The Case Against School Suspensions: Promoting Positive Discipline

Table of Contents
The Ineffectiveness of School Suspensions
School suspensions, a common disciplinary practice in many schools, are often perceived as a quick solution to disruptive behavior. However, evidence suggests that this approach is not only ineffective but also detrimental to students' academic and social-emotional development.
Increased Rates of Truancy and Dropping Out
Suspensions disrupt a student's learning, leading to academic setbacks and a significantly increased likelihood of truancy and dropping out of school.
- Statistics: Studies show a strong correlation between school suspensions and increased dropout rates. For example, one study found that students suspended even once were three times more likely to drop out.
- Examples: A student suspended for a week might miss crucial lessons, tests, and assignments, making it difficult to catch up and negatively impacting their GPA. The cumulative effect of multiple suspensions can lead to significant academic failure and a sense of disengagement from school.
- Keywords: School suspension consequences, dropout rates, academic failure, truancy, chronic absenteeism.
Failure to Address the Root Cause of Misbehavior
Suspensions primarily focus on punishing the behavior, rather than addressing the underlying issues that contribute to it. This short-sighted approach often fails to resolve the root problem, leading to a cycle of repeated suspensions and escalating behavioral problems.
- Underlying Issues: Many behavioral issues stem from factors such as learning disabilities, undiagnosed mental health conditions, trauma, neglect, or challenging home environments.
- Restorative Justice: Instead of punishment, restorative justice practices focus on repairing harm and restoring relationships. They emphasize dialogue, accountability, and repairing the harm caused by the misbehavior. This approach addresses the root causes, fostering empathy and understanding.
- Keywords: Behavioral issues in schools, restorative justice, root cause analysis, underlying causes of misbehavior, trauma-informed care.
The Negative Impact on School Climate
School suspensions contribute to a more punitive and less supportive learning environment. The removal of students creates a climate of fear and anxiety, affecting both the suspended student and their peers.
- Learning Atmosphere: A school environment characterized by frequent suspensions fosters a culture of distrust and negativity, undermining the sense of community and collaboration essential for effective learning.
- Increased Fear and Anxiety: The constant threat of suspension can increase anxiety among students, leading to decreased engagement and academic performance. It can also contribute to a climate of fear and bullying.
- Keywords: School climate, safe learning environment, bullying, discipline strategies, positive behavior support.
The Benefits of Positive Discipline Strategies
Positive discipline strategies offer a more effective and humane approach to managing student behavior, focusing on prevention, intervention, and fostering a supportive learning environment.
Restorative Justice Practices
Restorative justice emphasizes repairing harm and restoring relationships, rather than simply punishing offenders. It involves bringing together all parties affected by the misbehavior to collaboratively address the issue and find solutions.
- Examples: Restorative practices include conflict resolution, peer mediation, restorative circles, and community conferencing. These methods promote dialogue, empathy, and accountability.
- Positive Outcomes: Studies show that restorative justice programs reduce suspensions, improve school climate, and enhance students' social-emotional skills.
- Keywords: Restorative justice practices, conflict resolution, peer mediation, restorative circles, restorative conferences.
Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
Social-emotional learning (SEL) equips students with the skills they need to manage their emotions, build positive relationships, and make responsible decisions. It addresses the root causes of misbehavior by fostering self-awareness, self-regulation, and empathy.
- Reduced Behavioral Issues: Effective SEL programs have been shown to significantly reduce behavioral problems and improve academic performance.
- Examples: SEL programs incorporate various techniques such as mindfulness practices, conflict resolution training, and emotional literacy activities.
- Keywords: Social emotional learning, SEL programs, emotional intelligence, problem-solving skills, self-regulation.
Collaborative and Supportive School Environments
Creating a collaborative and supportive school environment is crucial for preventing misbehavior and promoting positive student outcomes. This involves establishing clear expectations, providing consistent support, and fostering a culture of mutual respect and understanding.
- Positive Behavior Interventions and Supports (PBIS): PBIS is a proactive, data-driven framework for creating positive school climates and reducing problem behaviors. It involves teaching and reinforcing positive behaviors through clear expectations, consistent routines, and positive reinforcement.
