The ECB On Inflation: The Impact Of Continued Fiscal Support After The Pandemic
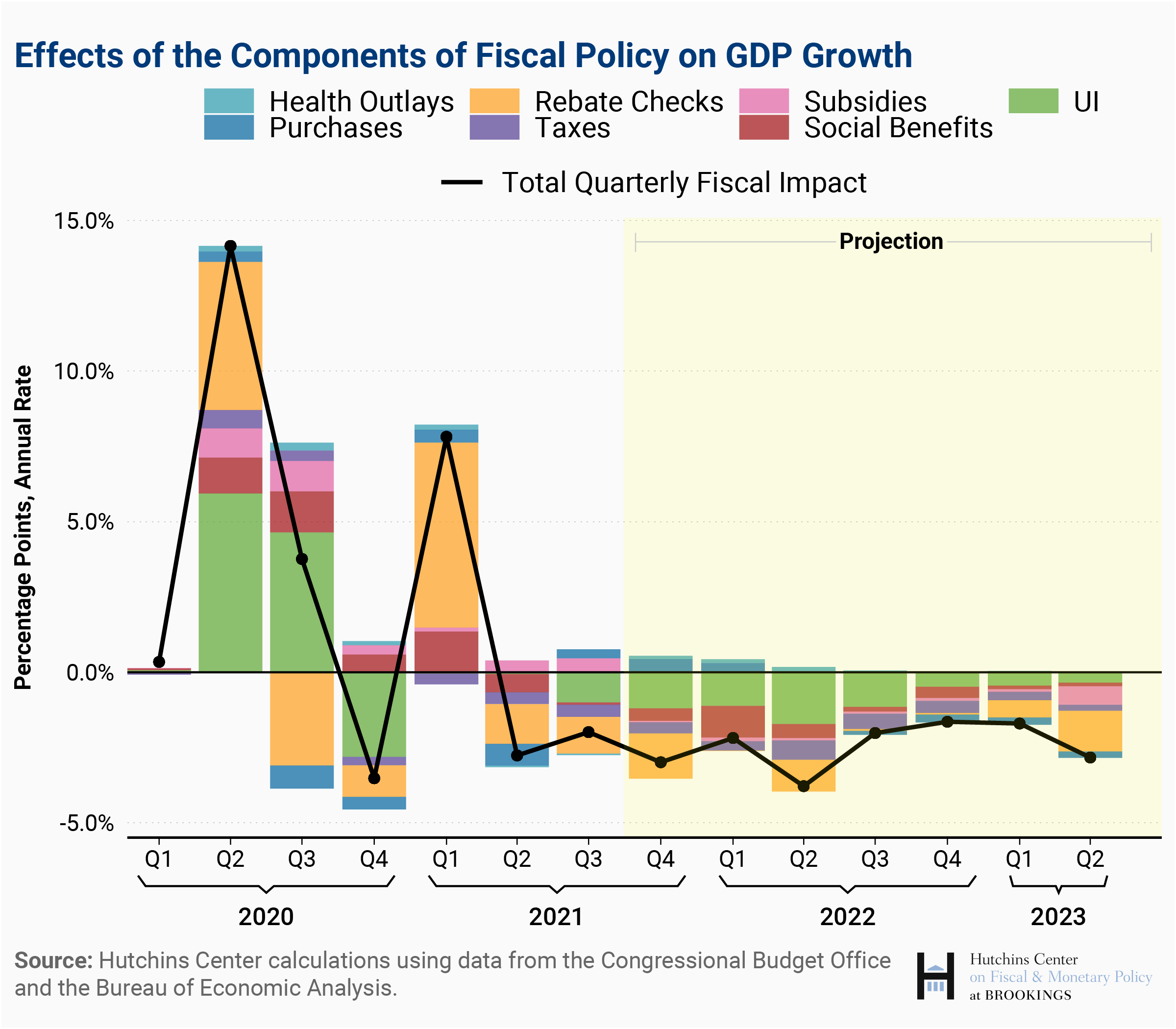
Table of Contents
The Pandemic's Economic Aftermath and Fiscal Stimulus
The COVID-19 pandemic delivered a severe shock to the Eurozone economy, causing widespread lockdowns, business closures, and a sharp rise in unemployment. To mitigate the economic fallout, governments across the Eurozone implemented extensive fiscal stimulus packages. These measures aimed to support businesses and households, preventing a deeper and more prolonged recession.
- Types of Fiscal Measures: These included substantial increases in unemployment benefits, government-backed loans for businesses (like the German KfW loans), and direct cash payments to citizens.
