The Complexities Of ADHD: A Look Inside Our ADHD Minds
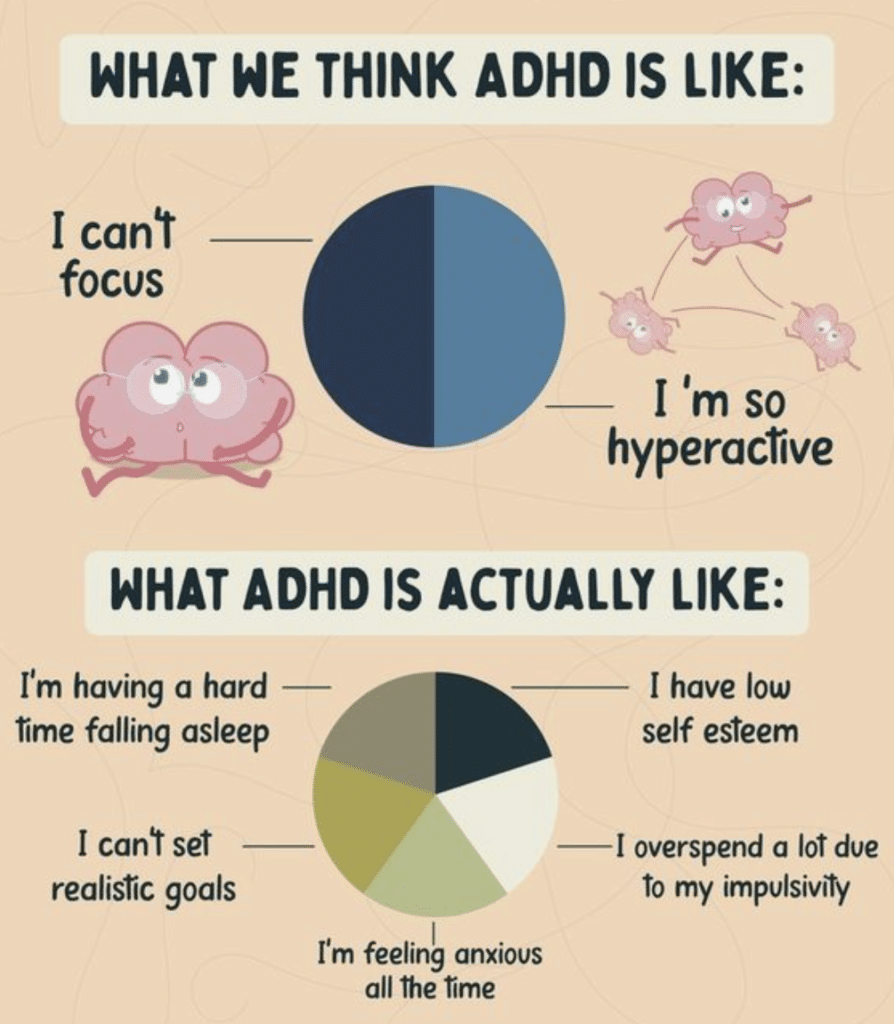
Table of Contents
The Neuroscience of ADHD: Understanding the Brain Differences
At the core of ADHD lies a neurological difference in brain structure and function. While not a single, easily identifiable cause exists, research points to imbalances in key neurotransmitters – dopamine and norepinephrine – which are vital for attention, focus, and impulse control. These imbalances affect several brain regions, most notably the prefrontal cortex (responsible for executive functions like planning and decision-making) and the basal ganglia (involved in motor control and habit formation).
- Smaller brain volume: Studies have indicated a smaller volume in certain brain regions, including the prefrontal cortex and cerebellum, in individuals with ADHD. [Link to reputable scientific source 1]
- Differences in brain connectivity: Research suggests altered connectivity between different brain regions, affecting communication and coordination. [Link to reputable scientific source 2]
- Variations in brain activity patterns: Brain imaging studies show variations in brain activity patterns during tasks requiring attention and impulse control. [Link to reputable scientific source 3]
These neurological differences contribute to the characteristic symptoms of ADHD, making it crucial to understand that ADHD is a brain-based condition, not a matter of willpower or discipline.
Common Symptoms and Their Manifestations: Beyond Inattention and Hyperactivity
While inattention and hyperactivity are often associated with ADHD, the complexities of ADHD extend far beyond these typical symptoms. The presentation varies greatly across individuals, with symptoms manifesting differently in children and adults.
- Emotional Dysregulation: Intense emotional responses, difficulty managing frustration, and frequent mood swings are common, often overlooked symptoms.
- Impulsivity in Various Contexts: Impulsivity isn't limited to hyperactivity; it can manifest as impulsive spending, risky sexual behavior, or difficulty maintaining healthy relationships.
- Working Memory Challenges: Difficulties retaining and manipulating information in the mind, impacting learning and daily task completion.
- Time Blindness: A distorted perception of time, leading to chronic lateness and difficulty managing schedules.