- Keywords: Positive school culture, supportive classroom environment, PBIS, positive behavior interventions, positive reinforcement.
Conclusion: Embracing Positive Discipline Over School Suspensions
School suspensions are ineffective and harmful; they do not address the root causes of misbehavior and negatively impact students' academic and social-emotional well-being. Positive discipline strategies, such as restorative justice and social-emotional learning, offer a superior alternative. These strategies create safer, more supportive learning environments, reduce suspensions, and foster a culture of mutual respect and understanding. Let's move beyond the outdated practice of school suspensions and embrace positive discipline to create safer, more supportive learning environments for all students. Learn more about effective positive discipline strategies and advocate for their implementation in your schools – let's end school suspensions and build a better future for our students.

Featured Posts
-
 Shell Recharge Raya Promotion Up To 100 Rebate On East Coast Hpc Ev Chargers
May 03, 2025
Shell Recharge Raya Promotion Up To 100 Rebate On East Coast Hpc Ev Chargers
May 03, 2025 -
 Alhjwm Ela Alqaflt Alinsanyt Tghtyt Wsayl Alielam Alerbyt Llahdath Qbalt Malta
May 03, 2025
Alhjwm Ela Alqaflt Alinsanyt Tghtyt Wsayl Alielam Alerbyt Llahdath Qbalt Malta
May 03, 2025 -
 Kl Almelwmat En Blay Styshn 6 Mwasfat Ser Wtarykh Alisdar
May 03, 2025
Kl Almelwmat En Blay Styshn 6 Mwasfat Ser Wtarykh Alisdar
May 03, 2025 -
 I Skia Tis Diafthoras Pos Epireazei I Poleodomiki Diafthora Tin Epanidrysi Toy Kratoys
May 03, 2025
I Skia Tis Diafthoras Pos Epireazei I Poleodomiki Diafthora Tin Epanidrysi Toy Kratoys
May 03, 2025 -
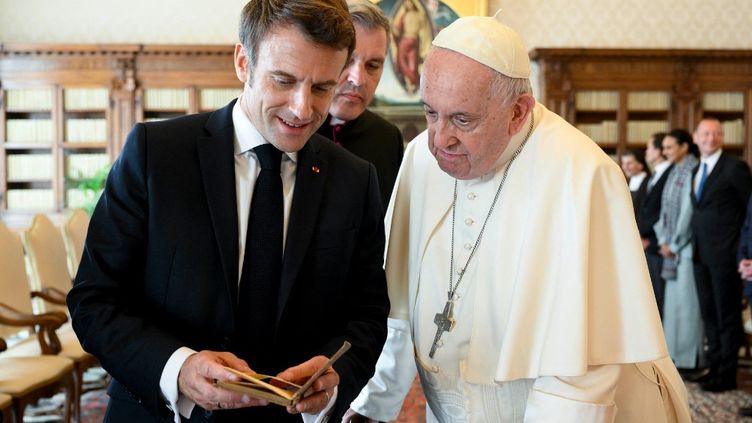 Rumeurs De Manipulation Macron Et L Election Du Prochain Pape A Rome
May 03, 2025
