The Great Decoupling And Its Effect On Global Trade
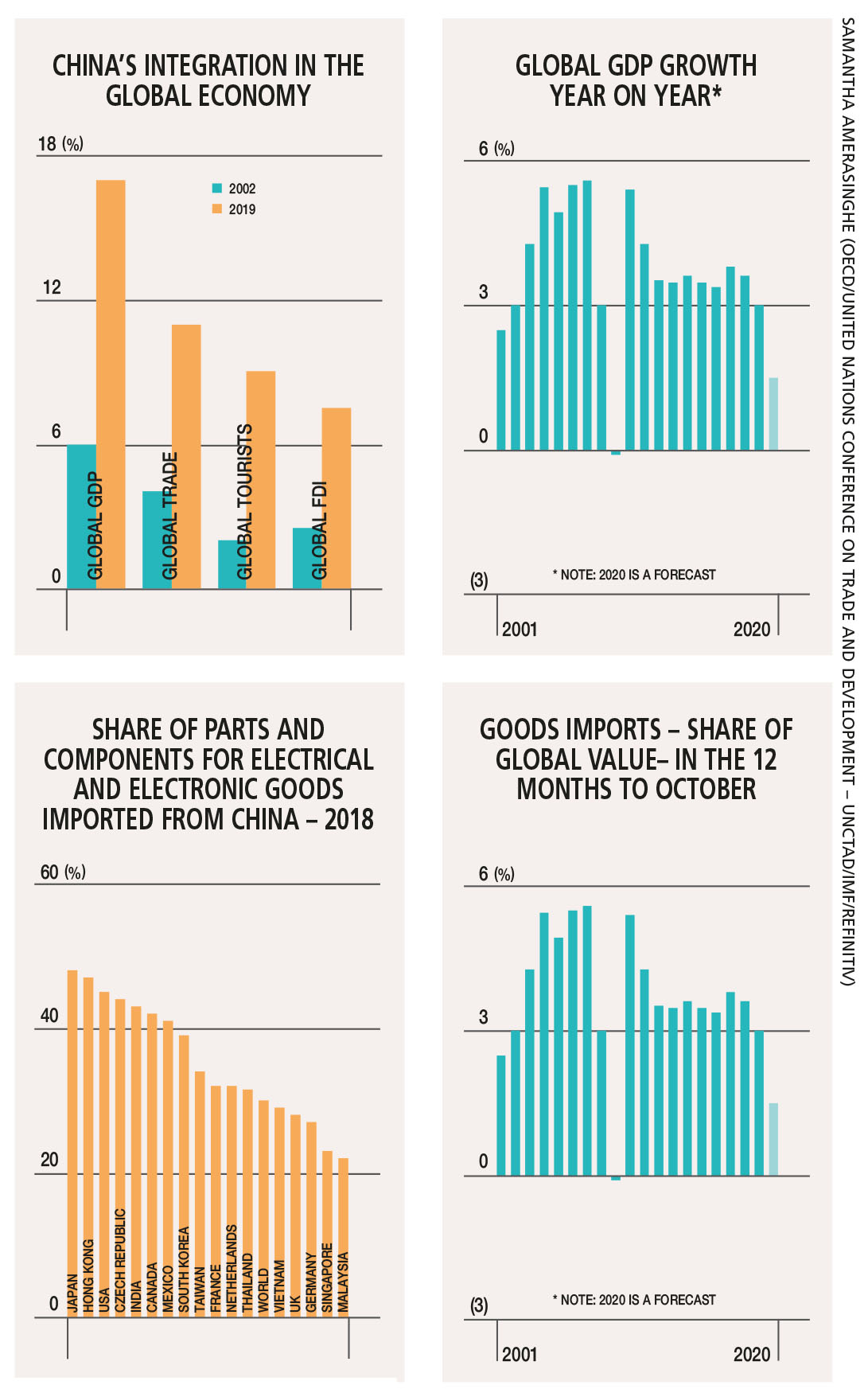
Table of Contents
Causes of The Great Decoupling
Several interconnected factors contribute to the rise of The Great Decoupling.
Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Wars
Rising nationalism and protectionism have fueled a surge in trade wars, significantly impacting global trade flows. The US-China trade war, for example, exemplifies this trend.
- Specific Trade Disputes and Impact: Tariffs imposed on goods between the US and China disrupted established supply chains and led to increased prices for consumers. Similar disputes between other nations have created uncertainty and hampered international commerce.
- Trade Barriers: Tariffs, sanctions, and non-tariff barriers, like stricter regulations and bureaucratic hurdles, are increasingly used as tools to limit trade and protect domestic industries, furthering economic decoupling. This protectionist approach often prioritizes national interests over global economic integration.
Technological Rivalry and Security Concerns
Intense competition for technological dominance, particularly in sectors like semiconductors and 5G technology, is driving countries to prioritize domestic capabilities and limit access to critical technologies.
- Restriction of Access to Critical Technologies: Countries are implementing policies to restrict the export of sensitive technologies or prevent foreign investment in strategically important industries. This includes efforts to secure domestic semiconductor production and limit reliance on foreign suppliers.
