outreach initiatives, creating a holistic learning experience.
Community outreach initiatives involving the campus farm strengthen the connection between the university and the local community. Farmers' markets provide a venue for students to sell their produce, while educational programs offer opportunities to share their knowledge and promote sustainable agriculture practices. These community gardens often become centers for food security initiatives and contribute significantly to the social impact of the university.
Conclusion
The campus farm provides an invaluable resource for life cycle studies, offering students a hands-on, experiential learning environment that fosters environmental awareness and promotes sustainable practices. By actively participating in the entire process, from seed to table, students gain a deeper understanding of ecological principles, develop research skills, and contribute to community engagement initiatives. Embrace the potential of the campus farm as a living laboratory and integrate it into your curriculum to promote life cycle studies and cultivate a more sustainable future. Explore the benefits of establishing a campus farm or enhancing your existing one to strengthen your institution's commitment to life cycle studies and environmental sustainability.

Featured Posts
-
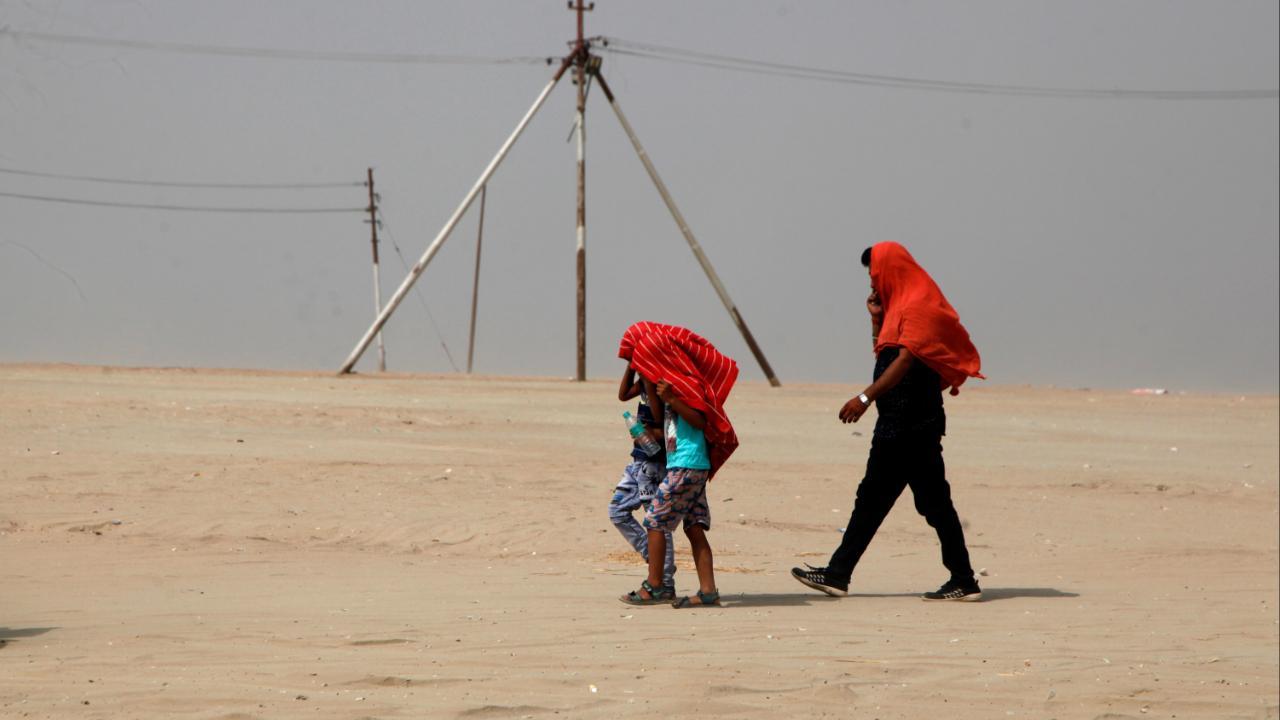 Nmmcs Aala Unhala Niyam Pala Campaign Navi Mumbais Heatwave Advisory
May 13, 2025
Nmmcs Aala Unhala Niyam Pala Campaign Navi Mumbais Heatwave Advisory
May 13, 2025 -
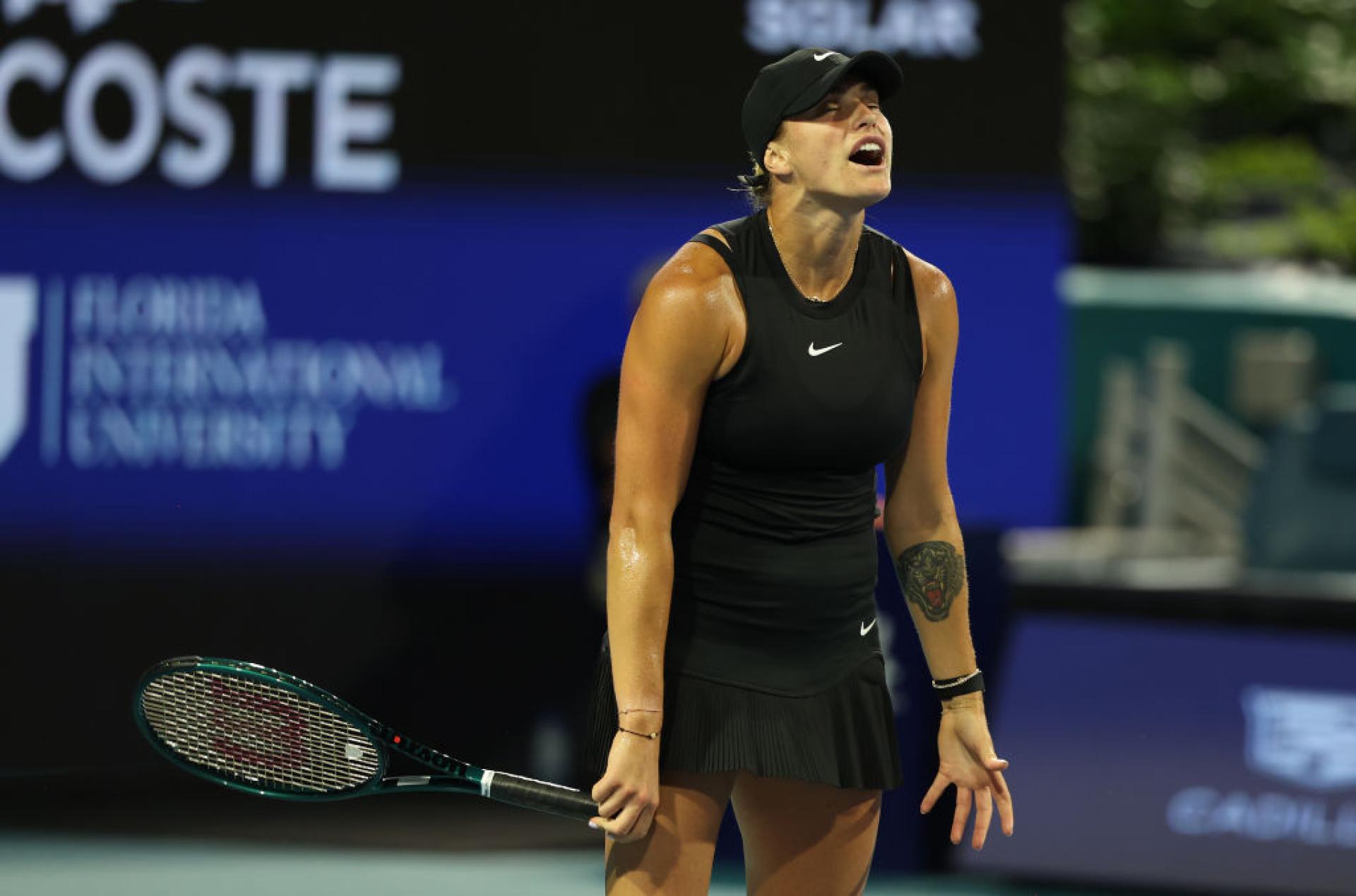 Aryna Sabalenka Claims 19th Wta Title In Miami
May 13, 2025
Aryna Sabalenka Claims 19th Wta Title In Miami
May 13, 2025 -
 Jelena Ostapenkos Repeat Victory Over Iga Swiatek Sends Her To Stuttgart Semis
May 13, 2025
Jelena Ostapenkos Repeat Victory Over Iga Swiatek Sends Her To Stuttgart Semis
May 13, 2025 -
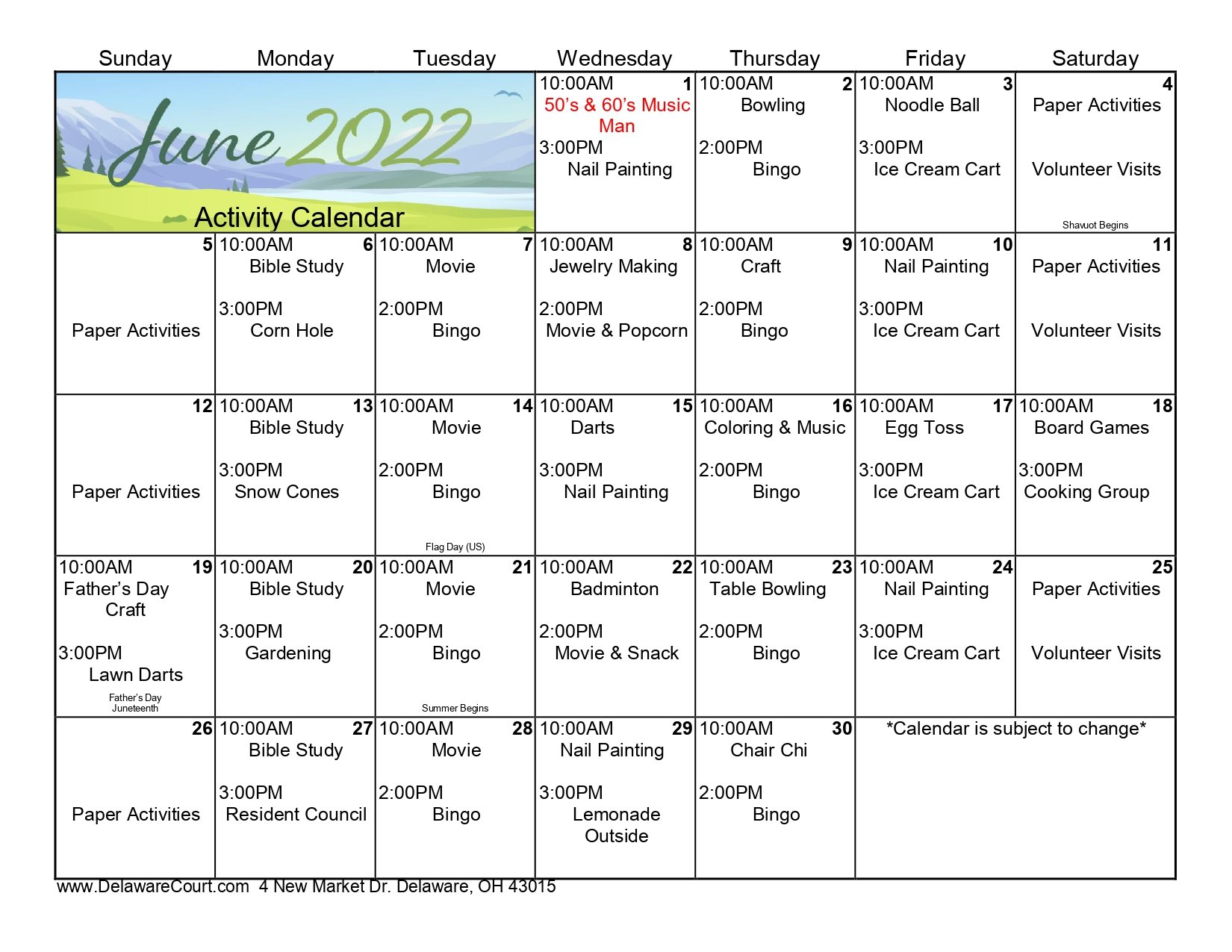 Senior Activities Calendar Trips And Events For Seniors
May 13, 2025
Senior Activities Calendar Trips And Events For Seniors
May 13, 2025 -
 Sabalenka And Gauffs Smooth Sailing In Rome Avoiding Early Exit
May 13, 2025
Sabalenka And Gauffs Smooth Sailing In Rome Avoiding Early Exit
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Application Invited Professorship In Fine Arts Spatial Concepts Focus
May 13, 2025
Application Invited Professorship In Fine Arts Spatial Concepts Focus
May 13, 2025 -
 Seeking A Professorship In Fine Arts Focus On Spatial Design
May 13, 2025
Seeking A Professorship In Fine Arts Focus On Spatial Design
May 13, 2025 -
 Professorship In Fine Arts Exploring Spatial Concepts
May 13, 2025
Professorship In Fine Arts Exploring Spatial Concepts
May 13, 2025 -
 Alle Schueler In Sicherheit Entwarnung An Braunschweiger Schule Nach Alarm
May 13, 2025
Alle Schueler In Sicherheit Entwarnung An Braunschweiger Schule Nach Alarm
May 13, 2025 -
 Braunschweiger Grundschule Entwarnung Nach Sicherheitsalarm
May 13, 2025
Braunschweiger Grundschule Entwarnung Nach Sicherheitsalarm
May 13, 2025