- Impact on Aggregate Demand: This massive injection of government spending significantly boosted aggregate demand. While necessary to prevent a catastrophic economic collapse, this increased demand contributed to inflationary pressures.
- Pandemic Fiscal Policy and Inflation: The increased money supply, coupled with supply chain disruptions caused by the pandemic, created a perfect storm for rising prices. This highlights the complex relationship between pandemic fiscal policy, Eurozone recovery, and government spending's impact on inflation.
ECB's Monetary Policy Response to Rising Inflation
Initially, the ECB adopted an extremely accommodative monetary policy stance to combat the economic downturn. This involved:
- Low Interest Rates: Interest rates were slashed to near-zero levels.
- Quantitative Easing (QE): The ECB engaged in large-scale asset purchases to inject liquidity into the financial system.
However, as inflation began to rise persistently above the ECB's target of 2%, the central bank shifted its policy stance. This shift involved:
- ECB Interest Rate Hikes: A series of interest rate increases aimed to curb inflation by making borrowing more expensive.
- End of Quantitative Easing: The ECB gradually phased out its quantitative easing program.
The ECB faced the difficult challenge of balancing economic growth with inflation control. Aggressive monetary tightening risks slowing economic growth or even triggering a recession, while insufficient tightening risks allowing inflation to become entrenched. Managing ECB interest rates and quantitative easing effectively became paramount in their monetary policy tightening strategy aimed at inflation targeting.
The Interplay Between Fiscal and Monetary Policies
The relationship between continued government spending and the ECB's efforts to control inflation is complex and fraught with challenges. Continued fiscal stimulus, even after the immediate crisis has passed, can exacerbate inflationary pressures by fueling aggregate demand.
- Fiscal Dominance: Concerns exist about "fiscal dominance," a situation where the government's fiscal policy overwhelms the central bank's ability to control inflation. This could undermine the ECB's independence and its ability to effectively manage ECB inflation.
- Monetary-Fiscal Policy Mix: The effectiveness of the ECB's actions depends heavily on the fiscal policy stance adopted by Eurozone governments. Effective policy coordination between fiscal authorities and the ECB is crucial for optimal outcomes.
- Lack of Coordination: A lack of coordinated efforts can lead to conflicting policy signals, hindering the effectiveness of both monetary and fiscal policies in achieving macroeconomic stability.
Long-Term Impacts and Economic Outlook
The current inflationary environment poses significant risks to the long-term health of the Eurozone economy.
- Inflation Risks: High inflation erodes purchasing power, reduces investment, and can lead to wage-price spirals.
- Aggressive Monetary Tightening: Aggressive monetary tightening, while necessary to control inflation, also carries the risk of triggering a recession. The impact on long-term economic growth is a major concern.
- Sectoral Impacts: Different sectors of the Eurozone economy will be affected differently by high inflation and monetary tightening. Some sectors may benefit from higher prices, while others will struggle.
- Eurozone Economic Outlook: Forecasts for future inflation rates vary, depending on factors such as energy prices, supply chain disruptions, and the effectiveness of monetary and fiscal policies. The Eurozone economic outlook remains uncertain.
Conclusion: Understanding the ECB's Inflation Challenge: A Path Forward
The ECB faces an unprecedented challenge in managing inflation in the context of continued fiscal support following the pandemic. The interplay between fiscal and monetary policies is crucial, and a lack of coordination can hinder effective inflation control. The long-term economic consequences of both high inflation and aggressive monetary tightening remain significant risks. To better understand the complexities of ECB inflation control and its impact on the Eurozone, further research into the ECB's policies and the ongoing debate surrounding inflation management is strongly encouraged. Visit the ECB website for publications and data on Eurozone inflation and efforts to maintain economic stability. Understanding the intricacies of ECB inflation is key to navigating the current economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
 Toplo Vreme Sreschu Grip Ekspertno Mnenie Ot Prof Iva Khristova
Apr 29, 2025
Toplo Vreme Sreschu Grip Ekspertno Mnenie Ot Prof Iva Khristova
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Blue Origins New Shepard Launch Cancelled Technical Glitch
Apr 29, 2025
Blue Origins New Shepard Launch Cancelled Technical Glitch
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The High Cost Of Made In The Usa Understanding The Barriers
Apr 29, 2025
The High Cost Of Made In The Usa Understanding The Barriers
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Update British Paralympian Missing In Las Vegas Investigation Underway
Apr 29, 2025
Update British Paralympian Missing In Las Vegas Investigation Underway
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Ray Epps Sues Fox News For Defamation Jan 6th Falsehoods At The Center Of The Case
Apr 29, 2025
Ray Epps Sues Fox News For Defamation Jan 6th Falsehoods At The Center Of The Case
Apr 29, 2025