- Impact on Supply Chains and Innovation: The pursuit of technological self-reliance fragments global supply chains and potentially slows down the pace of technological innovation due to reduced collaboration and knowledge sharing. This creates a more fractured and less efficient global technological landscape.
Supply Chain Resilience and Diversification
The vulnerabilities exposed by the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical instability have prompted companies to prioritize supply chain resilience and diversification.
- Reshoring and Nearshoring: Businesses are actively reshoring (bringing production back to their home country) or nearshoring (moving production to geographically closer countries) to reduce dependence on distant suppliers and mitigate risks associated with disruptions.
- Automation and Technology in Resilient Supply Chains: Automation, advanced analytics, and digital technologies are being leveraged to improve the visibility, flexibility, and responsiveness of supply chains, making them less vulnerable to external shocks and promoting regionalization.
Effects of The Great Decoupling on Global Trade
The Great Decoupling is profoundly altering global trade patterns and having significant economic consequences.
Changes in Trade Patterns
Global trade flows are shifting, with a noticeable decline in traditional trade relationships and the emergence of new trading partnerships.
- Shifts in Export and Import Volumes: Countries are increasingly focused on regional trade agreements and diversifying their trading partners, resulting in changes to export and import volumes. Established trade routes are being re-evaluated and re-routed.
- Emergence of New Trading Blocs and Alliances: We are witnessing the formation of new regional economic blocs and alliances as countries seek to deepen trade relations within their immediate geographic proximity. This trend contributes to the fragmentation of the global trading system.
Impact on Economic Growth
The decoupling process has significant implications for economic growth, potentially impacting GDP growth, inflation, and employment.
- Winners and Losers from Decoupling: Some countries and industries may benefit from the shift towards regionalization and reshoring, while others may experience economic setbacks due to disrupted trade relationships.
- Decreased Overall Economic Efficiency: The fragmentation of global supply chains and reduced economic interdependence can lead to decreased overall economic efficiency and higher production costs. This reduction in efficiency can slow down global economic growth and negatively impact global competitiveness.
Implications for International Cooperation
The Great Decoupling presents challenges to international cooperation and multilateral institutions.
- Impact on WTO: The effectiveness of organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO) is challenged by increased protectionism and a less collaborative global trade environment.
- Difficulty in Resolving Trade Disputes: The rise of regional trading blocs and bilateral agreements complicates the resolution of trade disputes and makes it harder to establish a consistent set of global trade rules.
The Future of Global Trade in the Age of Decoupling
Predicting the future of global trade in the context of The Great Decoupling requires careful consideration of several potential scenarios.
Scenarios and Predictions
Several scenarios are plausible, ranging from a continued fragmentation of the global economy to a new era of regionalized trade blocs.
- Predictions for the Future of Globalization: While globalization may not disappear completely, its future form is likely to be less integrated and more regionalized.
- Regionalization or Fragmentation: The global economy may become increasingly fragmented, with multiple regional trading blocks coexisting with limited inter-regional trade.
Strategies for Adaptation
Businesses and governments need to develop strategies to adapt to the changing global trade landscape.
- Diversification of Supply Chains: Companies need to diversify their supply chains, reducing their reliance on single sources and geographical locations.
- Investment in Technological Innovation and Automation: Investments in technology and automation can enhance supply chain resilience and efficiency in the face of decoupling.
- Strengthening Regional Trade Partnerships: Governments should prioritize strengthening regional trade partnerships to support economic growth and stability within their respective regions.
Conclusion: Understanding and Navigating The Great Decoupling
The Great Decoupling is a multifaceted phenomenon driven by geopolitical tensions, technological rivalry, and the pursuit of supply chain resilience. Its consequences are far-reaching, impacting global trade patterns, economic growth, and international cooperation. Understanding this trend is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike. To navigate this evolving landscape effectively, continuous monitoring of global trade developments, strategic adaptation of supply chains, and engagement with relevant organizations are essential. Stay informed about the ongoing developments related to global trade decoupling and economic decoupling to ensure your organization or policy remains responsive to the changing dynamics of this significant shift. Further research into the impact of The Great Decoupling on specific industries and regions is strongly encouraged.

Featured Posts
-
 Nottingham Attacks Retired Judge Appointed To Lead Independent Inquiry
May 09, 2025
Nottingham Attacks Retired Judge Appointed To Lead Independent Inquiry
May 09, 2025 -
 How Luis Enrique Reshaped Paris Saint Germain A Winning Strategy
May 09, 2025
How Luis Enrique Reshaped Paris Saint Germain A Winning Strategy
May 09, 2025 -
 Bayern Munich Stunned By Inter Milan In Champions League First Leg
May 09, 2025
Bayern Munich Stunned By Inter Milan In Champions League First Leg
May 09, 2025 -
 Don De Cheveux A Dijon Pour La Bonne Cause
May 09, 2025
Don De Cheveux A Dijon Pour La Bonne Cause
May 09, 2025 -
 Zolotaya Malina Dakota Dzhonson I Samye Provalnye Filmy Goda
May 09, 2025
Zolotaya Malina Dakota Dzhonson I Samye Provalnye Filmy Goda
May 09, 2025