Rumeurs De Manipulation Macron Et L Election Du Prochain Pape A Rome
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
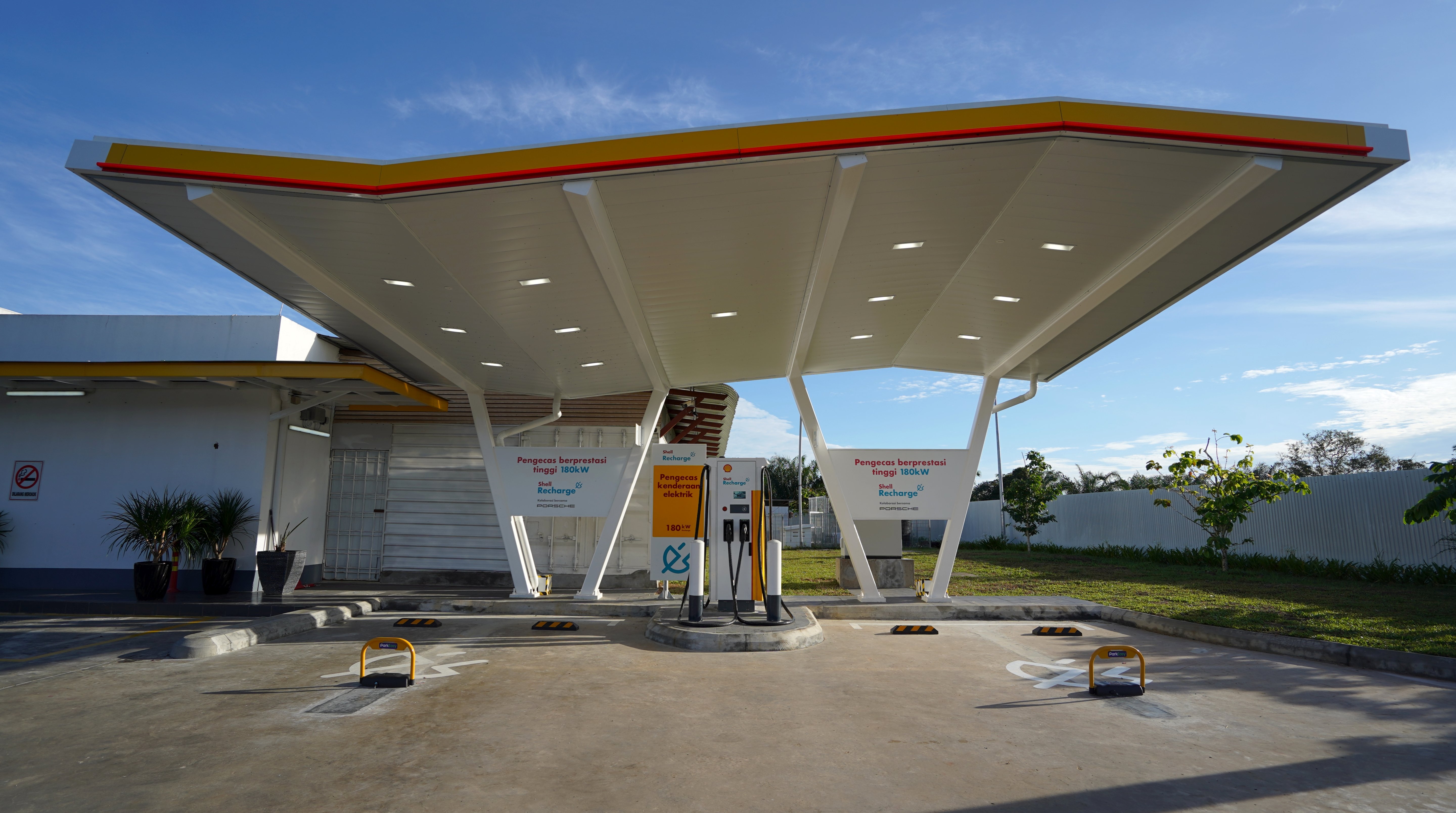 Raya Promotion 100 Rebate For Shell Recharge Hpc Ev Charging East Coast
May 04, 2025
Raya Promotion 100 Rebate For Shell Recharge Hpc Ev Charging East Coast
May 04, 2025 -
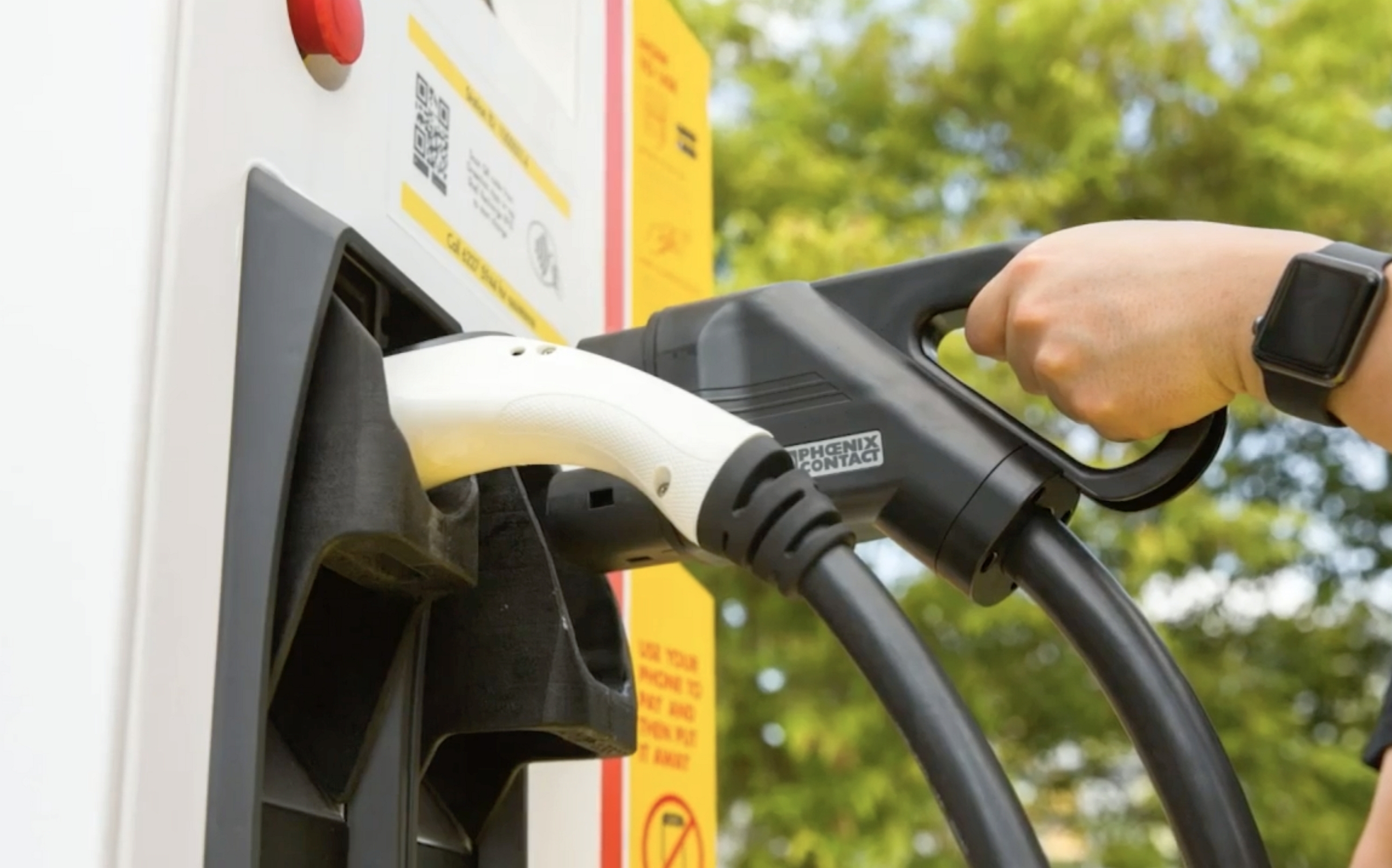 Enjoy Free Hpc Ev Charging This Raya With Shell Recharge On The East Coast
May 04, 2025
Enjoy Free Hpc Ev Charging This Raya With Shell Recharge On The East Coast
May 04, 2025 -
 Manfaatkan Limbah Rumah Tangga Cangkang Telur Untuk Pupuk Alami
May 04, 2025
Manfaatkan Limbah Rumah Tangga Cangkang Telur Untuk Pupuk Alami
May 04, 2025 -
 1 50 T
May 04, 2025
1 50 T
May 04, 2025 -
 Shell Recharge Members 100 Rebate On East Coast Hpc Ev Chargers This Raya
May 04, 2025
Shell Recharge Members 100 Rebate On East Coast Hpc Ev Chargers This Raya
May 04, 2025