- Difficulties with Organization and Planning: Struggling with organization, prioritizing tasks, and planning ahead, leading to significant challenges in academic and professional settings.
Recognizing this wide spectrum of symptoms is critical for accurate diagnosis and personalized management strategies. It’s crucial to remember that no two individuals with ADHD experience the condition identically.
The Impact of ADHD on Daily Life: Challenges and Strengths
The complexities of ADHD significantly impact various aspects of daily life. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing effective coping mechanisms and support systems.
Academic and Professional Life
Difficulties with sustained attention, organization, and time management often result in academic struggles, missed deadlines, and challenges in maintaining employment. Procrastination, poor planning, and difficulty prioritizing tasks become major obstacles.
Relationships and Social Interactions
Challenges in communication, emotional regulation, and impulsivity can strain relationships. Individuals with ADHD may struggle with social cues, leading to misunderstandings and conflict. Impulsive behaviors can damage trust and hinder the development of close bonds.
Mental Health
There is a significantly increased risk of co-occurring mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depression, further complicating the challenges faced by individuals with ADHD. The constant struggle with symptoms and the societal stigma surrounding ADHD contribute to increased stress and emotional distress.
Despite these challenges, individuals with ADHD often possess remarkable strengths, including creativity, innovation, and the ability to focus intensely on tasks that genuinely interest them. These strengths, when nurtured and harnessed, can contribute significantly to personal and professional success.
Effective Strategies for Managing ADHD: Beyond Medication
While medication can be a valuable tool for some, managing ADHD effectively involves a multifaceted approach extending beyond pharmacological interventions.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT provides individuals with skills to manage their symptoms, improve impulse control, and develop strategies for better organization and time management. It empowers them to take control of their lives and respond more effectively to challenges.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in managing ADHD. Prioritizing sleep hygiene, engaging in regular exercise, and adopting a healthy diet can significantly impact symptom severity and overall well-being.
Organizational Tools and Techniques
Utilizing organizational tools, such as planners, calendars, and technology-based reminders, can help mitigate the challenges related to time management, organization, and task completion. Finding strategies that work best for each individual is key.
Individualized treatment plans are paramount, taking into account the specific needs, strengths, and challenges of each person with ADHD. A collaborative approach involving healthcare professionals, therapists, family, and the individual themselves is essential for successful management.
Conclusion: Understanding and Supporting Those with ADHD
The complexities of ADHD are undeniable. This article has highlighted the neurological basis, the varied symptomatic presentations, and the significant impact on daily life. It's crucial to remember that ADHD is not a character flaw but a neurodevelopmental condition requiring understanding, support, and tailored management strategies. By dispelling myths and fostering a greater understanding of the diverse ways ADHD manifests, we can create a more supportive environment for individuals with this condition. Learn more about managing the complexities of ADHD and finding effective strategies for yourself or a loved one. Continue your research on the complexities of ADHD to foster greater understanding and support.

Featured Posts
-
 On This Day In 2024 Hit The Road Drax Sung At Protest
May 13, 2025
On This Day In 2024 Hit The Road Drax Sung At Protest
May 13, 2025 -
 Oregon Ducks Womens Basketball Season Ends With Duke Loss In Ncaa Tournament
May 13, 2025
Oregon Ducks Womens Basketball Season Ends With Duke Loss In Ncaa Tournament
May 13, 2025 -
 Analyzing Ethan Slaters Appearance In Elsbeth Season 2 Episode 17
May 13, 2025
Analyzing Ethan Slaters Appearance In Elsbeth Season 2 Episode 17
May 13, 2025 -
 Negative Cubs Fan Reaction To Kyle Tucker Report
May 13, 2025
Negative Cubs Fan Reaction To Kyle Tucker Report
May 13, 2025 -
 Japans Cherry Blossom Season Your Complete Springwatch Handbook
May 13, 2025
Japans Cherry Blossom Season Your Complete Springwatch Handbook
May 13, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Byd N Nousu Onko Trumpin Politiikka Auttanut Teslan Kilpailijaa
May 13, 2025
Byd N Nousu Onko Trumpin Politiikka Auttanut Teslan Kilpailijaa
May 13, 2025 -
 Fords Brazilian Legacy Fades As Byds Global Ev Lead Expands
May 13, 2025
Fords Brazilian Legacy Fades As Byds Global Ev Lead Expands
May 13, 2025 -
 Landman Season 2 Cast Update Sam Elliott Confirmed Report Details
May 13, 2025
Landman Season 2 Cast Update Sam Elliott Confirmed Report Details
May 13, 2025 -
 Byds Rise Fords Decline And Chinas Ev Dominance In Brazil
May 13, 2025
Byds Rise Fords Decline And Chinas Ev Dominance In Brazil
May 13, 2025 -
 Antoiko Trump Vahingossa Byd Lle Avaimet Teslan Kukistamiseen Analyysi
May 13, 2025
Antoiko Trump Vahingossa Byd Lle Avaimet Teslan Kukistamiseen Analyysi
May 13, 2025
